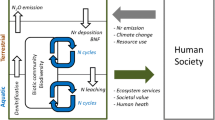
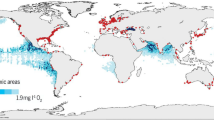
Abstract
Much of the research on the nitrogen cycle aims to improving scientific understanding but is not focused specifically on removing or reducing the scientific uncertainties that constrain policy makers in the formulation of appropriate responses to old or emerging environmental problems. Policy makers, for example, commonly find it difficult to assess the spatial or temporal importance of the various risks to human and ecosystem health that stem from man’s interference with the natural N cycle. This paper will justify this conclusion by reference to the findings of a recent study on non-point pollution from crop production in China. The findings concern the perceived risks of groundwater nitrate to human health; uncertainties about critical NOx levels and their interactions with other pollutants; various other dimensions of man’s impact on the N cycle. The paper will go on to suggest a more systematic process or pathway by which scientists can select and design their research in a manner that could give more effective support to policy makers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nevison, C., Review of the IPCC methodology for estimating nitrous oxide emissions associated with agricultural leaching and runoff, Chemosphere-Global Change Science 2000, 2: 493–500.
Denier van der Gon, H. A. C., Bleeker, A., Ligthart, T. et al., Indirect Nitrous oxide emissions from the Netherlands: Source strength, methodologies, uncertainties and potential for mitigation, TNO report no. R 2004/275
Shen, R. P., Sun, B., Zhao, Q. G., Spatial and temporal variability of N, P and K balances for agroecosystems in China, Pedosphere, 2005, 15(3): 347–355.
Ju, X. T., Liu, X. J., Zhang, F. S. et al., Nitrogen fertilization, soil nitrate accumulation, and policy recommendations in several agricultural regions of China, Ambio, 2004, 33: 300–305.
Zhu, Z. L., The present situation of nitrogen fertilizer use and the problems and strategies in China, in Fertilizer Problems in Sustainable Development of Agriculture in China (in Chinese) (eds. Li, Q. K., Zhu, Z. L., Yu, T. R.), Nanchang: Jiangxi Science and Technology Publishers, 1998, 38–51.
Zhu, Z. L., Chen, D. L., Nitrogen fertilizer use in China—Contributions to food production, impacts on the environment and best management practices, Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 2002, 63: 117–127
Wang, G. H., Dobermann, A., Witt, C. et al., Performance of site-specific nutrient management for irrigated rice in southeast China, Agronomy Journal, 2001, 90: 178–185.
Zhang, W. L., Wu, S. X., Ji, H. J. et al., Estimation of agricultural non-point source pollution in China and the alleviating strategies I Estimation of agricultural non-point source pollution in China in early 21 century, Scientia Agricutura Sinica, 2004, 36(7): 1008–1017.
Xing, G. X., Zhu, Z. L., Regional nitrogen budgets for China and its major watersheds, Biogeochemistry, 2002, 57/58: 405–427.
Zhang, W., Tian, Z., Zhang, N. et al., Nitrate pollution of groundwater in Northern China, Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 1996, 59: 223–231.
Yan, X., Akimoto, H., Ohara, T., Estimation of nitrous oxide, nitric oxide and ammonia emissions from croplands in East, Southeast and South Asia, Global Change Biology, 2003, 9: 1080–1096.
FAOSTAT, FAO database collections, Rome: FAO, 2004; http: //apps.fao.org/default.jsp.
Buresh, R., Peng, S., Huang, J. et al., Rice systems in China with high nitrogen inputs, in Agriculture and the Nitrogen Cycle—Assessing the Impacts of Fertilizer use on Food Production and the Environment (eds. Mosier, A. R., Syers, J. K., Freney, J. R.), Covelo CA: Island Press, 2004, 143–153.
Bruinsma, J., ed., World Agriculture: Toward 2015/30. An FAO Perspective, Earthscan, London on behalf of Rome: FAO, 2003.
World Health Organisation, Guidelines for drinking water quality, Geneva: WHO, 1984.
Zhang, W. L., Tian, Z. X., Zhang, N. et al., Investigation of nitrate pollution in ground waterdue to nitrogen fertilization in agriculture in North China. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Sciences (in Chinese), 1995, 1(2): 80–87.
Liu, H. B., Li, Z. H., Zhang, W. L. et al., Characteristics of nitrate distribution and accumulation in soil profiles under main agro-land use types in Beijing, Scientia Agricultura Sinica (in Chinese), 2004. 36(5): 692–698.
Forman, D., Al-Dabbagh, S., Doll, R., Nitrates, nitrites and gastric cancers, Nature, 1985, 313: 620–625.
Knight, T. M., Forman, D., Pirastu, R. et al., Nitrate and nitrite exposure in Italian populations with different gastric cancer rates, J. Epidemiology, 1990, 19: 510–515.
Pretty, J., Brett, C., Gee, D. et al., An assessment of the total external costs of UK agriculture, Agricultural Systems, 2000, 65: 113–136.
Norse, D., Li, J., Jin, L. et al., Environmental costs of rice production in China: Lessons from hunan and Hubei, Bethesda: Aileen International Press, 2001.
Yu, S. Z., Primary prevention of hepatocellular carcinoma, J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol, 1995, 10: 674–682
Ueno, Y., Nagata, S., Tsutsumi, T. et al., Detection of microsystins, a blue-green algal hepotoxin in drinking water sampled in Haimen and Fusui, endemic areas of primary cancer in China by highly sensitive immunoassay, Carcinogenesis, 1996, 17: 1317–1321.
Bouwmann, A. F., Van Drecht, G., Knoop, J. M. et al., Exploring changes in river nitrogen export to the world’s oceans, Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 2005, 19: 1–14.
Shuiwang, D., Shen, Z., and Hongyu, H., 2000 Transport of dissolved nitrogen from the major rivers to estuaries in China, Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 2000, 57: 13–22.
Xing, G. X., N2O emission from cropland in China, Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 1998, 52: 249–254.
Bouwman, A. F., Global Estimates of Gaseous Emissions from Agricultural Land, Rome: FAO, 2001.
Ma, W. Q., Mao, D. R., Zhang, F. S., The problems in fertilization and measurements of preventing them in protected vegetable fields in Shandong, in Fertilizing for sustainable production of high quality vegetables (eds. Li, X. L., Zhang, F. S., Mi, G. H.), Beijing: Chinese Agricultural University Press, 2000.
Bao X. M., Resource characteristics of organic fertilizer and nutrients recycling in China (in Chinese), Ph. D Thesis, China Agricultural University, 2002.
Zhang, W. L., Wu, A. G., Ji, H. J. et al., Estimation of agricultural non-point source pollution in China and the alleviation strategies 3 A review of the policies and practices for agricultural non-point source pollution control in China, Scientia Agricutura Sinica (in Chinese), 2004, 36(7) 1026–1033.
Integrated Monitoring Program on Acidification of Chinese Terrestrial Systems—Midterm Conference 2003; http://www.impacts. net.cn.
Bouwman, A. F., Lee, D. S., Asman, A. H. et al., A global high-resolution emission inventory for ammonia, Global Geochemical Cycles, 1997, 11: 561–587.
Yu’e, L., Erda, L., Emissions of N2O, NH2 and NOx from fuel combustion, industrial processes and the agricultural sectors in China, Nutrient Cycling in Agroecosystems, 2000, 57: 99–106.
Benton, J., Fuhrer, J., Gimeno, B. S. et al., An international cooperative programme indicates the widespread occurrence of ozone injury on crops, Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment, 2000, 57: 19–30.
Chameides, W. L., Li, X., Tang, X. et al., Is Ozone Pollution affecting crop yields in China? Geophysical Research Letters, 1999, 26: 867–870.
Hassan, I. A., Effect of O3 and Drought Stress on Egyptian Variety of Tomatoes (Lycopersicon Esculentum Mill. Cv. Baladey) Grown in Open-top Chambers. Gartenbauwissenschaft (The German Journal for Horticultural Science), 1999, 64, 1–4.
Ishi, S., Marshall, F. M., Bell, J. N. B. et al., Impact of ambient air pollution on locally grown rice cultivars (Oryza sativa L.) in Malaysia. Water, Air and Soil Pollution, 2004, 154: 187–201.
Ishi, S., The impacts and policy implications of urban air pollution on local agriculture in Malaysia, Ph.D. Thesis, University of London, 2004.
Wahid, A., Milne, E., Shamsi, S. R. A. et al., Effects of oxidants on soybean growth and yield in Pakistan Punjab, Environmental Pollution, 2001, 113: 271–280.
Goulding, K., Nitrate leaching from arable and horticultural land, Soil Use and Management, 2000, 16: 145–151.
Davies, D. B., The nitrate issue in England and Wales, Soil Use and Management, 2000, 16: 142–144.
Tornburn, P. J., Biggs, J. S., Weir, K. L. et al., Nitrate in groundwaters of intensive agricultural areas in coastal Northeastern Australia, Agriculture, Ecosystem and Environment, 2003, 94: 49–58.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Norse, D. The nitrogen cycle, scientific uncertainty and policy relevant science. Sci. China Ser. C.-Life Sci. 48 (Suppl 2), 807–817 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03187120
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03187120