Abstract
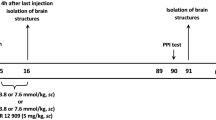
Monosodium glutamate (MSG) treatment of neonatal rats causes neuronal degeneration in various brain areas and leads to several neurochemical, endocrinological and behavioral alterations. However, relatively little is known about the development of neurological reflexes and motor coordination of these animals. Therefore, the aim of the present study was to examine the neurobehavioral development of newborn rats treated with MSG. Rats received MSG at postnatal days 1, 3, 5, 7, and 9. Appearance of neural reflexes and reflex performance as well as motor coordination were examined for 5 weeks after birth. The efficacy of MSG treatment was confirmed by histological examination of the arcuate nucleus. We found that MSG treatment delayed the appearance of forelimb placing, forelimb grasp and righting reflexes, besides the retarded somatic development. The treated pups performed surface righting in significantly longer times. Also, worse performance was observed in the foot-fault and rota-rod tests. However, MSG-treated rats reached control levels by the end of the fifth postnatal week. These results show that MSG treatment does not cause permanent alterations in the neurobehavioral development, only delays the appearance of some reflexes and leads to temporary changes in reflex performance and motor coordination signs.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Ali MM, M Bawari, UK Misra and GN Babu (2000) Locomotor and learning deficits in adult rats exposed to monosodium-L-glutamate during early life.Neurosci. Lett. 284, 57–60.
Altman J and K Sudarshan (1975) Postnatal development of loco- motion in the laboratory rat.Anim. Behav. 23, 896–920.
Araujo PE and J Mayer (1973) Activity increase associated with obesity induced by monosodium glutamate in mice.Am. J. Physiol. 225, 764–765.
Archer T, T Palomo and A Fredriksson (2002) Neonatal 6-hydroxy-dopamine-induced hypo/hyperactivity: blockade by dopamine reuptake inhibitors and effect of acute D-amphetamine.Neurotoxicity Res. 4, 247–266.
Archer T, N Schroder and A Fredriksson (2003) Neurobehavioural deficits following postnatal iron overload: II Instrumental learning performance.Neurotoxicity Res. 5, 77–94.
Arees EA and J Mayer (1970) Monosodium glutamate-induced brain lesions: electron microscopic examination.Science 170, 549–550.
Barth TM and BB Stanfield (1990) The recovery of forelimb placing behavior in rats with neonatal unilateral cortical damage involves the remaining hemisphere.J. Neurosci. 10, 3449–3459.
Beas-Zarate C, MI Perez-Vega and I Gonzalez-Burgos (2002) Neonatal exposure to monosodium L-glutamate induces loss of neurons and cytoarchitectural alterations in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons of adult rats.Brain Res. 952, 275–281.
Beninger RJ, A Jhamandas, H Aujla, L Xue, RV Dagnone, RJ Boegman and K Jhamandas (2002) Neonatal exposure to the glutamate receptor antagonist MK-801: effects on locomotor activity and pre-pulse inhibition before and after sexual maturity in rats.Neurotoxicity Res. 4, 477–488.
Bodnar RJ, T Portzline and G Nilaver (1985) Differential alterations in opioid analgesia following neonatal monosodium glutamate treatment.Brain Res. Bull. 15, 299–305.
Borella A, M Bindra and PM Whitaker-Azmitia (1997) Role of the 5HT1A receptor in development of the neonatal rat brain: preliminary behavioral studies.Neuropharmacology 36, 445–450.
Bowers WJ, JS Nakai, I Chu, MG Wade, D Moir, A Yagminas, S Gill, O Pulido and R Meuller (2004) Early developmental neurotoxicity of a PCB/organochlorine mixture in rodents after gestational and lactational exposure.Toxicol. Sci. 77, 51–62.
Bures J, O Buresova and JP Huston (1983)Techniques and Basic Experiments for the Study of Brain and Behavior (Elsevier Science Publishers: Amsterdam), pp 77–97.
Chaparro-Huerta V, MC Rivera-Cervantes, BM Torres-Mendoza and C Beas-Zarate (2002) Neuronal death and tumor necrosis factor-α response to glutamate-induced excitotoxicity in the cerebral cortex of neonatal rats.Neurosci. Lett. 333, 95–98.
Dam K, FJ Seidler and TA Slotkin (2000) Chlorpyrifos exposure during a critical neonatal period elicits gender-selective deficits in the development of coordination skills and locomotor activity.Dev. Brain Res. 121, 179–187.
Dawson R and JF Lorden (1981). Behavioral and neurochemical effects of neonatal administration of monosodium L-glutamate in mice.J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol. 95, 71–84.
Donatelle JM (1977) Growth of the corticospinal tract and the development of placing reactions in the postnatal rat.J. Comp. Neurol. 175, 207–232.
Dubovicky M, D Tokarev, I Skultetyova and D Jezova (1997) Changes in exploratory behavior and its habituation in rats neonatally treated with monosodium glutamate.Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 56, 565–569.
Dunn AJ and EL Webster (1985) Neonatal treatment with monosodium glutamate does not alter grooming behavior induced by novelty or adrenocorticotropic hormone.Behav. Neur. Biol. 44, 80–89.
Felt BT, T Schallert, J Shao, Y Liu, X Li and JD Barks (2002) Early appereance of functional deficits after neonatal excitotoxic and hypoxic-ischemic injury: fragile recovery after development and role of the NMDA receptor.Dev. Neurosci. 24, 418–425.
Fisher KN, RA Turner, G Pineault, J Kleim and MJ Saari (1991) The postweaning housing environment determines expression of learning deficit associated with neonatal monosodium glutamate (M.S.G.).Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 13, 507–513.
Fox WM (1965) Reflex-ontogeny and behavioural development of the mouse.Anim. Behav. 13, 234–241.
Frieder B and VE Grimm (1987) Prenatal monosodium glutamate causes long-lasting cholinergic and adrenergic changes in various brain regions.J. Neurochem. 48, 1359–1365.
Gonzalez-Burgos I, MI Perez-Vega and C Beas-Zarate (2001) Neonatal exposure to monosodium glutamate induces cell death and dendritic hypotrophy in rat prefrontocortical pyramidal neurons.Neurosci. Lett. 297, 69–72.
Harry CJ (1998) Developmental neurotoxicology, In:Reproductive and Developmental Toxicology (Korach KS, Ed.) (Marcel Dekker:),pp 211–257.
Heath DL and R Vink (1997) Magnesium sulphate improves neurologic outcome following severe closed head injury in rats.Neurosci. Lett. 228, 175–178.
Heiman ML and N Ben-Jonathan (1983) Increase in pituitary dopa-minergic receptors after monosodium glutamate treatment.Am. J. Physiol. 245, E261-E265.
Hill JM, I Gozes, JL Hill, M Fridkin and DE Brenneman (1991) Vasoactive intestinal peptide antagonist retards the development of neonatal behaviors in the rat.Peptides 12, 187–192.
Ishikawa K, T Kubo, S Shibanoki, A Matsumoto, H Hata and S Atai (1997) Hippocampal degeneration inducing impairment of learning in rats: model of dementia?Behav. Brain Res. 83, 39–44.
Iwata S, M Ichimura, Y Matsusawa, Y Takasaki and M Sasaoka (1979) Behavioral studies in rats treated with monosodium l-glutamate during the early stages of life.Toxicol. Lett. 4, 345–357.
Jansen EM and WC Low (1996) Quantitative analysis of contralateral hemisphere hypertrophy and sensorimotor performance in adult rats following unilateral neonatal ischemic-hypoxic brain injury.Brain Res. 708, 93–99.
Kartje-Tillotson G, EJ Neafsey and AJ Castro (1985) Electrophysiological analysis of motor cortical plasticity after cortical lesions in newborn rats.Brain Res. 332, 103–111.
Katz RJ (1983) Neonatal monosodium glutamate differentially alters two models of behavioral activity in conjunction with reduced hypothalamic endorphins.Physiol. Behav. 31, 147–151.
Kim YW, DW Choi, YH Park, JY Huh, KC Won, KH Choi, SY Park, JY Kim and SK Lee (2005) Leptin-like effects of MTII are augmented in MSG-obese rats.Regul. Pept. 127, 63–70.
Klingberg H, J Brankack and F Klingberg (1987) Long-term effects on behavior after postnatal treatment with monosodium-L-glutamate.Biomed. Biochim. Acta 46, 705–711.
Kostrzewa RM, JP Kostrzewa and R Brus (2003) Dopamine receptor supersensitivity: an outcome and index of neurotoxicity.Neurotoxicity Res. 5, 111–118.
Kubo T, R Kohira, T Okano and K Ishikawa (1993) Neonatal glutamate can destroy the hippocampal CA1 structure and impair discrimination learning in rats.Brain Res. 616, 311–314. Lengvari I (1977) Effect of perinatal monosodium glutamate treatment on endocrine functions of rats in maturity.Acta Biol. Hung. 28, 133-141.
Le Roy I, F Perez-Diaz, A Cherfouh and PL Roubertoux (1999) Preweanling sensorial and motor development in laboratory mice: quantitative trait loci mapping.Dev. Psychobiol. 34, 138–158.
Lubics A, D Reglodi, A Tamas, P Kiss, M Szalai, L Szalontay and I Lengvari (2005) Neurological reflexes and early motor behavior in rats subjected to neonatal hypoxic-ischemic injury.Behav. Brain Res. 157, 157–165.
Markgraf CG, EJ Green, BE Hurwitz, E Morikawa, WD Dietrich, PM McCabe, MD Ginsberg and N Schneiderman (1992) Sensorimotor and cognitive consequences of middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats.Brain Res. 575, 238–246.
Markus EJ and TL Petit (1987) Neocortical synaptogenesis, aging, and behavior: lifespan development in the motor-sensory system of the rat.Exp. Neurol. 96, 262–278.
Mistlberger RE and MC Antle (1999) Neonatal monosodium glutamate alters circadian organization of feeding, food anticipatory activity and photic masking in the rat.Brain Res. 842, 73–83.
Miyabo S, I Yamamura, E Ooya, N Aoyagi, Y Horikawa and S Hayashi (1985) Effects of neonatal treatment with monosodium glutamate on circadian locomotor rhythm in the rat.Brain Res. 339, 201–208.
Olney JW (1969) Brain lesions, obesity, and other disturbances in mice treated with monosodium glutamate.Science 164, 719–721.
Palomo T, RJ Beninger, RM Kostrzewa and T Archer (2003) Brain sites of movement disorder: genetic and environmental agents in neurodevelopmental perturbations.Neurotoxicity Res. 5, 1–26.
Pesini P, JL Rois, L Menendez and S Vidal (2004) The neonatal treatment of rats with monosodium glutamate induces morphological changes in the subfornical organ.Acta Histol. Embryol. 33, 273–277.
Pizzi WJ and JE Barnhart (1976) Effects of monosodium glutamate on somatic development, obesity and activity in the mouse.Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 5, 551–557.
Poon TKY and DP Cameron (1978) Measurement of oxygen consumption and locomotor activity in monosodium glutamate-induced obesity.Am. J. Physiol. 234, E532-E534.
Reddy GR, A Suresh, KS Murthy and CS Chetty (2002) Lead neurotoxicity: heme oxigenase and nitric oxide synthase activities in developing rat brain.Neurotoxicity Res. 4, 33–39.
Reglodi D, P Kiss, A Tamas and I Lengvari (2003). The effects of PACAP and PACAP antagonist on the neurobehavioral development of newborn rats.Behav. Brain Res. 140, 131–139.
Reinoso BS and AJ Castro (1989) A study of corticospinal remodelling using retrograde fluorescent tracers in rats.Exp. Brain Res. 74, 387–394.
Rogers DC, CA Campbell, JL Stretton and KB Mackay (1997) Correlation between motor impairment and infarct volume after permanent and transient middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat.Stroke 28, 2060–2066.
Saari MJ, S Fong, A Shivji and JN Armstrong (1990) Enriched housing masks deficits in place navigation induced by neonatal monosodium glutamate.Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 12, 29–32.
Sanchis-Segura C and CMG Aragon (2002) Consequences of mono-sodium glutamate or goldthioglucose arcuate nucleus lesions on ethanol-induced locomotion.Drug Alcohol Depend. 68, 189–194.
Schoelch C, T Hubschle, I Schmidt and B Nuesslein-Hildesheim (2002) MSG lesions decrease body mass of suckling-age rats by attenuating circadian decreases of energy expenditure.Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 283, E604-E611.
Segura-Aguilar J and RM Kostrzewa (2004) Neurotoxins and neu-rotoxic species implicated in neurodegeneration.Neurotoxicity Res. 6, 615–630.
Seress L (1982) Divergent effects of acute and chronic monosodium glutamate treatment on the anterior and posterior parts of the arcuate nucleus.Neuroscience 7, 2207–2216.
Seress L, G Lazar, B Kosaras and RT Robertson (1984) Regional effect of monosodium-L-glutamate on the superficial layers of superior colliculus in rat.Cell Tissue Res. 235, 453–457.
Sisk DR, T Kuwabara and AD Kirsch (1984) Behavioral recovery in albino rats with glutamate-damaged retinas.Invest. Ophtalmol. Vis. Sci. 25, 1124–1128.
Smart JL and J Dobbing (1971a) Vulnerability of developing brain. II. Effects of early nutritional deprivation on reflex ontogeny and development on behavior in the rat.Brain Res. 28, 85–95.
Smart JL and J Dobbing (1971b) Vulnerability of developing brain. VI. Relative effects of foetal and early postnatal undernutrition on reflex ontogeny and development of behavior in the rat.Brain Res. 33, 303–314.
Squibb RE, HA Tilson, OA Meyer and CA Lamartiniere (1981) Neonatal exposure to monosodium glutamate alters the neurobehavioral performance of adult rats.Neurotoxicology 2, 471–484.
Stricker-Krongrad A and B Beck (2004) Up-regulation of neuropeptide Y receptors in the hypothalamus of monosdium glutamate-lesioned Sprague-Dawley rats.Nutr. Neurosci. 7, 241–245.
Stricker-Krongrad A, C Burlet and B Beck (1998) Behavioral deficits in monosodium glutamate rats: specific changes in the structure of feeding behavior.Life Sci. 62, 2127–2132.
Tamas A, R Gabriel, B Racz, V Denes, P Kiss, A Lubics, I Lengvari and D Reglodi (2004) Effects of pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide in retinal degeneration induced by mono-sodium-glutamate.Neurosci. Lett. 372, 110–113.
Towfighi J, C Houeman, RC Vannucci and DF Heitjan (1994) Effect of unilateral perinatal hypoxic-ischemic brain damage on the gross development of opposite cerebral hemisphere.Biol. Neonate 65, 108–118.
Urena-Guerrero ME, SJ Lopez-Perez and C Beas-Zarate (2003) Neonatal monosodium glutamate treatment modifies glutamic acid decarboxylase activity during rat brain postnatal development.Neurochem. Int. 42, 269–276.
Van Rijn CM, E Marani and WJ Rietveld (1986) The neurotoxic effect of monosodium glutamate (MSG) on the retinal ganglion cells of the albino rat.Histol. Histopathol. 1, 291–295.
Yin K, C Watanabe, H Inaba and H Satoh (1997) Growth and behavioral changes in mice prenatally exposed to methylmercury and heat.Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 19, 65–71.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kiss, P., Tamas, A., Lubics, A. et al. Development of neurological reflexes and motor coordination in rats neonatally treated with monosodium glutamate. neurotox res 8, 235–244 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03033977
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03033977