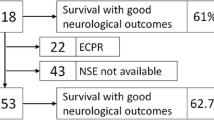
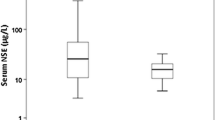
Abstract
The concentration of neuron-specific enolase (NSE) was measured in plasma of 18 patients after cardiac arrest and resuscitation (14 nonsurvivors and 4 survivors). In all patients, the NSE concentration was significantly higher in comparison to reference values. The highest concentration was measured in nonsurvivors. Time-course investigation in the first 24 h after cardiac arrest was performed in five patients. Two nonsurvivors and one survivor of the five patients showed a significant rise, and a NSE peak concentration of 42.7 μg/L, 13.6 μg/L, and 10.5 μg/L, respectively, was found 10–19 h after cardiac arrest.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Annéren G., Esscher T., Larsson L., Olsen L., and Pahlmann L. (1988) S-100 protein and neuron-specific enolase in amniotic fluid as markers of abdominal wall and neural tube defects in the fetus.Prenat. Diagn. 8, 323–328.
Dauberschmidt R., Marangos P. J., Zinsmeyer J., Bender V., Klages G., and Gross J. (1983) Severe head trauma and the changes of concentration of neuron-specific enolase in plasma and in cerebrospinal fluid.Clin. Chim. Acta 131, 165–170.
Dauberschmidt R., Zinsmeyer J., Marangos P. J., Bender V., Klages G., Gross J., and Meyer M. (1986) Neuronenspezifische Enolase und Schädel-Hirn-Trauma.Z. Med. Lab. Diagn. 27, 186–190.
Franis A., Rivett A. J., and Roth J. A. (1983) Activity of neuron-specific enolase in normal and lesioned rat brain.Brain Res. 263, 89–95.
Ghandour M. S., Langley O. K., and Keller A. (1981) A comparative immunohistological study of cerebellar enolase.Exp. Brain Res. 41, 271–279.
Ghobrial M., and Ross E. R. (1986) Immuno cytochemistry of neuron-specific enolase: A reevaluation.Prog. Neuropathol. 6, 199–221.
Hay E., Royds J. A., Davies-Jones G. A. B., Lewtas N. A., Timperley W. R., and Taylor C. B. (1984) Cerebrospinal fluid enolase in stroke.J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psych. 47, 724–729.
Jacobi C. and Reiber H. (1988) Clinical relevance of increased neuron-specific enolase concentration in cerebrospinal fluid.Clin. Chim. Acta 177, 49–54.
Kato K., Ishiguro Y., Suzuki F., Ito A., and Semba R. (1982) Distribution of nervous system-specific forms of enolase in peripheral tissues.Brain Res. 237, 441–448.
Longstreth W. T., Inui T. S., Cobb L. A., and Copass M. K. (1983) Neurologic recovery after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest.Ann. Int. Med. 98, 588–592.
Marangos P. J. and Schmechel D. E. (1987) Neuron-specific enolase, a clinically useful marker for neurons and neuroendocrine cells.Ann. Rev. Neurosci. 10, 269–295.
Mokuno K., Kato K., Kawai K., Matsuoka Y., Yanagi T., and Sobue I. (1983) Neuron-specific enolase and S-100 protein levels in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with various neurological diseases.J. Neurol. Sci. 60, 443–451.
Persson L., Hardemark H. G., Gustafsson J., Rundström G., Mendel-Hartvig I., Esscher T., and Pahlman S. (1987) S-100 protein and neuron-specific enolase in cerebrospinal fluid and serum: Markers of cell damage in human central nervous system.Stroke 18, 911–918.
Pickel V. M., Reis D. J., Marangos P. J., and Zomzely-Neurath C. (1975) Immunocytochemical localization of nervous system specific protein (NSP-R) in rat brain.Brain Res. 105, 184–187.
Royds J. A., Davies-Jones G. A. B., Lewtas N. A., Timperley W. R., and Taylor C. B. (1983) Enolase isoenzymes in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with diseases of the nervous system.J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psych. 46, 1031–1036.
Scarna H., Delafosse B., Steinberg R., Debilly G., Mandrand B., Keller A., and Pujol J. F. (1982) Neuron-specific enolase as a marker of neuronal lesions during various comas in man.Neurochem. Int. 4, 405–411.
Scarna H., Steinberg R., Delafosse B., Debilly G., Mandrand B., Keller A., and Pujol J. F. (1983) Neuron-specific enolase (NSE) in biological fluids: A marker of neuronal lesions, inProtides of the Biological Fluids (Peters H., ed.) pp. 55–60, Pergamon Press, Oxford.
Schmechel D. E., Marangos P. J., Zis A., Brightman P., and Goodwin F. K. (1978) The brain enolases as specific markers of neuronal and glial cells.Science 199, 313–315.
Schmechel D. E. (1985) γ-Subunit of the glucolytic enolase: non-specific or neuron specific.Lab. Invest. 52, 239–242.
Sowden G. R., Robins D. W., and Baskett P. J. F. (1984) Factors associated with survival and eventual cerebral status following cardiac arrest.Anaesthesia 39, 39–43.
Steinberg R., Scarna H., Keller A., and Pujol J. F. (1983) Release of neuronspecific enolase (NSE) in cerebrospinal fluid following experimental lesions of the rat brain.Neurochem. Int. 5, 145–151.
Steinberg R., Scarna H., and Pujol J. F. (1984a) Neuron-specific enolase in cerebrospinal fluid: A possible indicator of neuronal damage in kainic acid lesions.Neurosci. Letters 45, 147–150.
Steinberg R., Gueniau C., Scarna H., Keller A., Worcel M., and Pujol J. F. (1984b) Experimental brain ischemia: Neuron-specific enolase level in cerebrospinal fluid as an index of neuronal damage.J. Neurochem. 43, 19–24.
Vermuyten K., Lowenthal A., and Karcher D. (1990) Detection of neuron-specific enolase concentration in cerebrospinal fluid from patients with neurological disorders by means of a sensitive enzyme immunoassay.Clin. Chim. Acta 187, 69–78.
Zinsmeyer J., Marangos P. J., Issel E. P., and Gross J. (1987) Neuron-specific enolase in amniotic fluid—a possible indicator for fetal distress and brain implication.J. Perinat. Med. 15, 199–202.
Zinsmeyer J., Hübner R., Pohle R., Evers G., and Gross J. (1988) Neuron-specific enolase in infants after hypothermic circulatory arrest for surgical correction of ventricle septum defects, inAbstracts International Symposium on Hypoxia, Berlin, September 12–14, 1988 (Gerber G., Goeres E., Gross J., Scheuch D. W., and Lun A., eds.) p. 113, Nationales Druckhaus Berlin, Germany.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dauberschmidt, R., Zinsmeyer, J., Mrochen, H. et al. Changes of neuron-specific enolase concentration in plasma after cardiac arrest and resuscitation. Molecular and Chemical Neuropathology 14, 237–245 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03159939
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03159939