Abstract
Real-time PCR is a new fluorometric method for cycle-to-cycle quantification of PCR product growth rates. The real-time PCR method is fast and associated with a high reproducibility rate. It is used more often for monitoring MRD and chimerism in patients after allogeneic stem cell transplantation (SCT).
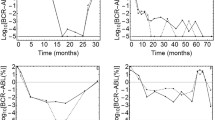
There are real-time PCR methods for patients with CML, AML and ALL patients with inv(16), t(8;21), t(15;17); t(1;19) and other chromosomal aberrations. For patients with AML monitoring MRD is useful to identify patients who were at high risk for relapse after receiving chemotherapy. In patients with CML monitoring MRD might be helpful to assess success of after allogeneic SCT, or response to therapies with interferon alfa or STI 571. We found, that it is possible to estimate the relapse stage in CML after SCT by the amount of bcr-abl fusion transcript detected using a real-time PCR method. The median measured bcr-abl amount differ significantly (P<0.001) between the various stages, which has relevant clinical implications because it enables early therapeutic decisions in relapsing patients after transplant as e.g. the application of DLI to induce graft-versus-leukemia effects.
Using real-time PCR it is possible to detect differences at alleles between recipient and donor at a single nucleotide basis (SNP) for chimerism analysis. The real-time PCR method enables to achieve a high a sensitivity of up to 1×10−4, which is much more sensitive than all other chimerism methods including VNTR-PCR, STR-PCR. Furthermore, chimerism in male recipients with a female donor can be monitored also by detecting y-chromosome specific sequences by real-time PCR after transplant, which might be the most sensitive method to detect host type gene sequences.
All in all, new real-time PCR methods offer a fast, reliable and very sensitive method to evaluate MRD and chimerism in patients after allogeneic SCT and therefore, to help to identify patients who are at high risk for leukemic relapse.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Elmaagacli AH, Freist A, Hahn M, et al. Estimating the relapse stage in chronic myeloid leukemia patients after alogeneic stem cell transplantation by the amount of BCR-ABL fusion transcripts detected using a new real-time polymerase chain reaction method.Br J Haematol. 2001;113:1072–1075.
Stentoft J, Pallisgaard N, Kjeldsen E, Holm MS, Nielsen JL, Hokland P. Kinetics of BCR-ABL fusion transcript levels in chronic myeloid leukemia patients treated with STI571 measured by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction.Eur J Haematol. 2001;67:302–308.
De Haas V, Breunis WB, Dee R, et al. The Tel-AML1 realtime quantitative PCR might replace the antigen receptor-bases genomic PCR in clinical MRD studies in children with ALL.Br J Haematol. 2002;116:87–93.
Buonamici S, Ottaviani E, Testoni N, et al. Real-time quantitation of minimal residual disease in inv(16)-positive AML may indicate risk for clinical relapse and may identify patients in a curable state.Blood. 2002;99:443–449.
Curry JD, Glaser MC, Smith MT. Real-time RT-PCR detection and quantification of t(1;19) (E2A-PBX1) fusion genes associated with leukaemia.Br J Haematol. 2001;115:826–830.
Krauter J, Heil G, Ganser A. The AML1/MTG8 fusion transcript in t(8;21) positive AML and its implication for the detection of minimal residual disease, malignancy.Hematol. 2001;5:369–381.
Slack JL, Bi W, Livak KJ, et al. Pre-clinical validation of a novel, highly sensitive assay to detect PML-RARalpha mRNA using real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction.J Mol Diagn. 2001;3:141–149.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Elmaagacli, A.H. Real-time PCR for monitoring minimal residual disease and chimerism in patients after allogeneic transplantation. Int J Hematol 76 (Suppl 2), 204–205 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03165118
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03165118