Summary
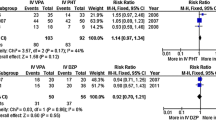
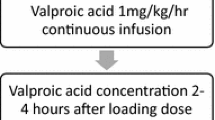
As predicted in previous studies where valproic acid (Depakine®, VPA, sodium valproate) was administered as an oral or rectal loading dose, VPA administered via injection was shown to be effective in the immediate treatment of status epilepticus (SE). This rapid efficacy is obtained simply by direct initial injection of 15 mg/kg and maintained by a 5- to 6-hour infusion at a rate of 1 mg/kg/h starting 30 minutes after the end of the bolus. With these doses, which are very close to those used traditionally with oral formulations, SE disappeared in less than 20 minutes in 19 of 23 cases. The clinical improvement was accompanied by the disappearance of critical electroencephalographic activities. The absence of impairment of concentration, and of respiratory or cardiovascular problems, and the maintenance of biological parameters, rendered the management of treatment with this VPA injectable form particularly easy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnes SE, Bland D, et al. The use of sodium valproate in a case of status epilepticus. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology 18: 236–237, 1976
Berkovic SF, Andermann F, Guberma A, Hipola D, Bladin PF. Valproate prevents the recurrence of absence status. Neurology 3: 1294–1297, 1989
Bourgeois BFD. Valproate, clinical use in antiepileptic drugs, 3rd Ed. pp. 633–642, Raven Press, New York, 1989
Bourgeois B, et al. Monotherapy with valproate in primary generalised epilepsia. Epilepsia 28 (Suppl. 2): S8–S11, 1987
Brodie MJ. Status epilepticus in adults. Lancet 336: 551–553, 1990
Callaghan N, et al. A prospective study between carbamazepine, phenytoin and sodium valproate as monotherapy in previously untreated and recently diagnosed patients with epilepsy. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry 68: 639–644, 1985
Carter Snead O, Miles MV. Treatment of status epilepticus in children with rectal sodium valproate. Clinical and Laboratory Observation 108: 323–325, 1984
Chadwick DW. Valproate monotherapy in the management of generalised and partial seizures. Epilepsia 28 (Suppl. 2): S12–S17, 1987
Feurstein J. A long term study of monotherapy with sodium valproate in primary generalised epilepsy. British Journal of Clinical Practice 27 (Suppl.): 17–23, 1983
Frey HH, Löscher W. Distribution of valproate across the interface between blood and cerebro-spinal fluid. Neuropharmacology 17: 637–642, 1978
Giroud M, Dumas R. Traitement des états de mal epileptiques par le valproate de sodium. Neurophysiologie Clinique 18: 21–32, 1988
Granneman GR, Lamm JE, Cavanaugh JH. Assessment of pharmacokinetics of sodium valproate injectable. Epilepsia 30: 668, 1989
Klotz U, Antonin KH. Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of sodium valproate. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 21: 736–743, 1977
Iivanainen M, Bergstrom L, Nuutila A, Viukari M. Psychosis-like absence status of elderly patients, successful treatment with sodium valproate. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry 47: 965–969, 1984
Leppik IE. Status epilepticus, the next decade. Neurology 40 (Suppl. 2), 1990
Loiseau P. Clinical pharmacokinetic study of sodium valproate injectable. Data on file, Sanofi, UK, 1981
Loiseau P, Jallon P. Valproate. Dictionnaire analytique d’epileptologie clinique, pp. 298–299, John Libbey-Eurotext, 1980
Manhire AR, Espir M. Treatment of status epilepticus with sodium valproate. British Medical Journal 3: 808, 1974
Marlow N, Cooke RWI. Intravenous sodium valproate in the neonatal intensive care unit. International Congress and Symposium Series, No. 152, pp. 208–210, Royal Society of Medicine Services. In Chadwick (Ed.) 4th International Symposium on Sodium Valproate and Epilepsy, Jersey, 26–28 April, 1989
Moore AJ, Bell BA, Berry DJ. Intravenous sodium valproate in neurosurgery: repeat dose pharmacokinetic study and safety assessment in neurosurgical patients. International Congress and Symposium Series, No. 152, pp. 204–207, Royal Society of Medicine Services. In Chadwick (Ed.) 4th International Symposium on Sodium Valproate and Epilepsy, Jersey, 26–28 April, 1989
Nitsche V, Mascher H. The pharmacokinetics of valproic acid after oral and parenteral administration in healthy volunteers. Epilepsia 23: 153–162, 1982
Perry JK, Dean JC. Valproate monotherapy in partial seizures. American Journal of Medicine (Suppl. AI): 14–16, 1988
Perucca E, Gatti G, Frigo GM, Crema A. Pharmacokinetics of valproic acid after oral and intravenous administration. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacokinetics 5: 313–318, 1978a
Perucca E, Gatti G, Frigo GM, Crema A. Disposition of sodium valproate in epileptic patients. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacokinetics 5: 495–499, 1978b
Price DJ. Intravenous valproate: experience in neurosurgery. International Congress and Symposium Series, No. 152, pp. 197–203, Royal Society of Medicine Services. In Chadwick (Ed.) 4th International Symposium on Sodium Valproate and Epilepsy, Jersey, 26–28 April, 1989
Steinberg A, Shalev S, Amir N. Valproic acid in neonatal status convulsivus. Brain Development 8: 278–280, 1986
Vajda FJE. Valproic acid in the treatment of status epilepticus. Advances in Neurology 34: 519–529, 1983
Vajda FJE, Mihaly GW, et al. Rectal administration of sodium valproate in status epilepticus. Neurology 28: 897–899, 1978
Viani F, Jussi M, Germano M. Rectal administration of sodium valproate for neonatal and infantile status epilepticus. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology 26: 678–679, 1984
Wilder BJ, Rangel RJ. Review of valproate monotherapy in the treatment of generalised tonic-clonic seizures. American Journal of Medicine 84 (Suppl. IA): 7–13, 1988
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giroud, M., Gras, D., Escousse, A. et al. Use of Injectable Valproic Acid in Status Epilepticus. Drug Invest 5, 154–159 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03258440
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03258440