Abstract
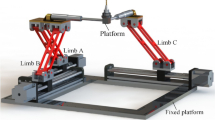
This paper presents inverse kinematic and dynamic analyses of HexaSlide type six degree-of-freedom parallel manipulators. The HexaSlide type parallel manipulators (HSM) can be characterized as an architecture with constant link lengths that are attached to moving sliders on the ground and to a mobile platform. In the inverse kinematic analyses, the slider and link motion (position, velocity, and acceleration) is computed given the desired mobile platform motion. Based on the inverse kinematic analysis, in order to compute the required actuator forces given the desired platform motion, inverse dynamic equations of motion of a parallel manipulator is derived by the Newton-Euler approach. In this derivation, the joint friction as well as all link inertia are included. Relative importance of the link inertia and joint frictions on the computed torque is investigated by computer simulations. It is expected that the inverse kinematic and dynamic equations can be used in the computed torque control and model-based adaptive control strategies.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A i :
-
Position vector ofi-th universal joint
- B i :
-
Position vector ofi-th spherical joint
- I :
-
Moment of inertia of mobile platform
- I li :
-
Moment of inertia ofi-th link
- R :
-
Orientation matrix of mobile platform
- R li :
-
Orientation matrix ofi-th link
- a i :
-
Unit vector along thei-th linear guide
- f si :
-
Frictional force ati-th prismatic joint
- f ui :
-
Frictional moment ati-th universal joint
- f pi :
-
Frictional moment ati-th spherical joint
- l :
-
Link length
- m si :
-
Equivalent mass ofi-th slider part
- m li :
-
Mass ofi-th link
- m :
-
Mass of mobile platform
- n i :
-
Unit vector alongi-th link length direction
- ω:
-
Angular velocity of mobile platform
- ω li :
-
Angular velocity ofi-th link
- τ i :
-
Articular force ofi-th actuator
- a × :
-
Skew-symmetric matrix
References
Codourey A., 1998, “Dynamic Modeling of Parallel Robots for Computed-Torque Control Implementation,”The International Journal of Robotic Research, Vol. 17, No. 12, pp. 1325–1336.
Dasgupta B., and Mruthyunjaya T. S., 1998, “A Newton-Euler Formulation for the Inverse Dynamics of the Stewart Platform Manipulator,”J. Mech. Mach. Theory, Vol. 33, No. 8, pp. 1135–1152.
Dasgupta B., and Choudhury P., 1999, “A General Strategy Based on the Newton-Euler Approach for the Dynamic Formulation of Parallel Manipulators,”J. Mech. Mach. Theory. Vol. 34, pp. 801–824.
Gosselin C. M., 1996, “Parallel Computation Algorithms for the Kinematics and Dynamics of Parallel Manipulators,”J. of Dynamic Systems Measurement & Control-Transactions of the ASME, V. 118 N. 1
Honegger M., 1998, “Nonlinear Adaptive Control of a 6 DOF Parallel Manipulator,”MOVIC ’98, Zurich, Switzerland, August 25–28, Vol. 3, pp. 961–966.
Ji A., 1993, “Study of the Effect of Leg Inertia in Stewart Platforms,”Proc. of the IEEE Conf. on Robot. and Automat.Los Alamitos, CA:IEEE, pp. 121–126
Kim M. K., Park C. G., and Lee K. I., 1998, “Dynamic Analysis Considering the Effect of Leg Inertia and Design of Adaptive Controller in a Stewart Platform,”Proc. of ’98 KSME fall annual meeting, Vol. A., pp. 657–662.
Lebret G., Liu K., and Lewis F. L., 1993, “Dynamic Analysis and Control of a Stewart Platform Manipulator,”J. Robot. Sys., 10 (5): 629–655.
Lee C. W., and Kim N. N., 1999, “Model-Based Control System Design and Sliding Mode Control of Stewart Platform Manipulator,”Trans. of KSME, A Vol. 23, No. 6, pp. 903–911.
Miller K., 1993, “The Proposal of a new Model of Direct-Drive Robot DELTA-4 Dynamics,”Proc. of ’93 ICAR, the Int. Conf. on Robot., pp. 411–416.
Reboulet C., and Berthomieu T., 1991, “Dynamic Models of a Six-Degree-of-Freedom Parallel Manipulator,”Proc. of ’91 ICAR, the Int. Conf. on Adv. Robot., Vol. 2, pp. 1153–1157.
Toyoda, 1996, “Parallel Mechanism Based Milling Machine,” Cat. No. 96 1110-0 JO. Merlet, J-P., 1997,Les Robots Paralleles, 2e éd., Hermès, Paris.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, JP., Ryu, J. Inverse kinematic and dynamic analyses of 6-DOFPUS type parallel manipulators. KSME International Journal 16, 13–23 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03185151
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03185151