Abstract
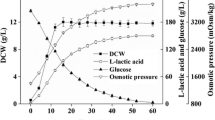
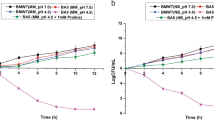
We compared the function of L- and D-proline as compatible solute inEscherichia coli K-12 cells under high osmolarity. Growth ofE. coli K-12 in a Davis minimal medium was inhibited at 0.5 M and 1 M NaCl, but it was recovered by the addition of L-proline. Glucose uptake was reduced with increase of external NaCl concentrations, but it was improved by the addition of L-proline. On the other hand, the addition of D-proline did not show the role of compatible solute although accumulated in cells. On the analysis ofE. coli proline transporter mutants, difference of the affinity of proline transporters for D-proline was observed at PutP and ProP. These results presumed that the functional disorder of D-proline as compatible solute was caused by its structural feature in cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barron A., Jung J.L, Villarejo M. (1987). Purification and characterization of a glycine betaine-binding protein fromEscherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem., 254: 10931–10935.
Bremer E., Krämer R. (2000). Coping with osmotic challenges: Osmoregulation through accumulation and release of compatible solutes in bacteria. In: Story G., Hengge-Arnis R., Eds, Bacterial Stress Responses, ASM Press, Washington D.C., pp. 79–97.
Davis B.D., Mingioli E.S. (1950). Mutants ofEscherichia coli requiring methionine or vitamin B12. J. Bacteriol., 60: 17–28.
Galinski E.A. (1993). Compatible solutes of halophilic eubacteria: molecular principles, water-solute interaction, stress protection. Experientia, 49: 487–496.
Grothe S.G., Krogsrud R.L., McClellan D.J., Milner J.L., Wood J.M. (1986). Proline transport and osmotic stress response inEscherichia coli K-12. J. Bacteriol., 166: 253–259.
May G.E., Villarejo F.M., Bremer M. (1986). Binding protein dependent transport of glycine betaine and its osmotic regulation inEscherichia coli K12. Mol. Gen. Genet., 255: 225–233.
Milner J.L., McClellan D.J., Wood J.M., (1987). Factors reducing and promoting the effectiveness of proline as an osmoprotectant inEscherichia coli K12. J. Gen. Microbiol., 133: 1851–1860.
Nagata S., Sasaki H., Oshima A., Takeda S., Hashimoto Y., Ishida A. (2005). Effect of proline and K+ on the stimulation of cellular activities inEscherichia coli K-12 under high salinity. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem., 69: 740–746.
Sasaki H., Ishida A., Hashimoto Y., Takeda S., Oshima A., Kawai H., Nagata S. (2006). Utilization of proline inEscherichia coli K-12 at different osmolarities. J. Biol. Sci., 6: 675–679.
Shahjee H.M., Banerjee K., Ahmad F. (2002). Comparative analysis of naturally occurring L-amino acid osmolytes and their D-isomers on protection ofEscherichia coli against environmental stresses. J. Biosci., 27: 515–520.
Soutourina J., Plateau P., Blanquet S. (2000). Metabolism of Daminoacyl-tRNAs inEscherichia coli andSaccharomyces cerevisiae cells. J. Biol. Chem., 275: 32535–32542.
Stalmach M.E., Grothe S., Wood J.M. (1983). Two proline porters inEscherichia coli K-12. J. Bacteriol., 156: 481–486.
Whatmore A.M., Chudek J.A., Reed R.H. (1990). The effects of osmotic upshock on the intracellular solute pools ofBacillus subtilis. J. Gen. Microbiol., 136: 2527–2535.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sasaki, H., Takaki, A., Oshima, A. et al. Comparison of the function of L- and D-proline as compatible solute inEscherichia coli K-12 under high osmolarity. Ann. Microbiol. 57, 265–268 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03175217
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03175217