Abstract
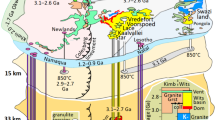
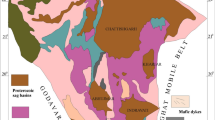
Four40Ar/39Ar age groups of mica, hornblende and K-feldspar were obtained from Proterozoic and early Paleozoic metamorphic rocks in the Aksay-Dangjin Pass area, western China. The samples away from the middle shear zone of the Altyn fault belt yield two plateau age groups in the range of 461-445.2 Ma and 414.9-342.8 Ma, respectively. They represent the tectono-thermal events that had been recorded in the rocks that were displaced by the Altyn strike-slip fault in late Ordovician-early Silurian and Devonian, respectively. These two age groups should be related to the closures of Northern and Southern Qilian Oceans. The deformed granitic gneiss from the northern belt gives a plateau age group of 178.4-137.5 Ma, which is interpreted as the active age of the Altyn fault in the middle-late Jurassicearly Cretaceous and should be related to the accretion of Lhasa block to the north. The sample from the middle shear zone of the Altyn fault belt yields two plateau ages of 36.4 and 26.3 Ma, respectively, suggesting the strike-slip movement with strong metamorphism at greenschist facies along the Altyn fault in the late Eocene. This event occurred in the most areas of the northern Tibet Plateau and should be in response in the north to the collision between Indian and Eurasian continents. The present study demonstrates that the Altyn fault is characterized by multiple pulse-style activities under the tectonic setting of convergence between the Indian and Eurasian continents.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xu, Z. Q., Yang, J. S., Zhang, J. X. et al., A comparison between the tectonic units on the two slides of the Altun sinistral strike-slip fault and the mechanism of lithospheric shearing, Acta Geologica Sinica (in Chinese), 1999, 73(3): 193–205.
Sobel, E. R., Arnaud, N., A possible middle Paleozoic suture in the Altyn Tagh, NW China, Tectonics, 1999, 18(1): 64–74.
Cui, J. W., Tang, Z. M., Deng, J. G. et al., Altun fault system (in Chinese), Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1999, 1–242.
Li, H. B., Yang, J. S., Xu, Z. Q. et al., Geological and chronological evidence of Indo-Chinese strike-slip movement in the Altyn Tagh fault zone, Chinese Science Bulletin, 2002, 1(2): 27–32.
Arnaud, N., Delville, N., Montel, J. M. et al., Paleozoic to Cenozoic deformation along the Altyn Tagh fault in the Altun Shan massif area, Eastern Qilian Shan, NE Tibet, China, American Geophysical Union Annual Meeting Abstracts, 1999, F1018.
Zheng, J. D., Tectonics and evolution of the Altun Tagh Mountain, Geosciences (Journal of Graduate School, China University of Geosciences) (in Chinese), 1991, 5(4): 347–354.
Peter, R., An, Y., Rick, B. et al., Oligocene initiation of deformation of northern Tibet, evidence from the Tarim basin, NE China, Abstract for GSA, 1997, 29: A-143.
Zuo, G. C., Wu, H. Q., A bisubduction-collsion orogenic model of early-Paleozoic in the middle part of north Qi Lian Area (in Chinese), Advance in Earth Science, 1997, 12(4): 315–323.
Liou, J. G., Wang, X. M., Coleman, R. G. et al., Blueschists in major suture zones China, Tectonics, 1989, 8: 609–619.
Liu, Y. J., Neubauer, F., Ge, X. H., Blueschists from Qingshuigou in north Qilian Mountains, China, Abstracts Volume of 31 st International Geological Congress (CD version), Brazil, 2000.
Zhang, J. X., Zhang, Z. M., Xu, Z. Q. et al., Discovery of khondalite series from the western segment of Altyn Tagh and their petrological and geochronological studies, Science in China, Ser. D, 2000, 43(3): 308–316.
Jolivet, M., Roger, F., Arnaud, N., Exhumation history of the Altun Shan with evidence for the timing of the subduction of the Tarim block beneath the Altyn Tagh system, North Tibet, Earth & Planetary Sci., 1999, 329: 749–755.
Sobel, E. R., Arnaud, N., Jolivet, M. et al., Jurassic to Cenozoic exhumation history of the Altyn Tagh range, northwest China constrained by40Ar/39Ar and apatite fission track thermochronology, Paleozoic and Mesozoic Tectonic Evolution of Central and Eastern Asia: From Continental Assembly to Intracontinental Deformation (eds. Hendrix, M. S., Davis, G A.), Geological Society of America Memoir, 2001, 194: 247–267.
Zhang, J. X., Yang, J. S., Xu, Z. Q. et al., Peak and retrograde age of eclogites at northern margin of Qaidam basin, northwestern China: evidence from U-Pb and Ar-Ar dates (in Chinese), Geochimica, 2000, 29(3): 217–222.
Jolivet, M., Brunei, M., Seward, D. et al., Mesozoic and Cenozoic tectonics of the northern edge of the Tibetan plateau: fission-track constraints, Tectonophysics, 2001, 343: 111–134.
Mock, C., Arnaud, N. O., Cantagrel, J. M., An early unroofing in northeastern Tibet? Constraints from Ar-40/Ar-39 thermochronology on granitoids from the eastern Kunlun range (Qianghai, NW China), Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1999, 171: 107–122.
Sobel, E. R., Dumitru, T. A., Thrusting and exhumation around the margins of the western Tarim basin during the India-Asia collision, J. Geophys. Res., 1997, 102(B3): 5043–5063.
Chung, S. -L., Lo, C. -H., Lee, T. -Y. et al., Diachronous uplift of the Tibetan plateau starting 40 Myr ago, Nature, 1998, 394: 769–773.
Searle, M., Corfield, R. I., Stephenson, B., Structure of the North Indian continental margin in the Ladakh-Zanskar Himalayas: implications for the timing of obduction of the Spontang ophiolite, India-Asia collision and deformation events in the Himalaya, Geol. Mag., 1997, 134(3): 297–316.
Rowley, D. B., Minimum age of initiation of collision between India and Asia north of Everest based on the subsidence history of the Zhepure Mountain section, J. Geol., 1998, 106: 229–235.
Zhang, L. S., Scharer, U., Age and origin of magmatism along the Cenozoic Red River shear belt, China, Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 1999, 134: 67–85.
Ge, X. H., Liu, J. L., Broken “Western China Craton”, Acta Petrologica Sinica (in Chinese), 2000, 16(1): 59–66.
Liu, Y. J., Ye, H. W., Ge, X. H. et al., Laser probe40Ar/39Ar dating of micas on the deformed rocks from Altyn fault and its tectonic implications, western China, Chinese Sciences Bulletin, 2001, 4(46): 322–325.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Genser, J., Ge, X. et al. 40Ar/39Ar age evidence for Altyn fault tectonic activities in western China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 48, 2024–2030 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03183998
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03183998