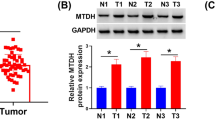
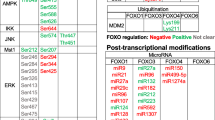
Abstract
Restin, a member of melanoma-associated antigen superfamily gene, was first cloned from differentiated leukemia cell induced by all trans-retinoic acid, and was able to inhibit cell proliferation, but the molecular mechanism was not clear. Since Restin was localized in cell nucleus, and its homolog member, Necdin (neuronal growth suppressor factor), could interact with transcription factors p53 and E2F1, we proposed that Restin might also function as Necdin through interacting with some transcription factors. In this study, transcription factors p53, AP1, ATFs and E2Fs were cloned and used in the mammalian two-hybrid system to identify their interaction with Restin. The results showed that only ATF3 had a strong interaction with Restin. It is interesting to know that ATF3 was an important transcription factor for G1 cell cycle initiation in physiological stress response. It was possible that the inhibition of cell proliferation by Restin might be related with the inhibition of ATF3 activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chomez, P., De Backer, O., Bertrand, M. et al., An overview of the MAGE gene family with the identification of all human members of the family, Cancer Res., 2001, 61: 5544–5551.
Zhu, F., Yan, W., Zhao, Z. L. et al., Related improved PCR-based subtractive hybridization strategy for cloning differentially expressed genes, Biotechniques, 2000, 29(2): 310–313.
Maruyama, K., Usami, M., Aizawa, T., Yoshikawa, K., A novel brain-specific mRNA encoding nuclear protein (necdin) expressed in neurally differentiated embryonal carcinoma cells, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 1991, 178(1): 291–296.
Lucas, S., Brasseur, F., Boon, T., A new MAGE gene with ubiquitous expression does not code for known MAGE antigens recognized by T cells, Cancer Res., 1999, 59: 4100–4103.
Zhao, Z. L., Lu, F., Zhu, F., Yang, H., Chai, Y. B., Chen, S. M., Cloning and biological comparison of Restin, a novel member of Mage superfamily, Science in China, Ser. C, 2002, 45(4): 412–420.
Taniura, H., Taniguchi, N., Hara, M., Yoshikawa, K., Necdin, a postmiotic neron-specific growth suppressor, interacts with viral transforming proteins and cellular transcription factor E2F1, J. Bio. Chem., 1998, 273: 720–728.
Taniura, H., Matsumoto, K., Yoshikawa, K., Physical and functional interactions of neuronal growth suppressor necdin with p53, J. Biol. Chem., 1999, 274: 16242–16248.
Salehi, A. H., Roux, P. P., Kubu, C. J. et al., NRAGE, a novel MAGE protein, interacts with the p75 neurotrophin receptor and facilitates nerve growth factor-dependent apoptosis, Neuron, 2000, 27: 279–288.
Liang, G. S., Wolfgang, C. D., Hai, T. et al., ATF3 gene genomic organization, promoter, and regulation, J. Biol. Chem., 1996, 271: 1695–1701.
Hai, T., Hartman, M. G., The molecular biology and nomenclature of the activating transcription factor/cAMP responsive element binding family of transcription factors: Activating transcription factor proteins and homeostasis, Gene, 2001, 273: 1–11.
Allan, A. L., Chris, A., Richard, G. P. et al., Activating transcription factor 3 induces DNAsysthesis and expression of cyclin D1 in hepatocytes, J. Biol. Chem., 2001, 276: 27272–27280.
Kawauchi, J., Zhang, C., Nobori, K. et al., Transcriptional repressor activating transcription factor 3 protects human umbilical vein endothelial cells from tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced apoptosis through down-regulation of p53 transcription, J. Biol. Chem., 2002, 277(41): 39025–39034.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Y., Lu, F., Qi, Y. et al. Interaction of Restin with transcription factors. Sci. China Ser. C.-Life Sci. 48, 256–262 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03183619
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03183619