Summary
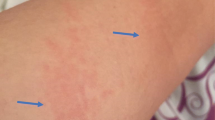
Auranofin (triethylphosphine gold), an oral gold preparation, has recently been made available, and along with injectable gold preparations, is of therapeutic value for rheumatoid arthritis. Serious gold toxicity is uncommon, and drug-related deaths rare. Many potential adverse reactions are similar, including dermatitis, stomatitis, thrombocytopenia, leucopenia, and proteinuria, generally with increased incidence in the injectable gold-treated patients. Oral gold is associated with benign lower gastrointestinal side effects, including diarrhoea, loose stools and abdominal cramps that are often dose-related and resolve spontaneously. The incidence of severe reactions such as thrombocytopenia, aplastic anaemia and exfoliative dermatitis is lower with oral gold than injectable preparations, and contributes to a superior risk-benefit ratio. The treatment of gold toxicity depends on the type and extent of organ involvement.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adachi JD, Bensen WG, Singal DP, Powers PJ. Gold-induced thrombocytopenia: platelet associated IgG and HLA typing in three patients. Journal of Rheumatology 11: 355–357, 1984
Alarcon GS, Gotuzzo E. Pulmonary reaction to chrysotherapy. Correspondence. New England Journal of Medicine 295: 507, 1976
Baldwin JL, Storb R, Thomas ED, Mannik M. Bone marrow transplantation in patients with gold-induced marrow aplasia. Arthritis and Rheumatism 20: 1043–1048, 1977
Ball GV. Gold-induced thrombocytopenia response to vincristine? Arthritis and Rheumatism 20: 288–289, 1977
Bardin T, Dryll A, Debeyre N, Ryckewaert A, Legrand I, et al. HLA system and side effects of gold salts and d-penicillamine treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 41: 599–601, 1982
Barger BO, Acton RT, Koopman WJ, Alarcon GS. DR antigens and gold toxicity in white rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis and Rheumatism 27: 601–605, 1984
Baum J. Arthritis rounds: discussion. Arthritis and Rheumatism 20: 1029, 1977
Bensen WG, Moore N, Tugwell P, D’Souza M, Singal DP. HLA antigens and toxic reactions to sodium aurothiomalate in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Journal of Rheumatology 11: 358–361, 1984
Blau SP. Metabolism of gold during lactation. Arthritis and Rheumatism 16: 777, 1973
Blocka K. Auranofin versus injectable gold: comparison of pharmacokinetic properties. American Journal of Medicine 75 (Suppl.): 114–122, 1983
Blocka KLN, Paulus HE, Furst DE. Clinical pharmacokinetics of oral and injectable gold compounds. Clinical Pharmacokinetics 11: 133–143, 1986
Blodgett Jr RC, Heuer MA, Pietrusko RG. Auranofin: a unique oral chrysotherapeutic agent. Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism 13: 255–273, 1984
Browning JS, Rice RM, Lee WV, Baker LM. Gold therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. New England Journal of Medicine 237: 428–431, 1947
Coblyn JS, Weinblatt M, Holdsworth D, Glass D. Gold-induced thrombocytopenia. Annals of Internal Medicine 95: 178–181, 1981
Cohen DL, Orzel J, Taylor A. Infants of mothers receiving gold therapy. Arthritis and Rheumatism 24: 104–105, 1981
Combs RJ, Dentino MM, Lehrman L, Szwed JJ. Gold toxicity and peritoneal dialysis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 19: 936–938, 1976
Davidson P, Engelman EP. Effect of orally administered d-penicillamine on gold deposited in the rat kidney. Arthritis and Rheumatism 7: 406–413, 1964
Davis P. Barraclough D. Interaction of d-penicillinamine with gold salts. Arthritis and Rheumatism 20: 1413, 1977
Davis P, Menard H, Thompson J, Harth M, Beaudet F. One-year comparative study of gold sodium thiomalate and auranofin treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Journal of Rheumatology 12: 60–67, 1985
Deren B, Masi R, Weksler M, Nachman RL. Gold-associated thrombocytopenia. Archives of Internal Medicine 134: 1012–1015, 1974
Edelman J, Donnelly R, Graham DN, Percy JS. Liver dysfunction associated with gold therapy for rheumatoid arthritis. Journal of Rheumatology 10: 510–511, 1983
Eiseman JL, Alvares AP. Heme metabolism in the fetoplacental unit and neonatal livers during lactation: effect of gold sodium thiomalate. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 214: 250–256, 1980
Evans RB, Ettensohn DB, Fawaz-Estrup F, Lally EV, Kaplan SR. Gold lung: recent developments in pathogenesis and therapy. Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism 16: 196–205, 1987
Eyring EJ, Engelman EP. Interaction of gold and penicillamine. Arthritis and Rheumatism 6: 216–223, 1963
Fam AG, Paton TW, Shamess CJ, Lewis AJ. Fulminant colitis complicating gold therapy. Journal of Rheumatology 7: 479–485, 1980
Fam AG, Gordon DA, Sarkozi J, Blair GRD, Cooper PW, et al. Neurologic complications associated with gold therapy for rheumatoid arthritis. Journal of Rheumatology 11: 700–706, 1984
Favreau M, Tannenbaum H, Lough J. Hepatic toxicity associated with gold therapy. Annals of Internal Medicine 87: 717–719, 1977
Ford PM. HLA antigens and drug toxicity in rheumatoid arthritis. Journal of Rheumatology 11: 259–261, 1984
Forestier J. Rheumatoid arthritis and its treatment by gold salts. Journal of Laboratory and Clinical Medicine 20: 827–840, 1935
Garland JS, Sheth KJ, Wortmann DW. Poor clearance of gold using peritoneal dialysis for the treatment of gold toxicity. Arthritis and Rheumatism 29: 450–451, 1986
Geddes DM, Brostoff J. Pulmonary fibrosis associated with hypersensitivity to gold salts. British Medical Journal 1: 1444, 1976
Gibson J, McGirr EE, York J, Kronenberg H. Aplastic anemia in association with gold therapy for rheumatoid arthritis. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Medicine 13: 130–135, 1983
Godfrey NF, Peter A, Simon TN, Lorber A. IV n-acetylcysteine treatment of hematologic reactions to chrysotherapy. Journal of Rheumatology 9: 519–526, 1982
Gottlieb NL. Chrysotherapy. Bulletin on the Rheumatic Diseases 27: 912–917, 1976-1977
Gottlieb NL. Comparative pharmacokinetics of parenteral and oral gold compounds. Journal of Rheumatology 9 (Suppl. 8): 99–109, 1982
Gottlieb NL. Gold compounds. In Kelley et al. (Eds) Textbook of rheumatology, pp.789–809, WB Saunders Co., Philadelphia, 1985a
Gottlieb NL. Auranofin. In Roth et al. (Eds) Rheumatic therapeutics pp. 442–456, McGraw-Hill Book Co, New York, 1985b
Gottlieb NL, Brown HE. Acute myocardial infarction following gold sodium thiomalate induced vasomotor (nitritoid) reaction. Arthritis and Rheumatism 20: 1026–1028, 1977
Gottlieb NL, Gray RG. Diagnosis and management of adverse reactions from gold compounds. Journal of Analytical Toxicology 2: 173, 1978
Gottlieb NL, Major JC. Ocular chrysiasis correlated with gold concentrations in the crystalline lens during chrysotherapy. Arthritis and Rheumatism 21: 704–708, 1978
Gould PW, McCormack PL, Palmer DG. Pulmonary damage associated with sodium aurothiomalate therapy. Journal of Rheumatology 4: 252–260, 1977
Gran JT, Husby G, Thorsby E. HLA DR antigens and gold toxicity. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 42: 63–66, 1983
Gray RG, Gottlieb NL. Adverse reactions from antirheumatic drugs. In Utsinger et al. (Eds) Rheumatoid arthritis, pp. 655–681, JB Lippincott, Philadelphia 1985
Harth M, Hickey JP, Coulter WK, Thompson JN, Disney TF. Gold-induced thrombocytopenia. Journal of Rheumatology 5: 165–172, 1978
Hashimoto A, Maeda Y, Ito H, Okazaki M, Hara T. Corneal chrysiasis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 15: 309–312, 1972
Heuer MA, Morris RW. Smith Kline & French worldwide clinical experience with auranofin: a review. In Capell et al. (Eds) International Symposium on auranofin, pp. 474–503, Excerpta Medica, Amsterdam, 1983
Heuer MA, Pietrusko RG, Morris RW, Scheffler BJ. An analysis of worldwide safety experience with auranofin. Journal of Rheumatology 12: 695–699, 1985
Holness L, Tenenbaum J, Cooter NBE, Grossman RF. Fatal bronchiolitis obliterans associated with chrysotherapy. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 42: 593–596, 1983
James DW, Whimster WF, Hamilton EBD. Gold lung. British Medical Journal 1: 1523–1524, 1978
Jarner D, Nielsen AM. Auranofin induced enterocolitis in rheumatoid arthritis: a case report. Scandinavian Journal of Rheumatology 12: 254–256, 1983
Jeffrey DA, Biggs DF, Percy JS, Russell AS. Quantitation of gold in skin in chrysiasis. Journal of Rheumatology 2: 28–35, 1975
Kaplinsky N, Pras M, Frankl O. Severe enterocolitis complicating chrysotherapy. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 32: 574–577, 1973
Katz WA, Blodgett Jr RC, Pietrusko RG. Proteinuria in gold-treated rheumatoid arthritis. Annals of Internal Medicine 101: 176–179, 1984
Kay A. Depression of bone marrow and thrombocytopenia associated with chrysotherapy. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 32: 277–278, 1973
Kean WF, Anastassiades TP. Long term chrysotherapy. Arthritis and Rheumatism 22: 495–501, 1979
Kean WF, Bellamy N, Brooks PM. Gold therapy in the elderly rheumatoid arthritis patient. Arthritis and Rheumatism 26: 705–711, 1983
Kidston ME, Beck F, Lloyd JB. The teratogenic effects of myochrysine injection in rats. Journal of Anatomy 108: 590–591, 1971
Klinefelter EL. Reinstitution of gold therapy in rheumatoid arthritis after mucocutaneous reactions. Journal of Rheumatology 2: 21–27, 1975
Koch R. Report of address at tenth international medical congress, Berlin, August 4, 1890. Deutsche Medizinische Wochenschrift 16: 756–757, 1890
Levin HA, McMillan R, Tavassoli M, Longmire RL, Yelenoseky R, et al. Thrombocytopenia associated with gold therapy. American Journal of Medicine 59: 274–280, 1975
Levinson ML, Lynch JP, Bower JS. Reversal of progressive, life-threatening gold hypersensitivity pneumonitis by corticosteroids. American Journal of Medicine 71: 908–912, 1981
Lockie LM, Norcross BM, Cross CW. Treatment of two reactions due to gold. Journal of the American Medical Association 133: 754–755, 1947
Madhok R, Pullar T, Capell H, Dawood F, Sturrock R, et al. Chrysotherapy and thrombocytopenia. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 44: 589–591, 1985
McCarty DJ, Brill JM, Harrop D. Aplastic anemia secondary to gold-salt therapy. Journal of the American Medical Association 179: 655–657, 1962
McCormick J, Cole S, Laherre M, et al. Pneumonitis caused by gold salt therapy, evidence for the role of cell-mediated immunity in its pathogenesis. American Review of Respiratory Disease 122: 145–152, 1980
Menard HA, Beaudet F, Davis P, et al. Gold therapy in rheumatoid arthritis: interim report of the Canadian multicenter prospective trial comparing sodium aurothiomalate and auranofin. Journal of Rheumatology 9: 179–183, 1982
Miyamoto T, Miyaji S, Horiochi Y, Hara M, Ishihara K. Gold therapy in bronchial asthma: special emphasis upon blood levels of gold and its teratogenicity. Journal of Japanese Society of Internal Medicine 63: 1190–1197, 1970
Miyachi S, Iwai K, Makino S, et al. Studies on pneumonitis occurring during chrysotherapy. Japanese Journal of Thoracic Diseases 13: 653–662, 1975
Nelson DC, Birchmore DA. Renal vein thrombosis associated with nephrotic syndrome and gold therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. Southern Medical Journal 72: 1616–1618, 1979
Penneys NS, Ackerman AB, Gottlieb NL. Gold dermatitis. Archives of Dermatology 109: 372–376, 1974
Perrier P, Raffoux C, Thomas P, Tamisier JN, Busson M, et al. HLA antigens and toxic reactions to sodium aurothiopropanol sulphonate and d-penicillamine in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 44: 621–624, 1985
Pessayre D, Feldman G, Degott C, et al. Gold salt-induced cholestasis. Digestion 19: 56–64, 1979
Podell TE, Klinenberg JR, Kramer LS, Brown HV. Pulmonary toxicity with gold therapy. Arthritis and Rheumatism 23: 347–350, 1980
Prouse PJ, Kanski JJ, Gumpel JM. Corneal chrysiasis and clinical improvement with chrysotherapy in rheumatoid arthritis. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 40: 564–566, 1981
Prupas HM. Stroke-like syndrome after gold sodium thiomalate induced vasomotor reaction. Journal of Rheumatology 11: 235–236, 1984
Reidenberg MM, Lowenthal DT. Adverse nondrug reactions. New England Journal of Medicine 279: 678–679, 1968
Roberts W, Wolter JR. Ocular chrysiasis. Archives of Ophthalmology 56: 48–52, 1974
Rocker I, Henderson WJ. Transfer of gold from mother to fetus. Lancet 2: 1246, 1976
Roe M, Sears AD, Arndt JH. Gold reaction panenteritis: a case report with radiographic findings. Radiology 104: 59, 1972
Rogers JG, Anderson RM, Chow CW, Gillam GI, Markman I. Possible teratogenic effects of gold. Australian Pediatric Journal 16: 194–195, 1980
Roquer J, Herraiz J, Maymo J, Oliva A, Carbonell J. Miller-Fisher syndrome (Guillain-Barre syndrome with ophthalmoplegia) during treatment with gold salts in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 28: 838–839, 1983
Ross GL. Idiosyncratic reactions to gold salt preparations. Arthritis and Rheumatism 21: 281, 1978
Rubin M, Sliwinski A, Photias M, et al. Influence of chelation on gold metabolism in rats. Proceeding of the Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine 124: 290–296, 1967
Savilhati M. Pulmonary complications following use of gold salts. Annals of Internal Medicine 37: 263–266, 1948
Scharf J, Nahir M, Nirenberg L. Ventricular tachycardia caused by gold overdose. Arthritis and Rheumatism 19: 1373–1374, 1976
Scharf J, Nahir M, Kleinhaus U, et al. Diffuse pulmonary injury associated with gold therapy. Journal of the American Medical Association 237: 2412, 1977
Schenker S, Olson KN, Dunn D, Breen MB, Combes B. Intrahepatic cholestasis due to therapy of rheumatoid arthritis. Gastroenterology 64: 622–629, 1973
Scherak O, Smollen JS, Mayr WR, Mayrhofer F, Kolarz G, et al. HLA antigens and toxicity to gold and penicillamine in rheumatoid arthritis. Journal of Rheumatology 11: 610–614, 1984
Schlumpf U, Meyer M, Ulrich J, et al. Neurologic complications induced by gold treatment. Arthritis and Rheumatism 26: 825–831, 1983
Scott DL, Bradby GVH, Aitman TJ, Zaphiropoulos GC, Hawkins CF. Relationship of gold and penicillamine therapy to diffuse interstitial lung disease. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 40: 136–141, 1981
Segawa K. Electron microscopy of the trabecular meshwork in open-angle glaucoma associated with gold therapy. Glaucoma: 257–258, 1981
Sepuya SM, Grzybowski S, Burton JD, et al. Diffuse lung changes associated with gold therapy. Canadian Medical Association Journal 118: 816–818, 1978
Shapiro R, Weisner K, McLaughlin GE, Utsinger PD. Evaluation as a prelude to management; management of patients. In Utsinger et al. (Eds) Rheumatoid arthritis, pp. 504–544, JB Lippincoth Philadelphia, 1985
Sharma RP, Smillie J, Palmer DG. Gold concentrations and toxicity during oral gold treatment with auranofin. Pharmacology 30: 115–120, 1985
Silverberg DS, Kidd EG, Shnitka TK, Ulan RA. Gold nephropathy. Arthritis and Rheumatism 13: 812–825, 1970
Skrifvars BV, Tornroth TS, Tallqvist GN. Gold-induced immune complex nephritis in seronegative rheumatoid arthritis. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 36: 549–566, 1977
Smith RT, Peak WP, Kron KM. Increasing the effectiveness of gold therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. Journal of the American Medical Association 167: 1197–1204, 1958
Smith W, Ball GV. Lung injury due to gold treatment. Arthritis and Rheumatism 23: 351–354, 1980
Speerstra F, Reekers P, van de Putte LBA, Vandenbroucke JP, Rasker JJ, et al. HLA-DR antigens and proteinuria induced by aurothioglucose and d-penicillamine in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Journal of Rheumatology 10: 948–953, 1983
Stein HB, Urowitz MB. Gold-induced enterocolitis. Journal of Rheumatology 3: 21–26, 1976
Szabo KT, Guerriero FJ, Kang YJ. The effects of gold-containing compounds on pregnant rats and their fetuses. Veterinary Pathology (S) 15: 89–96, 1978a
Szabo KT, DiFebbo ME, Phelan DG. The effects of gold-containing compounds on pregnant rabbits and their fetuses. Veterinary Pathology (S) 15: 97–102, 1978b
Szpak MW, Johnson RC, Brady CE, et al. Gold (Au) induced enterocolitis. Gastroenterology 76: 1257, 1979
Tarp U, Graudal H. A followup study of children exposed to gold compounds in utero. Arthritis and Rheumatism 28: 235–236, 1985
Tornroth TS, Skrifvars B. Gold nephropathy: prototype of membranous glomerulonephritis. American Journal of Pathology 75: 573–590, 1974
Vaamonde CA, Hunt FR. The nephrotic syndrome as a complication of gold therapy. Arthritis and Rheumatism 13: 826–834, 1970
Wenger ME, Bernard GC, Heller MD, et al. Therapy for rheumatoid arthritis: transferring treatment from injectable gold to aurarofin. In Capell et al. (Eds) Internation Symposium on Auranofin, pp. 201–210, Excerpta Medica, Amsterdam 1983
Winterbauer RH, Wilske KR, Wheelis RF. Diffuse pulmonary injury associated with gold treatment. New England Journal of Medicine 294: 919–921, 1976
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tozman, E.C.S., Gottlieb, N.L. Adverse Reactions With Oral and Parenteral Gold Preparations. Med Toxicol Adverse Drug Exp 2, 177–189 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03259863
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03259863