Abstract
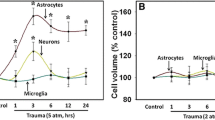
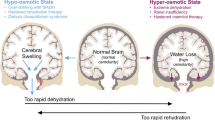
Swelling of brain slices is shown to occur in response to elevated potassium levels or glutamate, which is accompanied by astrocytic swelling. Cl−/HCO −3 anion exchange inhibitors, such as SITS (4-acetamido-4′-isothiocyanostilbene-2,2′-disulfonic acid) or furosemide, but not the specific cotransport inhibitor bumetanide, inhibit swelling or increased ion uptake in rat brain slices caused by elevated potassium although there were marked species differences in sensitivity. A novel anion exchange inhibitor,l-644,711, inhibits swelling and increased ion uptake caused by glutamate in rat and cat brain slices, as well as inhibiting [3H]glutamate uptake in primary rat astrocyte cultures. Possible mechanisms of action of the inhibitors are discussed.l-644,711 was also found to be effective in promoting recovery from a trauma plus hypoxia head injury model in cats. Marked perivascular astrocytic swelling is associated with this head injury model, andl-644,711 also inhibited such astroglial swelling as determined ultrastructurally. The significance of these findings in relation to possible connections between astrocytic swelling and brain pathology is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bakay L. and Lee J. C. (1968) The effect of acute hypoxia and hypercapnia on the ultrastructure of the central nervous system.Brain 91, 697–706.
Bakay L., Lee J. C., Lee G. C., and Peng J.-R. (1977) Experimental cerebral concussion. Part I. An electron microscopic study.J. Neurosurg. 47, 525–531.
Barron K. D., Dentinger M. P., Kimelberg H. K., Nelson L. R., Bourke R. S., Keegan S., Mankes R., and Cragoe E. J., Jr. (1988) Ultrastructural features of a brain injury model in cat. 1. Vascular and neuroglial changes and the prevention of astroglial swelling by a fluorenyl (aryloxy)alkanoic acid derivative (l-644,711).Acta Neuropath. (Berlin)75, 295–307.
Bevan S., Chiu S. Y., Gray P. T. A., and Ritchie J. M. (1985) The presence of voltage-gated sodium, potassium and chloride channels in rat cultured astrocytes.Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B. 225, 299–313.
Bonting S. L. (1970) Na+−K+ activated ATPase and cation transport,Membranes and Ion Transport, vol. I (Bittar E. E., ed.), pp. 258–263, Wiley, New York.
Bourke R. S. and Tower D. B. (1966) Fluid compartmentation and electrolytes of cat cerebral cortexin vitro. II. Sodium, potassium and chloride of mature cortex.J. Neurochem. 13, 1099–1117.
Bourke R. S., Kimelberg H. K., Daze M. A., and Popp A. J. (1979) Studies on the formation of astroglial swelling and its inhibition by clinically useful agents,Neural Trauma (Popp A. J., Nelson L. R., Bourke, R. S., and Kimelberg, H. K., eds.), pp. 95–113, Raven, New York.
Bourke R. S., Kimelberg H. K., Daze M., and Church G. (1983) Swelling and ion uptake in cat cerebrocortical slices: Control by neurotransmitters and ion transport mechanisms.Neurochem. Res. 8, 5–24.
Bowman C. L. and Kimelberg H. K. (1984) Excitatory amino acids directly depolarize rat brain astrocytes in primary culture.Nature 311, 656–659.
Brazy P. C. and Gunn R. B. (1976) Furosemide inhibition of chloride transport in human red blood cells.J. Gen. Physiol. 68, 583–599.
Cabantchik Z. I., Knauf P. A., and Rothstein A. (1978) The anion transport system of the red blood cell. The role of membrane protein evaluated by the use of probes.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 515, 239–302.
Casper D. S., Trelstad R. L., and Reif-Lehrer L. (1982) Glutamate-induced cellular injury in isolated chick embryo retina: Muller cell localization of initial effects.J. Comp. Neurol. 209, 79–90.
Chan P. H., Yurko M., and Fishman R. A. (1982) Phospholipid degradation and cellular edema induced by free radicals in brain cortical slices.J. Neurochem. 38, 525–531.
Chan P. H., Yu A. C. H., and Fishman R. A. (1988) Free fatty acids and excitatory neurotransmitter amino acids as determinants of pathological swelling of astrocytes in primary culture,The Biochemical Pathology of Astrocytes (Norenberg M. D., Hertz L., and Schousboe A., eds.), pp. 327–335, Liss, New York.
Coles J. A., Tsacopoulos M., Rabineau P., and Gardner-Medwin A. R. (1981) Movement of potassium into glial cells in the retina of the drone, Apis mellifera, during photostimulation,Ion-selective Microelectrodes and Their Use in Excitable Tissues (Sykova E., Hnik P., and Vyklicky, eds.), pp. 345–349, Plenum, New York.
Cragoe E. J., Jr., Gould N. P., and Woltersdorf O. W., Jr., Ziegler C., Bourke R. S., Nelson L. R., Kimelberg H. K., Waldman J. B., Popp A. J., and Sedransk N. (1982) Agents for the treatment of brain injury. 1. (Aryloxy)alkanoic acids.J. Med. Chem. 25, 567–579.
Cragoe E. J., Jr., Woltersdorf O. W., Jr., Gould N. P., Pietruszkiewicz A. M., Ziegler C., Sakurai Y., Stokker G. E., Anderson P. S., Bourke R. S., Kimelberg H. K., Nelson L. R., Barron K. D., Rose J. R., Szarowski D., Popp A. J., and Waldman J. B. (1986) Agents for the treatment of brain edema. 2. [(2,3,9,9a-tetrahydro-3-oxo-substituted-1 H-fluoren-7-yl)oxy] alkanoic acids and some of their analogues.J. Med. Chem. 29, 825–841.
Dietzel I., Heinemann U., Hofmeier G., and Lux H. D. (1980) Transient changes in the size of the extracellular space in the sensorimotor cortex of cats in relation to stimulus-induced changes in potassium concentration.Exp. Brain Res. 40, 432–439.
Duffy P. E. (1983)Astrocytes: Normal, Reactive and Neoplastic, Raven, New York.
Franck G., Grisar T., and Moonen G. (1983) Glial and neuronal Na+, K+ pump.Advances in Cellular Neurobiology 4, 133–159.
Frangakis M. V. and Kimelberg H. K. (1984) Dissociation of neonatal rat brain by dispase for preparation of primary astrocyte cultures.Neurochem. Res. 9, 1685–1693.
Frelin C., Chassande O., and Lazdunski M. (1986) Biochemical characterization of the Na+/K+/Cl− co-transport in chick cardiac cells.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 134, 326–331.
Garay R. P., Hannaert P. R., Nazaret C., and Cragoe E. J., Jr. (1986) The significance of the relative effects of loop diuretics and anti-brain edema agents on the Na+, K+, Cl− cotransport system and the Cl−/NaCO −3 anion exchanger.Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 334, 202–209.
Garcia J. H. and Lossinsky A. S. (1979) Brain edema: Introduction,Cerebrovascular Diseases (Price T. R. and Nelson, E., eds.), pp. 125–130, Raven, New York.
Garcia J. H., Kalimo H., Kamijyo Y., and Trump B. F. (1977) Cellular events during partial cerebral ischemia. I. Electron microscopy of feline cerebral cortex after middle cerebral artery occlusion.Virchows Arch. B. Cell. Path. 25, 191–206.
Gray P. T. A. and Ritchie J. M. (1986) A voltage-gated chloride conductance in rat cultured astrocytes.Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B. 228, 267–288.
Griffiths D. R., Burns N., and Crawford A. R. (1978) Early vascular changes in the spinal gray matter following impact injury.Acta Neuropathol. (Berlin)41, 33–39.
Herndon R. M., Coyle J. T., and Addicks E. (1980) Ultrastructural analysis of kainic acid lesion to cerebellar cortex.Neuroscience 5, 1015–1026.
Hertz J. (1979) Functional interactions between neurons and astrocytes. I. Turnover and metabolism of putative amino acid transmitters.Prog. in Neurobiol. 13, 277–323.
Hirano A. (1981) Astrocytes,A Guide to Neuropathology, pp. 204–224, Igaku Shoin, Tokyo.
Hirata H., Slater N. T., and Kimelberg H. K. (1983) Alpha-adrenergic receptor-mediated depolarization of rat neocortical astrocytes in primary culture.Brain Res. 270, 358–362.
Hodgkin A. L. and Horowicz P. (1959) The influence of potassium and chloride ions on the membrane potential of single muscle fibres.J. Physiol. 148, 127–160.
Jenkins L. W., Povlishock J. T., Becker D. P., Miller J. D., and Sullivan H. G. (1979) Complete cerebral ischemia. An ultrastructural study.Acta Neuropathol. (Berlin)48, 113–125.
Jenkins L. W., Becker D. P., and Coburn T. H. (1984) A quantitative analysis of glial swelling and ischemic neuronal injury following complete cerebral ischemia.Recent Progress in the Study and Therapy of Brain Edema (Go T. G. and Baethmann A., eds.), pp. 523–537, Plenum, New York.
Kalimo H., Rehncrona S., Soderfeldt B., Olsson Y., and Siesjö, B. K. (1981) Brain lactic acidosis and ischemic cell damage. 2. Histopathology.J. Cerebr. Blood Flow Metab. 1, 313–327.
Kimelberg H. K. (1979) Glial enzymes and ion transport in brain swelling,Neural Trauma (Popp A. J., Bourke R. S., Nelson L. R., and Kimelberg, H. K., eds.), pp. 137–153, Raven, New York.
Kimelberg H. K. (1981) Active accumulation and exchange transport of chloride in stroglial cells in culture.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 646, 179–184.
Kimelberg H. K. (1987) Anisotonic media and glutamate-induced ion transport and volume responses in primary astrocyte cultures.J. Physiol. (Paris)82, 294–303.
Kimelberg H. K. and Bourke R. S. (1982) Anion transport in the nervous system,Handbook of Neurochemistry (Lajtha, A., ed.), pp. 31–67, Plenum, New York.
Kimelberg H. K. and Frangakis M. V. (1985) Furosemide- and bumetanide-sensitive ion transport and volume control in primary astrocyte cultures from rat brain.Brain Res. 361, 125–134.
Kimelberg H. K. and Frangakis M. V. (1986) Volume regulation in primary astrocyte cultures.Advances in the Biosciences 61, 177–186.
Kimelberg H. K. and Ransom B. R. (1986) Physiological and pathological aspects of astrocytic swelling,Astrocytes, vol. 3 (Fedoroff S. and Vernadakis A., eds.), pp. 129–166, Academic, New York.
Kimelberg H. K., Biddelcome S., and Bourke R. S. (1979) SITS-inhibitable Cl− transport and Na+-dependent H+ production in primary astroglial cultures.Brain Res. 173, 111–124.
Kimelberg H. K., Bowman C. L., and Hirata H. (1986) Anion transport in astrocytes.Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 481, 334–353.
Kimelberg H. K., Pang S., and Treble D. H. (1989a) Excitatory amino-acid stimulated uptake of22Na+ in primary astrocyte cultures.J. Neurosci. 9, 1141–1149.
Kimelberg H. K., Goderie S., and Waniewski, R. A. Hypoosmotic media-induced release of amino acids from astrocytes.Soc. Neurosci. Abst. (in press).
Kimelberg H. K., Bowman C., Biddlecome S., and Bourke R. S. (1979b) Cation transport and membrane potential properties of primary astroglial cultures from neonatal rat brains.Brain Res. 177, 533–550.
Kimelberg H. K., Bourke R. S., Stieg P. E., Barron K. D., Hirata H., Pelton E. W., and Nelson L. R. (1982) Swelling of astroglia after injury to the central nervous system: Mechanisms and consequences,Head Injury: Basic and Clinical Aspects (Grossman R. G. and Gildenberg P. L., eds.), pp. 31–44, Raven, New York.
Kimelberg H. K., Cragoe E. J., Jr., Nelson L. R., Popp A. J., Szarowski D., Rose J. W., Woltersdorf O. W., Jr., and Pietruszkiewicz A. M. (1987) Improved recovery from a traumatic-hypoxic brain injury in cats by intracisternal injection of an anion transport inhibitor.Central Nervous System Trauma 4, 3–14.
Klatzo I. (1967) Neuropathological aspects of brain edema.J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 26, 1–13.
Klatzo I., Chui E., Fujiwara K., and Spatz M. (1980) Resolution of vasogenic brain edema (VBE),Brain Edema, Advances in Neurology, vol. 28, (Cervos-Navarro J. and Ferszt R., eds.), pp. 359–374, Raven, New York.
Klatzo I., Suszuki R., Orzi F., Schuier F., and Nitsch C. (1984) Pathomechanisms of ischemic brain edema,Recent Progress in the Study and Therapy of Brain Edema (Go T. G. and Baethmann, A., eds.), pp. 1–10, Plenum, New York.
Kletzien R. F., Pariza M. W., Becker J. E., and Potter V. R. (1975) A method using 3-0-methyl-d-glucose and phloretin for the determination of intracellular water space of cells in monolayer culture.Anal. Biochem. 68, 537–544.
Koechel D. A. (1981) Ethacrynic acid and related diuretics: Relationship of structure to beneficial and detrimental actions.Ann. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 21, 265–293.
Kraig R. P., Pulsinelli W. A., and Plum F. (1985a) Hydrogen ion buffering during complete brain ischemia.Brain Res. 342, 281–290.
Kraig R. P., Pulsinelli W. A., and Plum F. (1985b) Heterogeneous distribution of hydrogen and bicarbonate ions during complete brain ischemia.Prog. Brain. Res. 63, 155–166.
Kregenow F. M. (1981) Osmoregulatory salt transport mechanisms: Control of cell volume in anisotonic media.Ann. Rev. Physiol. 43, 493–505.
Lowe A. G. and Lambert A. (1983) Chloride-bicarbonate exchange and related transport processes.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 694, 353–374.
Lund-Anderson H. and Hertz L. (1970) Effects of potassium and of glutamate on swelling and on sodium and potassium content in brain cortex slices from adult rats.Exp. Brain Res. 11, 199–212.
Martin D. L. and Shain W. (1979) High affinity transport of taurine and beta-alanine and low affinity transport of gamma-aminobutyric acid by a single transport system in cultured glioma cells.J. Biol. Chem. 254, 7076–7084.
Matyja E. (1986) Morphologic evidence of a primary response of glia to kainic acid administration into the rat neostriatum; studiedin vivo andin vitro.Expt. Neurol. 92, 609–623.
Matakas F., Birkle J., and Cervos-Navarro J. (1978) The effect of prolonged experimental hypercapnia on the brain.Acta Neuropathol. (Berlin)41, 207–210.
Nelson L. R., Bourke R. S., Popp A. J., Cragoe E. J., Jr., Signorelli A., Foster V. V., and Creel W. (1979) Evaluation of treatment modalities in severe head injuries using an animal model,Neural Trauma (Popp A. J., Bourke R. S., Nelson L. R., and Kimelberg H. K., eds.), pp. 297–313, Raven, New York.
Nelson L. R., Auen E. L., Bourke R. S., Barron K. D., Malik A. B., Cragoe E. J., Jr., Waldman J. B., Kimelberg H. K., Foster V. V., Creel W., and Schuster L. (1982) A comparison of animal head injury models developed for treatment modality evaluation,Head Injury: Basic and Clinical Aspects, (Grossman R. G. and Gildenberg, P. J., eds.), pp. 117–127, Raven, New York.
Norenberg M. D. (1986) Hepatic encephalopathy: A disorder of astrocytes,Astrocytes, vol 3 (Fedoroff S. and Vernadakis A., eds.), pp. 425–460, Academic, New York.
Norenberg M. D. and Lapham L. W. (1974) The astrocyte response in experimental portal-systemic encephalopathy: An electron microscopic study.Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 33, 422–435.
Pappius H. M. and Elliott K. A. C. (1956) Factors affecting the potassium content of incubated brain slices.Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 34, 1053–1067.
Plum F. (1983) What causes infarction in ischemic brain?Neurology 33, 222–233.
Siesjö, B. K. (1981) Cell damage in the brain: A speculative synthesis.J. Cerebr. Blood Flow Metab. 1, 155–185.
Siesjö, B. K. (1984) Brain acid-base metabolism in health and disease,Cerebral Ischemia (Bes A., Braquet P., Paoletti, R., and Siesjö B. K., eds.), pp. 157–165, Elsevier, B. V., Amsterdam.
Sontheimer H., Kettenmann H., Backus K. H., and Schachner, M. (1988) Glutamate opens Na+/K+ channels in cultured astrocytes.Glia 1, 328–336.
Sykova E. (1983) Extracellular K+ accumulation in the central nervous system.Prog. Biophys. Molec. Biol. 42, 135–189.
Trachtenberg M. C. (1982) Brain cell responses to extracellular protein,Head Injury: Basic and Clinical Aspects (Grossman R. G. and Gildenberg P. L., eds.), pp. 169–178, Raven, New York.
Van Harreveld A. (1982) Swelling of the Müller fibers in the chicken retina.J. Neurobiol. 13, 519–536.
Van Harreveld A. and Fifkova E. (1971) Light- and electron-microcopic changes in central nervous tissue after electrophoretic injection of glutamate.Exp. Mol. Pathol. 15, 61–81.
Walz W. and Hertz L. (1984) Intense furosemide-sensitive potassium accumulation in the presence of pathologically high extracellular potassium levels.J. Cerebr. Blood Flow Metab. 4, 301–304.
Walz W. and Hinks E. C. (1985) Carrier-mediated KCl accumulation accompanied by water movements is involved in the control of physiological K+ levels by astrocytes.Brain Res. 343, 44–51.
Waniewski R. A. and Martin D. L. (1983) Selective inhibition of glial versus neuronal uptake ofl-glutamic acid by SITS.Brain Res. 268, 390–394.
Waniewski R. A. and Martin D. L. (1984) Characterization ofl-glutamic acid transport by glioma cells in culture: Evidence for sodium-independent, chloride-dependent high affinity influx.J. Neurosci. 4, 2237–2246.
Warnock D. G., Greger R., Dunham P. B., Benjamin M. A., Fizzell R. A., Field, M., Spring K. R., Ives H. E., Aronson P. S., and Seifter J. (1983) Ion transport processes in apical membrane of epithelia.Fed. Proc. 43, 2473–2487.
Yu M. C., Bakay L., and Lee J. C. (1972) Ultrastructure of the central nervous system after prolonged hypoxia. I. Neuronal alterations.Acta Neuropathol. (Berlin)22, 222–234.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kimelberg, H.K., Rose, J.W., Barron, K.D. et al. Astrocytic swelling in traumatic-hypoxic brain injury. Molecular and Chemical Neuropathology 11, 1–31 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03160036
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03160036