Abstract
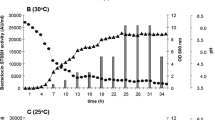
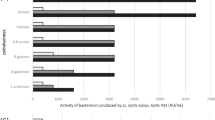
Detection of lactic acid bacteria (LAB) bacteriocins producers is of great significance for food industry to establish starter bacterial association and to improve food safety. Eighty oneLactococcus lactis strains, isolated from traditional Tunisian dairy products, were screened for their antibacterial activity. Bacteriocin production in the supernatant was demonstrated for twelve strains by the well diffusion assay, protease susceptibility and by direct detection of the activity on SDS-PAGE. By using PCR with primers targeting structural genes of nisin and lactoccocin 481, we were able to predict their presence in 10 and one strain respectively. No amplifications were recorded with primers targeting lactococcin A, lactococcin 972 and bacteriocin J46 ofL. lactis. The remaining unidentified bacteriocin produced by strain BMG 6.25 and designed as lactococcin IAF 25, was further characterised. IAF 25 was shown to be a heat-stable proteinaceous inhibitory factor sensitive to papain and trypsin but resistant to proteinase K treatment. IAF 25 has an apparent molecular weight of 6 kDa and showed a narrow antimicrobial activity spectrum against closely related bacteria and genera. These original characteristics amongL. lactis bacteriocins coupled with cross inhibition tests with bacteriocin producers reference strains, led to the assumption of the novelty of lactococcin IAF 25.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cai Y., Ng L.-K., Farber J.M. (1997). Isolation and characterization of nisin-producingLactococcus lactis from bean-sprouts. J. Appl. Microbiol., 83: 499–507.
Cherif A., Chehimi S., Limem F., Hansen B.M., Hendriksen N.B., Daffonchio D., Boudabous A. (2003). Detection and characterization of the novel bacteriocin entomocin 9, and safety evaluation of its producer,Bacillus thuringiensis subsp.entomocidus HD9. J. Appl. Microbiol., 95: 990–1000.
Coetzee J.C.J., Todorov S.D., Gorgens J.F., Dicks L.M.T. (2007). Increased production of bacteriocin ST4SA byEnterococcus mundtii ST4A in modified corn steep liquor. Ann. Microbiol., 57: 617–622.
Corroler D., Mangin I., Desmasures N., Gueguen M. (1998). An ecological study of lactococci isolated from raw milk in the camembert cheese registered designation of origin area. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 64: 4729–4735.
De Man, J.C., Rogosa, M., Sharpe, M.E. (1984). A medium for the cultivation of lactobacilli. J. Appl. Microbiol., 23: 130–135.
De Vos W.M., Mulders J.M., Siezen R.J., Hugenholtz J., Kuipers O.P. (1993). Properties of Nisin Z and distribution of its gene,nisZ, inLactococcus lactis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 59: 213–218.
De Vuyst L., Vandamme E.J. (1994), Nisin, a lantibiotic produced byLactococcus lactis subsp lactis: properties, biosynthesis, fermentation and application. In: De Vuyst L., Vandamme E.J., Eds., Bacteriocins of Lactic Acid Bacteria. Microbiology, Genetics and Applications. Chapman & Hall, London, pp. 151–221.
Dufour A., Rince A., Uguen P., Le Pennec J.P. (2000). IS1675, a novel lactococcal insertion element, forms a transposon-like structure including the lacticin 481 lantibiotic operon. J. Bacteriol., 182: 5600–5605.
Dufour A., Hindre T., Haras D., Le Pennec J.P. (2007). The biology of lantibiotics from the lacticin 481group is coming of age. FEMS Microbiol. Rev., 31: 134–167.
Drider D., Fimland G., Héchard Y., McMullen L.M., Prévost H. (2006). The continuing story of class IIa bacteriocins. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev., 70: 564–582.
Ferchichi M., Frère J., Mabrouk K., Manai M. (2001). Lactococcin MMFII, a novel class IIa bacteriocin produced by Lactococcus lactis MMFII, isolated from a Tunisian dairy product. FEMS Microbiol. Lett., 205: 49–55.
Holo H., Nilssen O., Nes I. F. (1991). Lactococcin A, a new bacteriocin fromLactococcus lactis subsp.cremoris: isolation and characterisation of the protein and its gene. J. Bacteriol., 173: 3879–3887.
Horn N., Swindell S., Dodd H., Gasson M. (1991). Nisin biosynthesis genes are encoded by a novel conjugative transposon. Mol. Gen. Genet., 228: 129–135.
Huot E., Meghrous J., Barrena-Gonzalez C., Petitdemange H. (1996). Bateriocin J46, a new bacteriocin produced byLactococcus lactis subsp.cremoris J46: isolation and characterisation of the protein and its gene. Anaerobe, 2: 137–145.
Jack R.W., Tagg J.R., Ray B. (1995). Bacteriocins of gram-positive bacteria. Microbiol. Rev., 59: 171–200.
Juillard V., Spinnler H.E., Desmazeaud M.J., Boquien C.Y. (1987). Phénomènes de coopération et d’inhibition entre les bactéries lactiques utilisées en industrie laitière. Le lait, 67: 149–172.
Kaletta C., Entian K. D. (1989). Nisin, a peptide antibiotic: cloning and sequencing of the nisA gene and posttranslational processing of its peptide product. J. Bacteriol., 171: 1597–1601.
Kalman S., Kiehne L.K., Libs L.J., Yamamota T. (1993). Cloning of a novelcryIC-Type gene from a strain ofBacillus thuringiensis subsp.galleriae. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 59: 1131–1137.
Klaenhammer T.R., McKay L.L., Baldwin K.A. (1978). Improved lysis of group N streptococci for isolation and rapid characterization of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 35: 592–600.
Klaenhammer T.R. (1993). Genetics of bacteriocins produced by lactic acid bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 12: 39–68.
Klijn N., Weerkamp A.H., De Vos W.M. (1995). Detection and characterisation of lactose-utilizingLactococcus spp. in natural ecosystems. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 61: 788–792.
Laemmli U.K. (1970). Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of head of bacteriophage T4. Nature, 227: 680–685.
Martinez B., Fernandez M., Suarez J.E., Rodriguez A. (1999). Synthesis of lactococcin 972, a bacteriocin produced byLactococcus lactis IPLA 972, depends on the expression of a plasmid-encoded bicistronic operon. Microbiology, 145: 3155–3161.
Moll G., Ubbink-Kok T., Hildeng-Hauge H., Nissen-Meyer J., Nes I.F., Konings W.N., Driessen A.J. (1996). Lactococcin G is a potassium ion-conducting, two-component bacteriocin. J. Bacteriol., 178: 600–605.
Morgan S., Ross R.P., Hill C. (1995). Bacteriolytic activity caused by the presence of a novel lactococcal plasmid encoding lactococcin A, B, and M. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 61: 2995–3001.
Mulders J.W., Boerrigter I.J., Rollema H.S., Siezen R.J., Vos W.M. (1991). Identification and characterization of the lantibiotic nisin Z, a natural nisin variant. Eur. J. Biochem., 201: 581–584.
Nes I.F., Diep D.B., Havarstein L.S., Brurberg M.B., Eijsink V., Holo H. (1996). Biosynthesis of bacteriocins in lactic acid bacteria. Antoine Van Leeuwenhoek, 70: 113–128.
Nissen-Meyer J., Holo H., Havarstein L.S., Sletten K., Nes I. (1992). A novel lactococcal bacteriocin whose activity depends on the complementary action of two peptides. J. Bacteriol., 174: 5686–5692.
Noonpakdee W., Santivarangkna C., Jumriangrit P., Sonomoto K., Panyim S. (2003). Isolation of nisin-producingLactococcus lactis WNC 20 strain from nham, a traditional Thai fermented sausage. Int. J. Food Microbiol., 81: 137–145.
Olasupo N.A., Schillinger U., Narbad A., Dodd H., Holzapfel W.H. (1999). Occurrence of nisin Z production inLactococcus lactis BFE 1500 isolated from wara, a traditional Nigerian cheese product. Int. J. Food Microbiol., 53: 141–152.
Ouzari H., Cherif A., Mora D. (2002). Autolytic phenotype ofLactococcus lactis strains isolated from traditional Tunisian dairy products. J. Appl. Microbiol., 92: 812–820.
Ouzari H., Hassen A., Najjari A., Ettoumi B., Daffonchio D., Zagorec M., Boudabous A., Mora D. (2006). A novel phenotype based on esterase electrophoretic polymorphism for the differentiation ofLactococcus lactis subsp.lactis andcremoris. Lett. Appl. Microbiol., 43: 351–359.
Piard J. C., Delorme F., Giraffa G., Commissaire J., Desmazeaud M. (1990). Evidence for a bacteriocin produced byLactococcus lactis CNRZ 481. Neth. Milk Diary J., 44: 143–158.
Piard J.C., Kuipers O.P., Rollema H.S., Desmazeaud M.J., De Vos W.M. (1993). Structure, organization and expression of the lct gene for lacticin 481, a novel lantibiotic produced byLactococcus lactis. J. Biol. Chem., 268: 16361–16367.
Rauch P.J.G., de Vos W.M. (1992). Characterization of the novel nisin-sucrose conjugative transposon Tn5276 and its insertion inLactococcus lactis. J. Bacteriol., 174: 1280–1287.
Rodriguez J.M., Cintas L.M., Casaus P., Horn N., Dodd H., Hernandez P.E., Gasson M.J. (1995a). Isolation of nisin-producing strains from dry fermented sausages. J. Appl. Bacteriol., 78 109–115.
Rodriguez J.M., Cintas L.M., Casaus P., Suarez A., Hernandez P.E. (1995b). PCR detection of the Lactocin S structural gene in bacteriocin-producing lactobacilli from meat. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 61: 2802–2805.
Rodriguez J.M., Cintas L.M., Casaus P., Martinez M.I., Suarez A., Hernandez P.E. (1997). Detection of pediocin PA-1-producting pediococci by rapid molecular biology techniques. Food Microbiol., 14: 363–371.
Rodriguez E., Gonzalez B., Gaya P., Nunez M., Medina M. (2000). Diversity of bacteriocins produced by lactic acid bacteria isolated from raw milk. Int. Dairy J., 10: 7–15.
Ryan M.P., Rea M.C., Hill C., Ross R.P. (1996). An application in cheddar cheese manufacture for a strain ofLactococcus lactis producing a novel broad-spectrum bacteriocin, lacticin 3147. Appl. Env. Microbiol., 62: 612–619.
Ryan M.P., Jack R.W., Josten M., Sahl H.-G., Jung G., Ross R.P., Hill C. (1999). Extensive post-translational Modification, including serine to D-alanine conversion, in the two component lantibiotic, lacticin 3147. J. Biol. Chem., 274: 37544–37550.
Sambrook J., Fritsch E.F., Maniatis T. (1989). Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold. Spring Harbor, NY.
Todorov S.D., Dicks L.M.T. (2007). Partial characterisation of two bacteriocins produced bybactobacillus paracasei subsp.paracasei ST242BZ and ST284BZ and the effect of medium components on their production. Ann. Microbiol., 57: 363–368.
van Belkum M.J., Hayema B.J., Jeeninga R.E., Kok J., Venema G. (1991). Organization and nucleotide sequences of two lactococcal bacteriocin operons. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 57: 492–498.
van Belkum M.J., Kok J., Venema G. (1992). Cloning, sequencing, and expression inEscherichia coli ofIcnB, a third bacteriocin determinant from the lactococcal bacteriocin plasmid p9B4-6. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 58: 572–577.
Zendo T., Koga S., Shigeri Y., Nakayama J., Sonomoto K. (2006). Lactococcin Q, a novel two-peptide bacteriocin produced by Lactococcus lactis QU 4. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 72: 3383–3389.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Hadda Ouzari and Afef Najjari contributed equally to the work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ouzari, H., Najjari, A., Amairi, H. et al. Comparative analysis ofLactococcus lactis bacteriocins and preliminary characterisation of a new proteinase K resistant lactococcin member. Ann. Microbiol. 58, 83–88 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03179449
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03179449