Abstract
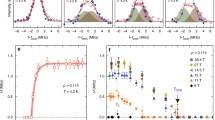
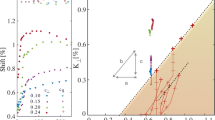
The authors carried out a low field (6.3 kOe) NMR measurement of the Gaussian component of63Cu nuclear spin-spin relaxation rate 1/T 2G at the planar Cu site in a high-T c superconductor YBa2Cu3O6.9 (T c=92 K). They demonstrate that the results provide quantitative information concerning the static spin susceptibility χ′(q) at non-zero wave vector q. The detailed analysis of the data assuming a model susceptibility peaked at the corner of first Brillouin zone q=Q (Q=(π/a, θ/a),a: lattice constant) shows that χ′(q) satisfies a Curie-Weiss law around q=Q. Stoner enhancement over the calculated Lindhard function at q=Q is estimated to be of the order of ∼10–20. They also demonstrate that combined analysis of 1/T 1 and 1/T 2G allows one to judge whether anomalous shift of the low frequency spectral weight of χ″(Q,ω) to higher frequencies (i.e.pseudo gap) exists or not. Application of the method to YBa2Cu3O6.9 revealed no appreciable pseudo gap in the material.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
For a review, Pennington C.H., Slichter C.P. in: Physical Properties of High Temperature Superconductors II, (Ginsberg D.M., ed.), p. 269. Singapore: World Scientific 1990.
Moriya T.: J. Phys. Soc. Jpn.18, 516 (1963)
(a) Takigawa M., Hammel P.C., Heffner R.H., Fisk Z.: Phys. Rev.B39, 7371 (1989); (b) Shimizu T., Yasuoka H., Tsuda T., Ueda H., Kosuge K.: Bulletin of Magnetic Resonance12, 39 (1991); (c) Walstedt R.E., Bell R.F., Schneemeyer L.F., Waszczak J.V., Espinosa G.P.: Phys. Rev.B45, 8074 (1992)
Slichter C.P.: Principles of Magnetic Resonance, (3rd ed.), Berlin: Springer-Verlag 1990.
|(a) Mali M., Brinkmann D., Pauli L., Roos J., Zimmermann H., Hulliger J.: Phys. Lett.A124, 112 (1987); (b) Walstedt R.E., Warren, Jr. W.W., Bell R.F., Brennert G.F., Espinosa G.P.: Phys. Rev.B38, 9299 (1988); (c) Kitaoka Y., Hiramatsu S., Kondo T., Asayama K.: J. Phys. Soc. Jpn.56, 3024 (1988); (d) Imai T., Shimizu T., Tsuda T., Yasuoka H., Takabatake T., Nakazawa Y., Ishikawa M.: J. Phys. Soc. Jpn.57, 1771 (1988); Imai T., Shimizu T., Yasuoka H., Ueda Y., Kosuge K.: J. Phys. Soc. Jpn.57, 2280 (1988); (e) Barrett S., Durand D.J., Pennington C.H., Slichter C.P., Friedmann T.A., Rice J.P., Ginzberg D.M.: Phys. Rev.B41, 6283 (1991)
Imai T., Yasuoka H., Shimizu T., Ueda Y., Kosuge K.: J. Phys. Soc. Jpn.58, 1528 (1989)
(a) Rossat-Mignod J., Regnault L.P., Vetter C., Bourget P., Bossy J., Henry J.Y., Lapertot G.: Physica C185–189, 86 (1991); (b) Tranquada J.M., Gehring P.M., Shirane G., Shamoto S., Sato M.: preprint (1992); (c) Mason T.E., Aeppli G., Mook H.A.: Phys. Rev. Lett.68, 1414 (1992); (d) Thurston T.R., Birgeneau R.J., Kastner M.A., Preyer N.W., Shirane G., Fujii Y., Yamada K., Endoh Y., Kakurai K., Matsuda M., Hidaka Y., Murakami T.: Phys. Rev.B40, 4584 (1989)
(a) Hammel P.C., Takigawa M., Heffner R.H., Fisk Z., Ott K.C.: Phys. Rev. Lett.63, 1992 (1989); (b) Yoshinari Y., Yasuoka H., Ueda H., Koga K., Kosuge K.: J. Phys. Soc. Jpn.59, 3698 (1990)
(a) Markert J.T., Noh T.W., Russek S.E., Cotts R.M.: Solid State Comm.63, 847 (1987); (b) Alloul H., Ohno T., Mendels P.: Phys. Rev. Lett.63, 700 (1989)
(a) Shastry B.S.: Phys. Rev. Lett.63, 1288 (1989); (b) Varma C.M., Littlewood P.B., Schmidt-Rink S., Abrahams E., Ruckenstein A.E.: Phys. Rev. Lett.63, 1996 (1989); (d) Lu J.P., Si Q., Kim J.H., Levin K.: Phys. Rev. Lett.65, 2466 (1990); (e) Bulut N., Hone D., Scalapino D.J., Bickers N.E.: Phys. Rev. Lett.64, 2723 (1990); (f) Millis A.J., Monien H., Pines D.; Phys. Rev.B42, 697 (1990); Monien H., Pines D., Takigawa M.: Phys. Rev.B43, 258 (1991); (g) Moriya T., Takahashi Y., Ueda K.: J. Phys. Soc. Jpn.59, 2905 (1990); (h) Tanamoto T., Kuboki K., Fukuyama H.: J. Phys. Soc. Jpn.60, 3072 (1991); (i) Singh R.R., Gelfand M.P.: Phys. Rev.B42, 996 (1990)
Pennington C.H., Slichter C.P.: Phys. Rev. Lett.66, 381 (1991)
Mila F., Rice T.M.: Physica C157, 561 (1989)
In anspin echo experiment for a quadrupolar splitted NMR line, the local fields due to nuclear spins that are not flipped byH 1 arerefocused by the echo formation. Therefore the second moment given by Eq.(11) is much smaller than the result forfree induction decay experiment calculated by Kambe K., Ollom F.: J. Phys. Soc. Jpn.11, 50 (1956)
Pennington C.H., Durand D.J., Slichter C.P., Rice J.P., Bukowski E.D., Ginsberg D.M.: Phys. Rev.B39, 274 (1989)
(a) Horvatic H., Sgransan P., Berthier C., Berthier Y., Butaud P.: Phys. Rev.B39, 7332 (1989); (b) Warren, Jr. W.W., Walstedt R.E., Brennert G.F., Cava R.J., Tycko R., Bell R.F., Dabbagh G.: Phys. Rev. Lett.62, 1193 (1989); (c) Imai T., Yasuoka H., Shimizu T., Ueda Y., Yoshimura K., Kosuge K.: Physica C162–164, 169 (1989)
Imai T.: J. Phys. Soc. Jpn.59, 2508 (1990)
Itoh Y., Yasuoka H., Yoko Fujiwara, Ueda Y., Machi T., Tomeno I., Tai K., Koshizuka N., Tanaka S.: submitted to J. Phys. Soc. Jpn.; also see Itoh Y., Yasuoka H., Ueda Y.: J. Phys. Soc. Jpn.59, 3463 (1990)
Song Y.Q., Halperin W.P.: Physica C191, 131 (1992), and private communication.
Barret S.E., Martindale J.A., Burand D.J., Pennington C.H., Slichter C.P., Friedmann T.A., Rice J.P., Ginzberg D.M.: Phys. Rev. Lett.66, 108 (1991)
1/T 1 results obtained by NQR (zero field) and NMR (8.3 Tesla) agreed within experimental errors, showing that field dependence is less than 3%. We note that very careful measurement is necessary especially for NMR measurement of 1/T 1 suppressingstimulated echo and taking care ofbackground signal originated from adjacent resonance lines.
Bulut N., Scalapino D.J.; Phys. Rev. Lett.67, 2798 (1991)
Xu J.-H., Watson-Yang T.J., Jaejun Yu, Freeman A.J.: Physics Lett.A120, 489 (1987); Though this value is calculated for doped La2CuO4, it must be a reasonable estimate for the present case (Jaejen Yu; private communication)
(a) Zimmermann H., Mali M., Brinkmann D., Karpinski J., Kaldis E., Rusiecki S.: Physica C159, 681 (1989); (b) Machi T., Tomeno I., Miyatake T., Koshizuka N., Tanaka S., Imai T., Yasuoka H.: Physica C173, 32 (1991)
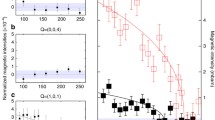
Recent NQR observation of the monotonic increase of 1/T 2G for YBa2Cu4O8 below 300 K [17] where 1/T 1 T shows a broad maximum [23] may be an evidence for the existence of pseudo gap in the material.
Millis A.J., Monien H.: Phys. Rev.B45, 3059 (1991)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Imai, T., Slichter, C.P., Paulikas, A.P. et al. Low field63Cu NMR study of indirect nuclear spin-spin coupling in YBa2Cu3O6.9. A new approach to probe strong correlation effects in high-T c superconductors. Appl. Magn. Reson. 3, 729–744 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03166292
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03166292