Summary
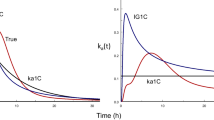
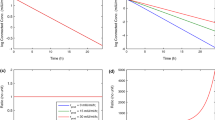
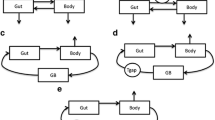
A multi-compartment pharmacokinetic model with enterohepatic circulation, was used in simulations and in a clinical trial with morphine. A hypothetical effect compartment was linked to either the central or the peripheral disposition compartment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dahlström B.E., Paalzow L.K. (1978): Pharmacokinetic interpretation of the enterohepatic recirculation and first-pass elimination of morphine in the rat. J. Pharmacokinet. Biopharm., 6, 505–519.
Colburn W.A. (1984): Pharmacokinetic analysis of concentration-time data obtained following administration of drugs that are recycled in the bile. J. Pharm. Sci., 73, 313–317.
Harrison L.I., Gibaldi M. (1976): Influence of cholestasis on drug elimination: pharmacokinetics. J. Pharm. Sci., 65, 1346–1348.
Steimer J.-L., Plusquellec Y., Guillaume A., Boisvieux J.-F. (1982): A time-lag model for pharmacokinetics of drugs subject to enterohepatic circulation. J. Pharm. Sci., 71, 297–302.
Veng Pedersen P., Miller R. (1980): Pharmacokinetics of doxycycline reabsorption. J. Pharm. Sci. 69, 204–207.
Shepard TA., Reuning R.H., Aarons L.J. (1985): Estimation of area under the curve for drugs subject to enterohepatic cycling. J. Pharmacokinet. Biopharm., 13, 589–608.
Labat C., Mansour K., Malmary MF., Terrissol M., Oustrin J. (1987): A variable reabsorption time-delay model for pharmacokinetics of drugs. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet., 12, 129–133.
Holford NHG, Sheiner L.B. (1981): Understanding the dose-effect relationship: clinical application of the pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic models. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 6, 429–453.
Colburn W.A. (1981): Simultaneous pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic modeling. J. Pharmacokinet. Biopharm., 9, 367–388.
Benet L.Z., Turi JS. (1971): Use of general partial fraction theorem for obtaining inverse Laplace transforms in pharmacokinetic analysis. J. Pharm. Sci., 60, 1593–1594.
Haborak G.E., Benmaman J.D., Warren. Jr W. (1979): Mathematical treatment of linear mammillary models using inverse Laplace transforms. J. Pharm. Sci. 68, 932–933.
Shepard T.A., Reuning R.H., Aarons L.J. (1985): Estimation of area under the curve for drugs subject to enterohepatic cycling. J. Pharmacokinet. Biopharm., 13, 589–608.
Westerling D., Frigeren L., Höglund P. Morphine pharmacokinetics and effects on salivation and continuous reaction times. Manuscript, submitted for publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Höglund, P., Ohlin, M. Effect modelling for drugs undergoing enterohepatic circulation. European Journal of Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics 18, 333–338 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03190182
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03190182