Summary
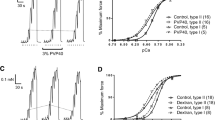
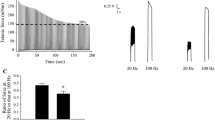
The effect of the dihydropyridine, nifedipine, on excitation-contraction coupling was compared in toad and rat skeletal muscle, using the mechanically skinned fibre technique, in order to understand better the apparently disparate results of previous studies and to examine recent proposals on the importance of certain intracellular factors in determining the efficacy of dihydropyridines. In twitch fibres from the iliofibularis muscle of the toad, 10 μM nifedipine completely inhibited depolarization-induced force responses within 30 s, without interfering with direct activation of the Ca2+-release channels by caffeine application or reduction of myoplasmic [Mg2+]. At low concentrations of nifedipine, inhibition was considerably augmented by repeated depolarizations, with half-maximal inhibition occurring at <0.1 μM nifedipine. In contrast, in rat extensor digitorum longus (EDL) fibres 1 μM nifedipine had virtually no effect on depolarization-induced force responses, and 10 μM nifedipine caused only ∼25% reduction in the responses, even upon repeated depolarizations. In rat fibres, 10 μM nifedipine shifted the steady-state force inactivation curve to more negative potentials by <11 mV, whereas in toad fibres the potent inhibitory effect of nifedipine indicated a much larger shift. The inhibitory effect of nifedipine in rat fibres was little, if at all, increased by the absence of Ca2+ in the transverse tubular (t−) system, provided that the Ca2+ was replaced with sufficient Mg2+. The presence of the reducing agents dithiothreitol (10 mM) or glutathione (10 mM) in the solution bathing a toad skinned fibre did not reduce the inhibitory effect of nifedipine, suggesting that the potency of nifedipine in toad skinned fibres was not due to the washout of intracellular reducing agents. The results are considered in terms of a model that can account for the markedly different effects of nifedipine on the two putative functions of the dihydropyridine receptor, as both t-system calcium channel and a voltage-sensor controlling Ca2+ release.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ADAMS, B. A. & BEAM, K. G. (1989) A novel calcium current in dysgenic skeletal muscle. J. Gen. Physiol. 94, 429–44.
BRANDT, N. R., KAWAMOTO, R. M. & CASWELL, A. H. (1985) Effects of mercaptans upon dihydropyridine binding sites on transverse tubules isolated from triads of rabbit skeletal muscle. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 127, 205–12.
CHAUDHARI, N. & BEAM, K. G. (1993) mRNA for cardiac calcium channels is expressed during development of skeletal muscle. Dev. Biol. 155, 507–15.
COGNARD, C., RIVET, M. & RAYMOND, G. (1990) The blockade of excitation/contraction coupling by nifedipine in patch-clamped rat skeletal muscle cells in culture. Pflügers Arch. 416, 98–105.
COGNARD, C., ROMEY, G., GALIZZI, J. P., FOSSET, M. & LAZDUNSKI, M. (1986) Dihydropyridine-sensitive Ca2+ channels in mammalian skeletal muscle cells in culture: electrophysiological properties and interactions with Ca2+ channel activator (BayK8644) and inhibitor (PN200-110). Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 83, 1518–22.
DORRSCHEIDT-KÄFER, M. (1976) The action of Ca2+, Mg2+ and H+ on the contraction threshold of frog skeletal muscle. Pflügers Arch. 362, 33–41.
DULHUNTY, A. F. & GAGE, P. W. (1988) Effects of extracellular calcium concentration and dihydropyridines on contraction in mammalian skeletal muscle. J. Physiol. 399, 63–80.
DUNN, S. M. J. & BLADEN, C. (1991) Kinetics of binding of dihydropyridine calcium channel ligands to skeletal muscle membranes: evidence for low-affinity sites and for involvement of G proteins. Biochem. 30, 5716–21.
FELDMEYER, D., MELZER, W., POHL, B. & ZÖLLNER, P. (1992) Modulation of calcium current gating in frog skeletal muscle by conditioning depolarization. J. Physiol. 457, 639–53.
FILL, M. D. & BEST, P. M. (1989) Block of contracture in skinned frog skeletal muscle fibers by calcium antagonists. J. Gen. Physiol. 93, 429–49.
FLEIG, A., TAKESHIMA, H. & PENNER, R. (1996) Absence of Ca2+ facilitation in skeletal muscle of transgenic mice lacking the type 1 ryanodine receptor. J. Physiol. 496, 339–45.
GALLANT, E. M. & GOETTL, V. M. (1985) Effects of calcium antagonists on mechanical responses of mammalian skeletal muscles. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 117, 259–65.
GAMBOA-ALDECO, R., HUERTA, M. & STEFANI, E. (1988) Effect of Ca2+ channel blockers on K+ contractures in twitch fibres of the frog (Rana pipiens). J. Physiol. 397, 389–99.
GARCIA, J., GAMBOA-ALDECO, R. & STEFANI, E. (1990) Charge movement and calcium currents in skeletal muscle fibers are enhanced by GTPγS. Pflügers Arch. 417, 114–16.
GARCIA, J., TANABE, T. & BEAM, K. G. (1994) Relationship of calcium transients to calcium currents and charge movements in myotubes expressing skeletal and cardiac dihydropyridine receptors. J. Gen. Physiol. 103, 125–47.
KASS, R. S., ARENA, J.P. & CHIN, S. (1991) Block of L-type calcium channels by charged dihydropyridines. J. Gen. Physiol. 98, 63–75.
KITAMURA, N., OHTA, T., ITO, S. & NAKAZATO, Y. (1994) Effects of nifedipine and Bay K 8644 on contractile activities in single skeletal muscle fibers of the frog. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 256, 169–76.
LAMB, G. D. (1986) Components of charge movement in rabbit skeletal muscle: the effect of tetracine and nifedipine. J. Physiol. 376, 85–100.
LAMB, G. D. (1992) DHP receptors and excitation-contraction coupling. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motif. 13, 394–405.
LAMB, G. D., JUNANKAR. P. R. & STEPHENSON, D. G. (1995) Raised intracellular [Ca2+] abolishes excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle fibres of rat and toad. J. Physiol. 489, 349–62.
LAMB, G. D. & STEPHENSON, D. G. (1990) Calcium release in skinned muscle fibres of the toad by transverse tubule depolarization or by direct stimulation. J. Physiol. 423, 495–517.
LAMB, G. D. & STEPHENSON, D. G. (1991a) Excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle fibres of rat and toad in the presence of GTPγS. J. Physiol. 444, 65–84.
LAMB, G. D. & STEPHENSON, D. G. (1991b) Effect of Mg2+ on the control of Ca2+ release in skeletal muscle fibres of the toad. J. Physiol. 434, 507–28.
LAMB, G. D. & STEPHENSON, D. G. (1994) Effects of intracellular pH and [Mg2+] on excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle fibres of the rat. J. Physiol. 478, 331–9.
LAMB, G. D. & WALSH, T. (1987) Calcium currents, charge movement and dihydropyridine binding in fast- and slow-twitch muscles of rat and rabbit. J. Physiol. 393, 595–617.
MCCLESKEY, E. W. (1985) Calcium channels and intracellular calcium release are pharmacologically different in frog skeletal muscle. J. Physiol. 361, 231–49.
MELZER, W., HERRMANN-FRANK, A. & LUTTGAU, H. Ch. (1995) The role of Ca2+ ions in excitation-contraction coupling of skeletal muscle fibres. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1241, 59–l16.
MÉRY, P.-F., HOVE-MADSEN, L., MAZET, J. -L., HANF, R. & FISCHMEISTER, R. (1996) Binding constants determined from Ca2+ current responses to rapid applications and washouts of nifedipine in frog cardiac myocytes. J. Physiol. 494, 105–20.
MURPHY, B. J., WASHKURAK, A. W. & TUANA, B.S. (1990) Dihydropyridine binding to the L-type Ca2+ channel in rabbit heart sarcolemma and skeletal muscle transverse-tubules: role of disulphide, sulfhydryl and phosphate groups. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1052, 333–9.
NEUHAUS, R., ROSENTHAL, R. & LÜTTGAU, H. Ch. (1990) The effects of dihydropyridine derivatives on force and Ca2+ current in frog skeletal muscle fibres. J. Physiol. 427, 187–209.
OWEN, V. J., LAMB, G. D., STEPHENSON, D. G. & FRYER, M. W. (1997) Relationship between depolarization-induced force responses and Ca2+ content in skeletal muscle fibres of rat and toad. J. Physiol. 498, 571–86.
PETERSON, B. Z. & CATTERALL, W. A. (1995) Calcium binding in the pore of L-type calcium channels modulates high affinity dihydropyridine binding. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 18201–4.
PIZARRO, G., BRUM, G., FILL, M., FITTS, R., RODRIGUEZ, I., URIBE, I. & RIOS, E. (1988) The voltage sensor of skeletal muscle excitation-contraction coupling: a comparison with Ca2+ channels. In The Ca Channel: Structure, Function and Implications (edited by MORAD, M., NAYLER, W., KAZDA, S. & SCHRAMM, M.) pp. 38–157. Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
POSTERINO, G. S. & LAMB, G. D. (1996) Effects of reducing agents and oxidants on excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle fibres of rat and toad. J. Physiol. 496, 809–25.
RIOS, E. & BRUM, G. (1987) Involvement of dihydropyridine receptors in excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle. Nature 325, 717–20.
SCHILLING, W. P. (1988) Effect of divalent cation chelation on dihydropyridine binding in isolated cardiac sarcolemma vesicles. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 943, 220–30.
SCHWARTZ, L. M., MCCLESKEY, E. W. & ALMERS, W. (1985) Dihydropyridine receptors in muscle are voltage-dependent but most are not functional calcium channels. Nature 314, 747–51.
STRÜBING, C., HERING, S. & GLOSSMANN, H. (1993) Evidence for an external location of the dihydropyridine agonist receptor site on smooth muscle and skeletal muscle calcium channels. Br. J. Pharmacol. 108, 884–91.
SUDA, N. (1995) Involvement of dihydropyridine receptors in terminating Ca2+ release in rat skeletal myotubes. J. Physiol. 486, 105–12.
TAKEKURA, H., NISHI, M., NODA, T., TAKESHIMA, H. & FRANZINI-ARMSTRONG, C. (1995) Abnormal junctions between surface membrane and sarcoplasmic reticulum in skeletal muscle with a mutation targeted to the ryanodine receptor. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 92, 3381–5.
TANABE, T., BEAM, K. G., POWELL, J. A. & NUMA, S. (1988) Restoration of excitation-contraction coupling and slow calcium current in dysgenic muscle by dihydropyridine receptor complementary DNA. Nature 336, 134–9.
VALDIVIA, H. H. & CORONADO, R. (1990) Internal and external effects of dihydropyridines in the calcium channel of skeletal muscle. J. Gen. Physiol. 95, 1–27.
YANG, J., ELLINOR, P. T., SATHER, W. A., ZHANG, J.-F. & TSIEN, R. W. (1993) Molecular determinants of Ca2+ selectivity and ion permeation in L-type Ca2+ channels. Nature 366, 158–61.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Posterino, G.S., Lamb, G.D. Effect of nifedipine on depolarization-induced force responses in skinned skeletal muscle fibres of rat and toad. Journal of Muscle Research and Cell Motility 19, 53–65 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03257390
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03257390