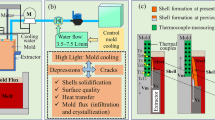
Abstract
To understand the effects of casting conditions on the formation of longitudinal surface crack, the crack morphology of over 2000 charges at scarfed beam blanks were investigated. The results whow that the most sensitive crack susceptibility range of carbon contents lie in the 0.12–0.13 wt.% range. This was due to the effect of shell irregularity between mold surface and solidified shell withdrawn by δ-γ transformation and the embrittlement phenomena by liquid film of soluble elements such as phosphorous and sulfur at the dendrite interface. It was found that the increase of crack formation is attributed to the increase of phosphorous and sulfur contents segregated at the dendrite interface. The increase of crack formation with increasing Phosphorous and Sulfur contents is due to the enlargement of the ΔT range, which is defined as the temperature difference between LIT (liquid impenetrable temperature) and ZDT (zero ductility temperature). The effect of casting speed on crack formation shows a linear relationship. As casting speed is increased, the solidified shell had little time to grow and the width of shell became smaller. As, the heat flux from the thinner shell increased, the thermal strain was increased, increasing crack formation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. N. Singh and K. E. Blazek,J. Met. 57, 16 (1974).
A. Grill and J. K. Brimacombe,Ironmaking & Steelmaking 3, 76 (1976).
T. Matsumiya, T. Saeki, and J. Tanaka,Tetsu-to-Hagane 68, 1782 (1982).
S. Nagata,Tetsu-to-Hagane 76, 214 (1990).
K. Nakai and T. Sakashita,Tetsu-to-Hagane 3, 498 (1987).
H. Mizukami,Tetsu-to-Hagane 81, 20 (1995).
Y. Sugitani,Tetsu-to-Hagane 67, 1508 (1981).
K. Nakai,Tetsu-to-Hagane 73, 498 (1987).
K. Yamamoto,ISIJ Int. 1, 115 (1987).
T. Saeki,ISIJ Int. 13, 1773 (1982).
J. E. Lee and J. K. Yoon,ISIJ. Int. 39, 455 (1998).
T. J. Yeo,Ph. D. Thesis, Seoul National University (1999).
H. G. Suzuki and S. Nishimura,Tetsu-to-Hagane 65, 2038 (1979).
A. Yamanaka,Tetsu-to-Hagane 82, 35 (1996).
H. Fujii and M. Oda,Tetsu-to-Hagane 64, 2148 (1978).
H. G. Suzuki, S. Nishimura, and Y. Nakamura,Trans. ISIJ 24, 55 (1984).
Y. Maehara and K. Yasumoto,Tetsu-to-Hagane 71, 1534 (1985).
K. Y. Kim and T. Yeo,ISIJ Int. 36, 284 (1996).
R. B. Mahapatra,Metall. Trans. B 22, 875 (1991).
B. G. Thomas,Proc. 6th Int. Iron and Steel Cong., Vol. 3, p. 348, Iron and Steel Inst, Nagoya, Japan (1990).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seok, Y.J., Yoon, J.K. The effect of casting conditions on the formation of longitudinal surface crack in the beam blank caster. Met. Mater. Int. 8, 543–550 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03178255
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03178255