Abstract
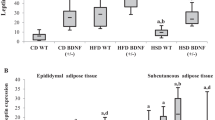
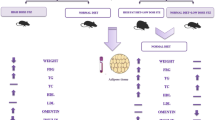
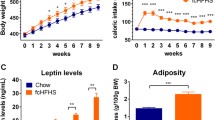
The aim of the present study was to identify the role of leptin and adiponectin in the development of resistance or susceptibility to diet-induced obesity in rats. For this purpose, male Wistar rats were fed with standard laboratory diet (control group) or cafeteria diet. After 15 days, two groups of rats with different response respect to the cafeteria diet were identified, and were assigned as diet-induced obesity (DIO) and diet resistant (DR) rats. The high-fat diet induced a very dignificant increase in both body and fat mass weight in DIO group. However, DR rats, gained even less weight than control-fed animals. Food intake was increased in cafeteria-fed rats (both DIO and DR) in comparison to control group; but hyperphagia was higher in DIO rats. In addition, feed efficiency (the ratio of weight gained to calories consumed) was significantly decreased in DR as compared to DIO rats. Regarding leptin, a significant increase in both adipose tissue gene expression and serum levels was observed in DIO rats in comparison with other groups (control and DR). A significant increase in both adiponectin circulating levels and adipose tissue mRNA expression was also observed in DIO animals as compared with the other groups. These data suggest that the susceptibility to obesity of DIO rats might be secondary, at least in part, to an earlier development of leptin resistance, which could lead to alterations in food intake (hyperphagia) and energetic metabolism. However, neither changes in leptin or adiponectin seem to be involved in the adaptive mechanisms that confer resistance to high fat intake.
Resumen
En el presente trabajo, se estudia el papel de la leptina y la adiponectina en la resistencia o susceptibilidad a la obesidad inducida por la dieta. Para ello, se alimentaron ratas Wistar macho con una dieta de laboratorio (grupo control) o con una dieta rica en grasa (dieta de cafetería). Tras 15 días, se identificaron dos grupos de ratas con diferente respuesta a la dieta de cafetería, los cuales fueron designados como susceptibiles (DIO) o resistentes (DR) al desarrollo de obesidad. Así, se observó un incremento muy significativo en el peso y la masa grasa corporal en el grupo DIO, mientras que los animales del grupo DR ganaron menos peso corporal que los animales control. La ingesta calórica fue significativamente superior en los grupos DR y DIO respecto del grupo control, aunque la hiperfagia fue significativamente superior en los animales susceptibles. Además, la eficiencia metabólica fue significativamente inferior en las ratas DR. En cuanto a la leptina y a la adiponectina, las ratas DIO mostraron un incremento significativo tato en la expresión de los genes correspondientes en tejido adiposo como en los niveles séricos de ambas hormonas. Esto datos sugieren que la susceptibilidad a la obesidad en las ratas DIO podría ser secundaria a un desarrollo temprano de resistencia a la leptina, que puede ir acompañada tanto de alteraciones en la ingesta (hiperfagia) como en el metabolismo energético. Sin embargo, ni los cambios en la leptina ni en la adiponectina parecen estar implicados en los mecanismos de adaptación que provocan resistencia a la obesidad.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arita, Y., Kihara, S., Ouchi, N., Takahashi, M., Maeda, K., Miyagawa, J., Hotta, K., Shimomura, I., Nakamura, T., Miyaoka, K., Kuriyama, H., Nishida, M., Yamashita, S., Okubo, K., Matsubara, K., Muraguchi, M., Ohmoto, Y., Funahashi, T. and Matsuzawa, Y. (1999):Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.,257, 79–83.
Berraondo, B., Marti, A., Duncan, J.S., Trayhurn, P. and Martínez, J. A. (2000):Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord.,24, 156–163.
Bullen, J. W., Jr., Ziotopoulou, M., Ungsunan, L., Misra, J., Alevizos, I., Kokkotou, E., Maratos-Flier, E., Stephanopoulos, G. and Mantzoros, CS. (2004):Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab.,287, E662–670.
Caro, J. F., Sinha, M. K., Kolaczynski, J. W., Zhang, P. L. and Considine, R. V. (1996):Diabetes,45, 1455–1462.
Chang, S., Graham, B., Yakubu, F., Lin, D., Peters, J. C. and Hill, J.O. (1990):Am. J. Physiol.,259, R1103–1110.
Collins, S., Martin, T. L., Surwit, R. S. and Robidoux, J. (2004):Physiol. Behav.,81, 243–248.
Havel, P. J. (2004):Diabetes,53,Suppl 1, S143-S151.
Hotta, K., Funahashi, T., Bodkin, N. L., Ortmeyer, H. K., Arita, Y. and Hansen, B. C. (2001):Diabetes,50, 1126–1133.
Hu, E., Liang, P. and Spiegelman, B. M. (1996):J. Biol. Chem.,271, 10697–10703.
Ioffe, E., Moon, B., Connolly, E. and Friedman, J. M. (1998):Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci.,95, 11852–11857.
Jang, I., Hwang, D., Lee, J., Chae, K., Kim, Y. and Kang, T. (2003):Exp. Anim.,52, 99–107.
Kubota, N., Terauchi, Y., Yamauchi, T., Kubota, T., Moroi, M., Matsui, J., Eto, K., Yamashita, T., Kamon, J., Satoh, H., Yano, W., Froguel, P., Nagai, R., Kimura, S., Kadowaki, T. and Noda, T. (2002):J. Biol. Chem.,277, 25862–25866.
Levin, B. E. and Keesey, R. E. (1998):Am. J. Physiol.:274, 412–419.
Levin, B. E. (1999):Am. J. Physiol.,276, 382–387.
Levin, B. E. and Dunn-Meynell, A. A. (2000):Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol.,278, 231–237.
Levin, B. E. and Dunn-Meynell, A. A. (2002):Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol.,282, 46–54
Levin, B. E., Dunn-Meynell, A. A., Ricci, M. R. and Cummings, D. E. (2003):Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab.,285, 949–957.
Levin, B. E., Dunn-Meynell, A. A. and Banks, W. A. (2004):Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol.,286, 143–150.
Li, J., Yu, X., Pan, W. and Unger, R. H. (2002):Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab.,282, E1334–1341.
Loos, R. J. and Bouchard, C. (2003):J. Intern. Med.,254, 401–425.
Lopez, I. P., Milagro, F. I., Marti, A., Moreno-Aliaga, M. J., Martínez, J. A. and De Miguel, C. (2004):Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.,318, 234–239.
Maeda, N., Shimomura, I., Kishida, K., Nishizawa, H., Matsuda, M., Nagarentani, H., Furuyama, N., Kondo, H., Takahashi, M., Arita, Y., Komuro, R., Ouchi, N., Kihara, S., Tochino, Y., Okutomi, K., Horie, M., Takeda, S., Aoyama, T., Funahashi, T. and Matsuzawa, Y. (2002):Nat. Med.,8, 731–737.
Maffei, M., Halaas, J., Ravussin, E., Pratley, R. E., Lee, G. H., Zhang, Y., Fei, H., Kim, S., Lallone, R. and Ranganathan, S. (1995):Nat. Med.,1, 1155–1161.
Margareto, J., Marti, A. and Martínez, J. A. (2001):J. Physiol. Biochem.,57, 347–348.
Marti, A., Berraondo, B. and Martínez, J. A. (1999):J. Physiol. Biochem.,55, 43–49.
Meier, U. and Gressner, A. M. (2004):Clin. Chem.,50, 1151–1525.
Montague, C. T., Farooqi, I. S., Whitehead, J. P., Soos, M. A., Rau, H., Wareham, N. J., Sewter, C. P., Digby, J. E., Mohammed, S. N., Hurst, J. A., Cheetham, C. H., Earley, A. R., Barnett, A. H., Prins, J. B. and O’Rahilly, S. (1997):Nature,387, 903–908.
Moreno, M. J. and Martínez, J. A. (2002):Anales sist. San. Navarra,25,Suppl 1, 29–39.
Moreno-Aliaga, M. J., Lamas, O., Marti, A. and Martínez, J. A. (2002):Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.,291, 1201–1207.
Moreno-Aliaga, M. J., Urresti, J., Lamas, O., Marti, A. and Martínez, J. A. (2003):Int. J. Obes.,37 (Supp. 1), S 56.
Morton, N. M., Paterson, J. M., Masuzaki, H., Holmes, M. C., Staels, B., Fievet, C., Walker, B. R., Flier, J. S., Mullins, J. J. and Seckl, J. R. (2004):Diabetes,53, 931–938.
Munzberg, H., Flier, J. S. and Bjorbaek, C. (2004):Endocrinology,145, 4880–4889.
Pérez-Matute, P., Marti, A., Martínez, J. A. and Moreno-Aliaga, M. J. (2003):J. Physiol. Biochem.,59, 201–208.
Qi, Y., Takahashi, N., Hileman, S. M., Patel, H. R., Berg, A. H. and Pajvani, U. B., Scherer P. E. and Ahima R. S. (2004):Nat. Med. 10, 524–529
Stefan, N. and Stumvoll, M. (2000):Horm. Metab. Res.,34, 469–474.
Surwit, R. S., Dixon, T. M., Petro, A. E., Daniel, K. W. and Collins, S. (2000):Endocrinology,141, 3630–3637.
Tkacs, N. C. and Levin, B. E. (2004):Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol.,287, 1110–1115.
Tomas, E., Tsao, T.S., Saha, A. K., Murrey, H. E., Zhang, Cc. C., Itani, S. I., Lodish, H. F. and Ruderman, N. B. (2002):Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A. 99, 16309–16313.
Tulipano, G., Vergoni, A. V., Soldi, D., Muller, E. E. and Cocchi, D. (2004):J. Endocrinol.,183, 289–298.
Zhang, Y., Proenca, R., Maffei, M., Barone, M., Leopold, L. and Friedman, J. M. (1994):Nature,372, 425–432.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pérez-Echarri, N., Pérez-Matute, P., Martínez, J.A. et al. Serum and gene expression levels of leptin and adiponectin in rats susceptible or resistant to diet-induced obesity. J. Physiol. Biochem. 61, 333–342 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03167050
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03167050