Summary
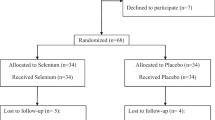
□Patients and Methods: Seventy patients with definitive rheumatoid arthritis were matched to built 2 groups, which were double-blind and randomized allocated to supplementation with sodium-selenit 200 µg/d or placebo for 3 months, each. Both groups were given fish oil fatty acids (30 mg/kg body weight), DMARDS were continued throughout the study, while variations in steroids or NSAD were admitted.
□Results: Selenium concentrations in erythrocytes of patients with rheumatoid arthritis were 85.1±26 µg/l, and significantly lower than found in an average German population (123±23 µg/l). During the observation period of 3 months normal selenium concentrations were not restored, despite supplementation higher than RDA. At the end of the experimental period the selenium supplemented group showed less tender or swollen joints, and morning stiffness. Selen-supplemented patients needed less cortison and NSAD than controls. In accordance with clinical improvement we found a decrease of laboratory indicators of inflammation (C-reactive protein, α2-globuline, prostaglandin E2).
□Conclusion: No side effects of supplementation with selenium were noted, which can be considered as adjuvant therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Adam, O., K. Krämer: Antioxidantientherapie bei chronischer Polyarthritis. Med. Klin. 90, Suppl. 1 (1995), 27–31.
Bendich, A: Antioxidant micronutrients and the immun system. In: Roitt, I. M., P. J. Delves: Encyclopedia of immunology. Academic Press, London-New York 1992, p. 151–153.
Biesalski, H. K., J. Frank: Antioxidantien in der Ernährung und ihre Bedeutung für die anti-/prooxidative Balance im Immunsystem. Immun. Infekt. 23 (1995), 166–178.
Fairburn, K., M. Grootveld, R. J. Ward, C. Abiuka, M. Kus, R. B. Williams, P. G. Winyard, D. R. Blake: Alphatocopherol, lipids and lipoproteins in knee-joint synovial fluid and serum from patients with inflammatory joint disease. Clin. Sci. 83 (1992), 657–664.
Fink, G.: Selen-Konzentration im Serum und im Vollblut bei Patienten mit chronischer Polyarthritis und Spondylitis ancylosans. Rheuma 9 (1989), 190–196.
Hartfiel, W., W. Schulte: Selenmangel in der Bundesrepublik. Akt. Ernährungsmed. 13 (1988), 75–116.
Heliovaara, M., P. Knekt, K. Aho, R. K. Aaran, G. Alfthan, A. Aromaa: Serum antioxidants and risk of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 53 (1994), 51–53.
Müller, U.: Zur Wirkung einer adjuvanten Selen-Supplementierung bei Patienten mit chronischer Polyarthritis. Vita Min Spur 5 (1990), 113–121.
O’Dell, J. R., S. Lemley-Gillepies, W. R. Palmer, A. L. Weaver, G. F. Moore, L. W. Klassen: Serum selenium in rheumatoid arthritis. Semin. Arthr. Rheum. 20 (1991), 305–318.
Peretz, A. M., J. D. Neve, J. Duchateau, J. P. Famaey: Adjuvant treatment of recent onset rheumatoid arthritis by selenium supplementation: preliminary observations. Brit. J. Rheum. 31 (1992), 281–186.
Peretz, A. M., J. D. Neve, J. P. Famaey JP: Selenium in rheumatic diseases. Semin. Arth. Rheum. 20 (1991), 305–316.
Situnayake, R. D., D. I. Thurnham, S. Kootathep, S. Chirico, J. Lunec, M. Davis, B. McConkey: Chain breaking antioxidant status in rheumatoid arthritis: clinical and laboratory correlates. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 50 (1991), 81–86.
Tarp, U., K. Stengaard-Pedersen, J. C. Hansen, E. B. Thorling: Glutathion redox cycle enzymes and selenium in severe rheumatoid arthritis: lack of antioxidative response to selenium supplementation in polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 51 (1992), 1044–1049.
Zurier, R. B.: Prostaglandins, leukotriens, and related compounds. In: Kelly, W. N., E. D. Harris, S. Ruddy, C. B. Sledge: Textbook of rheumatology, 4th ed. Saunders, Philadelphia-London-Toronto-Montreal-Sydney-Tokyo 1993, p. 201–212.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heinle, K., Adam, A., Gradl, M. et al. Selenkonzentration in den Erythrozyten bei Patienten mit rheumatoider Arthritis. Med Klin 92 (Suppl 3), 29–31 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03041958
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03041958