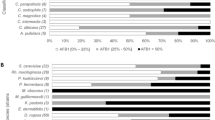
Abstract
Several biodegradation experiments were carried out using 10 different yeast strains.Saccharomyces spp., Kluyveromyces spp. andRhodotorula spp. were tested for biodegradation of selected mycotoxins (ochratoxin A, nivalenol, deoxynivalenol and fumonisin B1) standardsin vitro. There was confirmed that some yeast strains are able to degrade some mycotoxins. However, great differences between individual strains were observed. Moreover, 12Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains were tested for their potential capability to degrade zearalenone and fumonisins in Sabouraud broth. Two strains were capable to degrade zearalenone totally, one strain decreased the mycotoxin concentration up to 25%, and one strain up to 75% of original amount. Two strains were capable to degrade fumonisins partially.
Zusammenfassung
Verschiedene Stämme von Hefen wurdenin vitro zur Biodegradationsstudie herangezogen. ZehnSaccharomyces spp., Kluyveromyces spp. undRhodotorula spp. Stämme wurden auf ihre Biodegradationsfähigkeit ausgewählten Mykotoxinstandards (Ochratoxin A (OA), Nivalenol, Deoxynivalenol und Fumonisin)in vitro getestet. Es konnte gezeigt werden, daß manche Hefestämme imstande sind, einzelne Mykotoxine abzubauen, wobei große Unterschiede zwischen einzelnen Stämmen festgestellt wurden. Zusätzlich wurden 12Saccharomyces cerevisiae Stämme auf ihr potentielles Abbauvermögen von Zearalenon und Fumonisin B1 in einer Nährlösung geprüft. Zwei Stämme waren fähig Zearalenon gänzlich abzubauen, ein Stamm verringerte die anfangskonzentration um 25% und ein weiterer um 75%. Zwei Stämme konnten Fumonisin teilweise abbauen.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beeton S, Bull AT (1989) Biotransformation and detoxification of T-2 toxin by soil and freshwater bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 55: 190–197
Böhm J, Grajewski J, Asperger H, Cecon B, Rabus B, Razzazi E (2000) Study on biodegradation of some A- and B-Trichothecenes and ochratoxin A by use of probiotic microorganisms. Mycotoxin Research Vol. 16A 2/70–74
He P, Young LG, Forsberg C (1992) Microbial transformation of deoxynivalenol (vomitoxin). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 58: 3857–3863
Jesenská Z, Šajbidorová I (1991) T-2 toxin degradation by micromycetes. J. Hyg. Epidemiol. Microbiol. Immunol. 35: 41–49
Kiessling KH, Pettersson H, Sandholm K, Olsen M (1984) Metabolism of aflatoxin, ochratoxin, zearalenone, and three trichothecenes by intact rumen fluid, rumen protozoa, and rumen bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 47: 1070–1073
Megharaj M, Garthwaite I, Thiele JH (1997) Total biodegradation of the oestrogenic mycotoxin zearalenone by a bacterial culture. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 24: 329–333
Swanson SP, Nicoletti J, Rood HD Jr, Buck WB, Cote LM (1987) Metabolism of three trichothecene mycotoxins, T-2 toxin, diacetoxyscirpenol and deoxynivalenol, by bovine rumen microorganisms. J. Chromatogr. 414: 335–342
Swanson SP, Helaszek C, Buck WB, Rood HD Jr, Haschek WM (1988) The role of intestinal microflora in the metabolism of trichothecene mycotoxins. Food Chem. Toxicol. 26: 823–829
Westlake K, Mackie RI, Dutton MF (1987) T-2 toxin metabolism by ruminal bacteria and its effect on their growth. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 53: 587–592
Razzazi-Fazeli E, Böhm J, Luf W (1999) Determination of Nivalenol and Deoxynivalenol in wheat using Liquid Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry with Negative Ion Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionisation (APCI-) J. Chromatogr A 854, 45–55
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Štyriak, I., Conková, E., Kmec, V. et al. The use of yeast for microbial degradation of some selected mycotoxins. Mycotox Res 17 (Suppl 1), 24–27 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03036705
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03036705