Summary
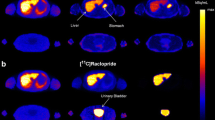
At the new heavy ion tumor therapy facility of the Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschung at Darmstadt positron emission tomography (PET) has been implemented for in-beam and in-situ therapy control, i. e. during the tumor irradiation. The components necessary for this dedicated PET-imaging and their integration into the framework of therapy planning and quality assurance of heavy ion cancer treatments are presented. Results of the first application of this PET-method to patient treatments are reported.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Enghardt W, Fromm WD, Geissel H, et al. The spatial distribution of positron emitting nuclei generated by relativistic light ion beams in organic matter. Phys Med Biol 1992;44:2127–31.
Haberer Th, Becher W, Schardt D, et al. Magnetic scanning system for heavy ion therapy. Nucl Instr and Meth 1993;A330:296–305.
Hasch BG. Die physikalischen Grundlagen einer Verifikation des Bestrahlungsplanes in der Schwerionen-Tumortherapie mit der Positronen-Emissions-Tomographie. PhD Thesis, Dresden University of Technology, 1996.
Jäkel O, Krämer M. Treatment planning for heavy ion irradiation. In: Abstracts of the 6th Workshop on Heavy Charged Particles in Biology and Medicine, 1997, GSI-Report 97-09: F1–F2.
Kawachi K, Kanai T, Ymada S, et al. Developments of irradiation technique at HIMAC. Oral presentation at the Annual Meeting of the European Hadron Therapy Group, Innsbruck, Austria, Oct. 1997.
Kraft G. The radiobiological and physical basis for radiotherapy with protons and heavy ions. Strahlenther Onkol 1990;166:10–3.
Llacer J. Positron emission medical measurements with accelerated radioactive beams. Nucl Sci Appl 1988;3:111–31.
Pawelke J, Enghardt W, Haberer Th, et al. In-beam PET imaging for the control of heavy-ion tumor therapy. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 1997;44:1492–8.
Rogers JG, Taylor AJ, Rahimi MF, et al. An improved multicrystal 2-D BGO detector for PET. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 1992;39:1063–8.
Shepp LA, Vardi Y. Maximum likelihood reconstruction for emission tomography. IEEE Trans Med Imag 1982;2:113–22.
Wienhard K, Eriksson L, Grootoonk S, et al. Performance evaluation of the positron scanner ECAT EXACT. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1992;16: 804–13.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Enghardt, W., Debus, J., Haberer, T. et al. The application of PET to quality assurance of heavy-ion tumor therapy. Strahlenther Onkol 175 (Suppl 2), 33–36 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03038884
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03038884