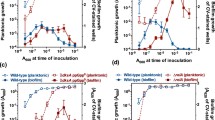
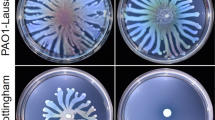
Abstract
Unicellular organisms naturally form multicellular communities, differentiate into specialized cells, and synchronize their behaviour under certain conditions. Swarming, defined as a movement of a large mass of bacteria on solid surfaces, is recognized as a preliminary step in the formation of biofilms. The main aim of this work was to study the role of a group of genes involved in exopolysaccharide biosynthesis during pellicle formation and swarming inBacillus subtilis strain 168. To assess the role of particular proteins encoded by the group ofepsI-epsO genes that form theeps operon, we constructed a series of insertional mutants. The results obtained showed that mutations inepsJ-epsN, but not in the last gene of theeps operon (epsO), have a severe effect on pellicle formation under all tested conditions. Moreover, the inactivation of 5 out of the 6 genes analysed caused total inhibition of swarming in strain 168 (that does not produce surfactin) on LB medium. Following restoration of thesfp gene (required for production of surfactin, which is essential for swarming of the wild-type bacteria), thesfp + strains defective ineps genes (exceptepsO) generated significantly different patterns during swarming on synthetic B medium, as compared to the parental strain 168sfp +.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blair KM, Turner L, Winkelman JT, Berg HC, Kearns DB, 2008. Amolecular clutch disables flagella in theBacillus subtilis biofilm. Science 320: 1636–1638.
Branda SS, González-Pastor JE, Ben-Yehuda SE, Kolter R, Losick R, 2001. Fruiting body formation byBacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98: 11621–11626.
Branda SS, González-Pastor JE, Dervyn E, Ehrlich SD, Losick R, Kolter R, 2004. Genes involved in formation of structured multicellular communities byBacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 186: 3970–3979.
Branda SS, Chu F, Kearns DB, Losic R, Kotler R, 2006. A major protein component of theBacillus subtilis biofilm matrix. Mol Microbiol 59: 1229–38.
Bowden MG, Kaplan HP, 1998. TheMyxococcus xanthus lipopolysaccharide O-antigen is required for social motility and multicellular development. Mol Microbiol 30: 275–284.
Brown II, Häse CC, 2001. Flagellum- independent surface migration ofVibrio cholerae andEscherichia coli. J Bacteriol 183: 3784–3790.
Chambers SP, Prior SE, Barstow DA, Minton NP, 1988. The pMTLnic − cloning vectors. I. Improved pUC polylinker regions to facilitate the use of sonicated DNA for nucleotide sequencing. Gene 68:139–149.
Chu F, Kearns DB, Branda SS, Kolter R, Losick R, 2006. Targets of the master regulator of biofilm formation inBacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol 59: 1216–1228.
Cosby WM, Vollenbroich D, Lee OH, Zuber P, 1998. Alteredsrf expression inBacillus subtilis resulting from changes in culture pH is dependent on the Spo0K oligopeptide permease and the ComQX system of extracellular control. J Bacteriol 180: 1438–1445.
Gygi D, Rahman MM, Lai HC, Carlson R, Guard-Petter J, Hughes C, 1995. A cell-surface polysaccharide that facilitates rapid population migration by differentiated swarm cells ofProteus mirabilis. Mol Microbiol 17: 1167–1175.
Hamon MA, Stanley DA, Britton RA, Grossman AD, Lazazzera AB 2004. Identification of AbrB-regulated genes involved in biofilm formation byBacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol 52:847–860.
Hamze K, Julkowska D, Autret S, Hinc K, Nagorska K, Sekowska A, et al. 2009. Identification of genes required for different stages of dendritic swarming inBacillus subtilis, with a novel role forphrC. Microbiology 155: 398–412.
Harshey RM, 2003. Bacterial motility on a surface: many ways to a common goal. Annu Rev Microbiol 57:249–273.
Inoue T, Shingaki R, Hirose S, Waki K, Mori H, Fukui K, 2007. Genome-wide screening of genes required for swarming motility inEscherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol 189: 950–957.
Ireton K, Rudner DZ, Siranosian KJ, Grossman AD, 1993. Integration of multiple developmental signals inBacillus subtilis through the Spo0A transcription factor. Genes Dev 7: 283–294.
Izquierdo L, Abitiu N, Coderch N, Hita B, Merino S, Gavin R, et al. 2002. The inner-core lipopolysaccharide biosyntheticwaaE gene: function and genetic distribution among some Enterobacteriaceae. Microbiology 148: 3485–3496.
Julkowska D, Obuchowski M, Holland IB, Seror SJ, 2004. Branched swarming patterns on a synthetic medium formed by wild-typeBacillus subtilis strain 3610: detection of different cellular morphologies and constellations of cells as the complex architecture develops. Microbiology 150: 1839–1849.
Julkowska D, Obuchowski M, Holland IB, Seror SJ, 2005. Comparative analysis of the development of swarming communities ofBacillus subtilis 168 and a natural wild type: critical effects of surfactin and the composition of the medium. J Bacteriol 187: 65–76.
Kearns DB, Losick R, 2003. Swarming motility in undomesticatedBacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol 49: 581–590.
Kearns DB, Chu F, Branda SS, Kolter R, Losick R, 2005. A master regulator for biofilm formation byBacillus subtilis. Mol. Microbiol 55: 739–749.
Kobayashi K, 2007.Bacillus subtilis pellicle formation proceeds through genetically defined morphological changes. J Bacteriol 189: 4920–4931.
Leclère V, Marti R, Béchet M, Fickers P, Jacques P, 2006. The lipopeptides mycosubtilin and surfactin enhance spreading ofBacillus subtilis strains by their surface-active properties. Arch Microbiol 186: 475–483.
Lombardía E, Rovetto AJ, Arabolaza AL, Grau RR, 2006. A LuxS-dependent cell-to-cell language regulates social behavior and development inBacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 188: 4442–4452.
Lu A, Cho K, Black WP, Duan XY, Lux R, Yang Z, et al. 2005. Exopolysaccharide biosynthesis genes required for social motility inMyxococcus xanthus. Mol Microbiol 55: 206–20.
Morikawa M, 2006. Beneficial biofilm formation by industrial bacteriaBacillus subtilis and related species. J Biosci Bioeng 101:1–8.
Nadell CD, Xavier JB, Foster KR, 2009. The sociobiology of biofilms. FEMS Microbiol Rev 33: 206–224.
Nagórska K, Hinc K, Strauch MA, Obuchowski M, 2008. Influence of the sigmaB stress factor and yxaB, the gene for a putative exopolysaccharide synthase under sigmaB Control, on biofilm formation. J Bacteriol 190: 3546–3556.
Nakano MM, Corbell N, Besson J, Zuber P, 1992. Isolation and characterization ofsfp: a gene that functions in the production of the lipopeptide biosurfactant, surfactin, inBacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet 232: 313–321.
Quadri LE, Weinreb PH, Lei M, Nakano MM, Zuber P, Walsh CT, 1998. Characterization of Sfp, aBacillus subtilis phosphopantetheinyl transferase for peptidyl carrier protein domains in peptide synthetases. Biochemistry 37: 1585–1595.
Rahman MM, Guard-Petter J, Asokan K, Hughes C, Carlson RW, 1999. The structure of the colony migration factor from pathogenicProteus mirabilis: A capsular polysaccharide that facilitates swarming. J Biol Chem 274: 22993–22998.
Ren D, Bedzyk AL, Setlow P, Thomas SM, Ye RW, Wood TK, 2004. Geneexpression inBacillus subtilis surface biofilms withandwithout sporulationandthe importance ofyveR for biofilm maintenance. Biotechnol Bioeng 86: 344–364.
Shapiro JA, 1998. Thinking about bacterial populations as multicellular organisms. Annu Rev Microbiol 52: 81–104.
Sharma M, Atend SK, 2002. Swarming: A coordinated bacterial activity. Current Science 83: 707–715.
Toguchi A, Siano M, Burkart M, Harshey RM, 2000. Genetics of swarming motility inSalmonella enterica serovar.typhimurium: critical role for lipopolysaccharide. J Bacteriol 182: 6308–6321.
Vagner V, Dervyn E, Ehrlich SD, 1998. Avector for systematic gene inactivation inBacillus subtilis. Microbiology 144: 3097–3104.
Vlamakis H, Aguilar C, Losick R, Kolter R, 2008. Control of cell fate by the formation of an architecturally complex bacterial community. Genes Dev 22: 945–953.
Wang Q, Frye JG, McClelland M, Harshey RM, 2004. Gene expression patterns during swarming inSalmonella typhimurium: genes specific to surface growth and putative new motility and pathogenicity genes. Mol Microbiol 52: 169–187.
Watnick P, Kolter R, 2000. Biofilm, city of microbes. J Bacteriol 182: 2675–2679.
Wu Y, Jiang Y, Kaiser D, Mark A, 2007. Social interactions in myxobacterial swarming. PLoS Computional Biology. 3: 2546–2558.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagórska, K., Ostrowski, A., Hinc, K. et al. Importance ofeps genes fromBacillus subtilis in biofilm formation and swarming. J Appl Genet 51, 369–381 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03208867
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03208867