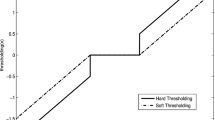
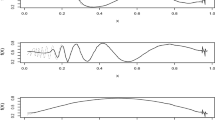
Abstract
The field of nonparametric function estimation has broadened its appeal in recent years with an array of new tools for statistical analysis. In particular, theoretical and applied research on the field of wavelets has had noticeable influence on statistical topics such as nonparametric regression, nonparametric density estimation, nonparametric discrimination and many other related topics. This is a survey article that attempts to synthetize a broad variety of work on wavelets in statistics and includes some recent developments in nonparametric curve estimation that have been omitted from review articles and books on the subject. After a short introduction to wavelet theory, wavelets are treated in the familiar context of estimation of «smooth» functions. Both «linear» and «nonlinear» wavelet estimation methods are discussed and cross-validation methods for choosing the smoothing parameters are addressed. Finally, some areas of related research are mentioned, such as hypothesis testing, model selection, hazard rate estimation for censored data, and nonparametric change-point problems. The closing section formulates some promising research directions relating to wavelets in statistics.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramovich, F., Sapatinas, T. andSilverman, B. W. (1998). Wavelet thresholding via a Bayesian approach. I. Royal Statist. Soc., Ser. B, part 4, 725–750.
Amato, U. andVuza, D. T. (1994). Wavelet Regularization for Smoothing Data. Technical report N. 108/94, Instituto per Applicazioni della Matematica, Napoli.
Amato, U. andVuza, D. T. (1996). An Alternate Proof of a Result of Johnstone and Silverman concering Wavelet Thresholding Estimators for Data with Correlated Noise.Revue Roumaine Math. Pures Appi. 41, 431–438.
Antoniadis, A. (1994). Smoothing noisy data with coiflets.Statistica Sinica 4 (2), 651–678.
Antoniadis, A. (1994). Smoothing noisy data with tapered coiflets series.Scand. Journal of Statistics 23, 313–330.
Antoniadis, A. andCarmona, R. (1991). Multiresolution analyses and wavelets for density estimation. Technical report, University of California, Irvine.
Antoniadis, A., Grégoire, G. andMcKeague, I. (1994). Wavelet methods for curve estimation.J. Amer Statist. Assoc. 89 (428), 1340–1353.
Antoniadis, A. andPham, D. T. (1995). Wavelet regression for random or irregular design. Technical report. University of Grenoble.
Antoniadis, A. andLavergne, C. (1995). Variance function estimation in regression with wavelet methods. In A. Antoniadis and G. Oppenheim (eds.),Wavelets and Statistics. Lecture Notes in Statistics,103, Springer-Verlag.
Antoniadis, A., Grégoire, G. andVial, P. (1997a). Random design wavelet curve smoothing.Statistics and Prob. Letters, vol. 35, 225–232.
Antoniadis, A., Gijbels, I. andGrégotre, G. (1997b). Model selection using wavelet decomposition and applications. Biometrika84 (4), 751–763.
Antoniadis, A., Grégoire, G. andNason, G. (1997c). Density and hazard rate estimation for right censored data using wavelet methods. Technical report. University of Grenoble.
Antoniadis, A. andGijbels, I. (1997). Detecting abrupt changes by wavelet methods. Technical report. University of Grenoble.
Averkamp, R. andHoudré, C. (1996). Wavelet thresholding for non (necessarily) Gaussian noise: a preliminary report. Technical report, Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta.
Beran, R. (1994). Bootsrap variable selection and confidence sets. Technical report, University of California, Berkeley.
Brillinger, D. R. (1994). Some River Wavelets.Environmetrics 5, 2 11–220.
Brillinger, D.R. (1995). Some Uses of Cumulants in Wvelet Analysis.J. Nonparam. Statistics 4.
Bruce, A. G. andGao, H.-Y. (1194).S + Wavelets, Users manual. StatSci, Seatle.
Bruce, A. G. andGao, H.-Y. (1996). Understanding WaveShrink: Variance and Bias Estimation. Biometrika83 (4), 727–746.
Bruce, A. G. andGao, H.-Y. (1997). WaveShink with firm shrinkage.Statistica Sinica, to appear.
Buckhett, J. B. andDonoho, D. (1995). Wavelab and Reproducible research. In A. Antoniadis and G. Oppenheim (eds.),Wavelet and Statistics, Lecture Notes in Statistics,103, Springer-Verlag.
Clyde, M. Parmigiani, G. andVidakovic, B. (1995). Multiple shrinkage and subset selection in wavelets. Technical report DP 95-37, Duke University.
Chipman, H. A., Kolaczyj, E. D. andMcculloch, R. E. (1995). Adaptive Bayesian Wavelet Shrinkage. Technical report, University of Chicago.
Chui, K. (1992).Wavelets: A Tutorial in Theory and Applications. Academic Press, Boston.
Cohen, A., Daubechies, I. andVial, P. (1993). Wavelets on the interval and fast wavelet transforms.Applied and Comp. Harmonic Analysis 1 (1), 54–81.
Cohen A. andRyan, R. D. (1995).Wavelets and Multiscale Signal Processing. Chapman & Hall, London.
Daubechies, I. (1992).Ten Lectures of Wavelets. CBMS-NSF regional conferences series in applied mathematics. SIAM, Philadelphia.
Daubechies, I. andLagarias, J. C. (1991). Two-scale difference equations: Existence and global regularity of solutions.SIAM Journal on Math. Analysis 22, 1388–1410.
Delyon, B. andJuditsky, A. (1996). On minimax wavelet estimators.Applied and Comp. Harmonic Analysis 3, 215–228.
DeVore, R. andLucier, B. J. (1992). Fast wavelet techniques for near-optimal signal processing. InIEEE Military Communication Conference, pp. 1129–1135.
DeVore, R., Jawerth, B. andPoov, V. (1988). Interpolation of Besov spaces.Trans. Amer Math. Soc. 305, 397–414.
Donoho, D. L. (1994). Asymptotic risk for sup-norm loss: solution via optimal recovery. Prob.Theory and Related Fields 99, 145–170.
Donoho, D. L. andJohnstone, I. M. (1992). Minimax estimation via wavelet shrinkage. Technical report, Stanford University.
Donoho, D. L. andJohnstone, I. M. (1994a). Ideal spatial adaptation by wavelet shrinkage.Biometrika 81, 425–455.
Donoho, D. L. andJohnstone, I. M. (1995). Adapting to unknown smoothness via wavelet shrinking.J. Am. Statist. Assoc. 90, 1200–1224.
Donoho, D. L. andJohnstone, I. M. (1994b). Ideal denoising in an orthonormal basis chosen from a library of bases.Compt. Rend. Acad. Sci. Paris A 319, 1317–1322.
Donoho, D. L., Johnstone, I. M., Kerkyacharian, G. andPicard, D. (1995). Wavelet shrinkage: asymptotia (with discussion)?J. Roy. Statist. Soc., Ser. B 57(2), 301–370.
Donoho, D. L., Johnstone, I. M., Kerkyacharian, G. andPicard, D. (1996). Density estimation by wavelet thresholding.Ann. Statist. 24 (2), 508–539.
Doukhan, P. (1990). Consistency of delta-sequence estimates of a density or of a regression function for a weakly dependent stationary sequence. Séminaire de Statistique d’Orsay, Université Paris Sud, 1991.
Doukhan, P. andLéon, J. (1990). Déviation quadratique d’estimateurs de densité par projection orthogonale.Compt. Rend. Acad. Sci. Paris A 310, 424–430.
Engel, J. (1990). Density estimation with Haar series.Statistics and Probability Letters 9, 111–117.
Fan, J. (1996). Test of significance based on wavelet thresholding and Neyman’s truncation.J. Am. Statist. Assoc. 91, 674–688.
Gao, H.-Y. (1993).Wavelet estimation of Spectral densities in Time series analysis. Ph. D. Thesis, University of California, Berkeley.
Gao, H.-Y. (1997). Wavelet Shrinkage Smoothing For Heteroscedastic Data. Technical report, ScatSci, Seatle.
Gasser, T. andMüller, H. (1979). Kernel estimation of regression functions. In Gasser, T. and Müller, H. (eds.),Curve Estimation, Springer-Verlag, Heidelberg.
Good, I. J. andGaskins, R. A. (1971). Density estimation and bump haunting by the penalized maximum likelihood method.J. Am. Statist. Assoc. 75, 42–69.
Hall, O. andNason, G. P. (1996). On choosing a non-integer resolution level when using wavelet methods. Technical report, University of Bristol.
Hall, P. andPatil, P. (1995). On wavelet methods for estimating smooth functions.Bernoulli 1, 41–58.
Hall, P. andPatil, P. (1996a). Effect of threshold rules on performance of wavelet-based curve estimators.Statistica Sinica 6, 331–345.
Hall, P. andPatil, P. (1996b). On the choice of smoothing parameter, threshold and truncation in nonparametric regression by nonlinear wavelet methods.J. Roy. Statist. Soc., Ser B 58, 361–377.
Härdle, W. (1990).Applied nonparametric regression. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Holschneider, M. (1995).Wavelets: An analysis tool. Clarendon Press, Oxford.
Jansen, M., Malfait, M. andBultheel, A. (1997). Generalized cross-validation for wavelet thresholding.Signal Processing,56 (1). To appear.
Johnstone, I. M., Kerkyacharian, G. andPicard, D. (1992). Estimation d’une densité de probabilityé par méthode d’ondelettes.Compt. Rend. Acad. Sci. Paris A 315, 211–216.
Johnstone, I. M. andSilverman, B. W. (1997). Wavelet threshold estimators for data with correlated noise.J. Roy. Statist. Soc., Ser B 59. In press.
Kerkyacharian, G. andPicard, D. (1992). Density estimation in Besov Spaces.Statistics and Probability Letters 13, 15–24.
Kolaczyk, E. (1994).Wavelet methods for the inversion of some homogeneous linear operators in the presence of noisy data. Ph. D. Thesis, Stanford University.
Mallat, S. G. (1989). A theory for multiresolution signal decomposition: the wavelet representation.IEEE Trans. on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 11, 674–693.
Marron, S. J., Adak, S., Johnstone, I., Neumann, M. andPatil, P. (1997). Exact risk analysis of wavelet regression.Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics. In press.
Masry, E. (1994). Probability density estimation from dependent observations using wavelet orthonormal bases.Statistics and Probability Letters 21, 181–194.
Masry, E. (1996). Multivariate probabilty density estimation by wavelet methods: strong consistency and rates for stationary time series. Technical report, University of California, San Diego.
Meyer, Y. (1990).Ondelettes et Opéerateurs I: Ondelettes. Hermann, Paris.
Michelli, C. A. andRivlin, T. J. (1975). A survey of optimal recovery. In Michelli, C. A. and Rivlin, T. J. (eds.),Optimal estimation in Approximating theory, pp. 1–54, Plenum, New York.
Müller, H. G. (1985). Empirical bandwidth choice for nonparametric kernel regression by means of pilot estimators.Statist. Decisions 2, 193–206.
Nason, G. P. (1996). Wavelet regression using cross-validation.J. Roy. Statist. Soc., Ser B 58, 463–479.
Nason, G. J. (1995). Choice of the threshold parameter in wavelet function estimation. In A. Antoniadis and G. Oppenheim (eds.),Wavelets and Statistics, pp. 261–280, Lecture Notes in Statistics, Springer-Verlag, New York.
Nason, G. J. andSilverman, B. W. (1994). The discrete wavelet transform inS.Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics 3, 163–191.
Neumann, M. H. (1994). Spectral density estimation via nonlinear wavelet methods for stationary non-Gaussian series. Technical report 99, Institute for applied and stochastic analysis, Berlin.
Neumann, M. H. andSpokoiny, V. G. (1993). On the efficiency of wavelet estimators under arbitrary error distributions.Discussion Paper No. 4, Hümboldt Universität zu Berlin.
Ogden, T. R. (1996).Essential wavelets for statistical applications and data analysis. Birkhäuser, Basel.
Oudshoorn, C. (1994). Wavelet-based nonparametric regression: optimal rate in the sup-norm. Technical report848, University Utrecht.
Penev, S. andDechevsky, L. (1997). On non-negative wavelet-based estimators. Technical report, University of New South Wales. To appear inJ. of Nonparam. Statistics.
Pinheiro, A. andVidakovic, B. (1995). Estimating the square root of a density via compactly supported wavelets. Technical reportDP 95-14, Duke University.
Potier, C. andVercken, C. (1994). Spline fitting Numerous Noisy Data with discontinuities. In Laurent et al. (eds.),Curves and Surfaces, pp. 477–480, Academic Press, New York.
Raimondo, M. (1996).Situations non ergodiques et utilisations de méthodes d’ondelettes. Ph. D. Thesis, University Paris 7.
Ramlau-Hansen, H. (1983). Smoothing counting processes by means of kernel functions.Ann. Statist.11, 453–466.
Saito, N. (1994). Simultaneous noise suppression and signal compression using a library of orthonormal bases and the minimum description length criterion. In Foufoula-Georgiou, E. and Kumar, P. (eds.),Wavelets in Geophysics, Academic Press, New York.
Stein, C. (1981). Estimation of the mean of a multivariate normal distribution.Ann. Statist.10, 1135–1151.
Sweldens, W. (1996). The lifting scheme: A custom-design construction of biorthogonal wavelets.Applied and Comp. Harmonic Analysis 3, 186–200.
Sweldens, W. (1996). The lifting scheme: A construction of second generation wavelets. Technical report 1995:6, Industrial Mathematics Initiative, Department of Mathematics, University of South Carolina.
Triebel, H. (1992).Theory of function spaces II. Birkhäuser, Basel.
Tribouley, K. (1995). Practical estimation of multivariate density using wavelet methods.Statistica Neerlandica 49, 41–62.
Vannucci, M. andVidakovic, B. (1995). Preventing the Dirac disaster: wavelet based density estimation. Technical reportDP 95-24, Duke University.
Vidakovic, B. (1994). Nonlinear wavelet shrinkage with Bayes rules and Bayes factors. Technical reportDP 94-24, Duke University.
von Sachs, R. andSchneider, K. (1996). Wavelet smoothing of evolutionary spectra by nonlinear thresholding. Applied and Comp.Harmonic Analysis 3 (3), 268–282.
Wahba, G. (1990).Spline models for observational data. CBMS-NSF regional conferences series in applied mathematics. SIAM, Philadelphia.
Walter, G. G. (1992). Approximation of the Delta Function by Wavelets.J. Approx. Theory 71, 329–343.
Walter, G. O. (1994).Wavelets and Other Orthogonal Systems with Applications. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida.
Wang, Y. (1995). Jump and Sharp Cusp Detection by wavelets.Biometrika 82, 385–397.
Wang, Y. (1996). Function estimation via wavelet shrinkage for long-memory data.Ann. Statist.24 (2), 466–484.
Weyrich, N. andWarhola, O. T. (1995). Denoising using wavelets and cross-validation. IN Singh, S. P. (ed.),Approximation Theory, wavelet and applications, NATO ASI series C, pp. 523–532.
Wickerhauser, M. V. (1994).Adapted Wavelet Analysis: From Theory to Software. AK Peters, Boston.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Research supported by the IDOPT project (CNRS-INRIA-UJF-INPG). This paper, the following discussions and the reply by A. Antoniadis are the result of a seminar hold in Rome, in September 1997. The editorial board wants to thank ISTAT for its financial support.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Antoniadis, A. Wavelets in statistics: A review. J. Ital. Statist. Soc. 6, 97 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03178905
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03178905