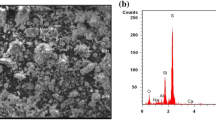
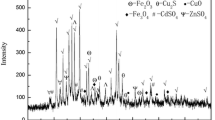
Abstract
A low-pressure, low-temperature chloride leach process called the Cashman process can be used to extract metals from arsenical flue dusts and residues and fix the arsenic in an environmentally stable form as ferric arsenate (scorodite). The process has been pilot tested in an integrated plant including continuous recycle; during the tests, several tonnes of flue dust were processed. Based on this pilot program, the process was deemed technically feasible, and its products are commercially salable. Residues from this pilot program were also subjected to a long-term stability test.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
CSS Management Corporation, U.S. patent 4,655,829 (April 7,1987).
A. Davis, “Anaconda Smelter Flue Dust Cashman Process Residue Long-Term Stability Study” (Boulder, CO: PTI Environmental Services, 1990).
Toxicity Leach Procedures (TCLP) (40 CFK, part 268: App 1).
“Comprehensive Feasibility Study of the Arsenical Flue Dust Treatment Anaconda, Montana,” I (1) (San Francisco, CA: Bechtel Corporation, March 1990), p. 7.
Vendor quotes (Koch-Knight #918-057 BP).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kunter, R.S., Bedal, W.E. Chloride-process treatment of smelter flue dusts. JOM 44, 35–38 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03223194
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03223194