Abstract
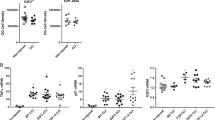
Cell death/survival following traumatic brain injury (TBI) may be a result of alterations in the intracellular ratio of death and survival factors. Bcl-2 family genes mediate both cell survival and the initiation of cell death. Using lysate RNase protection assays, mRNA expression of the anti-cell death genes Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL, and the pro-cell death gene Bax, was evaluated following experimental brain injuries in adult male Sprague-Dawley rats. Both the lateral fluid-percussion (LFP) and the lateral controlled cortical impact (LCI) models of TBI showed similar patterns of gene expression. Anticell death bcl-2 and bcl-xL mRNAs were attenuated early and tended to remain depressed for at least 3 days after injury in the cortex and hippocampus ipsilateral to injury. Pro-cell death bax mRNA was elevated in these areas, usually following the decrease in anti-cell death genes. These common patterns of gene expression suggest an important role for Bcl-2 genes in cell death and survival in the injured brain. Understanding the regulation of these genes may facilitate the development of new therapeutic strategies for a condition that currently has no proven pharmacologic treatments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams JH, D Doyle, DI Graham, AE Lawrence, DR McLellan, TA Gennarelli, M Pastuszko, and T Sakamoto (1985) The contusion index, a reappraisal in human and experimental non-missile head injury.Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 11, 299–308.
Akiyama H, S Barger, S Barnum, B Bradt, J Bauer, GM Cole, NR Cooper, P Eikelenboom, M Emmerling, BL Fiebich, CE Finch, S Frautschy, WS Griffin, H Hampel, M Hull, G Landreth, L Lue, R Mrak, IR Mackenzie, PL McGeer, MK O’Banion, J Pachter, G Pasinetti, C Plata-Salaman, J Rogers, R Rydel, Y Shen, W Streit, R Strohmeyer, I Tooyoma, FL Van Muiswinkel, R Veerhuis, D Walker, S Webster, B Wegrzyniak, G Wenk, and T Wyss-Coray (2000) Inflammation and Alzheimer’s disease.Neurobiol. Aging 21, 383–421.
Beschorner R, D Adjodah, JM Schwab, M Mittelbronn, I Pedal, R Mattern, HJ Schluesener, and R Meyermann (2000) Long-term expression of heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1, HSP-32) following focal cerebral infarctions and traumatic brain injury in humans.Acta Neuropathologica 100, 377–384.
Bredesen DE (1995) Neural apoptosis.Ann. Neurol. 38, 839–851.
Chen J, SH Graham, PH Chan, P Lan, RL Zhou, and RP Simon (1995) Bcl-2 is expressed in neurons that survive focal ischemia in the rat.NeuroReport 6, 394–398.
Chen J, RL Zhu, M Nakayama, K Kawaguchi, K Jin, RA Stetler, RP Simon and SH Graham (1996) Expression of the apoptosis-effec-tor gene, Bax, is up-regulated in vulnerable hippocampal CA1 neurons following global ischemia.J. Neurochem. 67, 64–71.
Chen J, SH Graham, M Nakayama, RL Zhu, K Jin, RA Stetler and RP Simon (1997) Apoptosis repressor genes Bcl-2 and Bcl-x-long are expressed in the rat brain following global ischemia.J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 17, 2–10.
Clark RS, J Chen, SC Watkins, PM Kochanek, M Chen, RA Stetler, JE Loeffert and SH Graham (1997) Apoptosis-suppressor gene bcl-2 expression after traumatic brain injury in rats.J. Neurosci. 17, 9172–9182.
Colicos MA and PK Dash (1996a) Apoptotic morphology of dentate gyrus granule cells following experimental cortical impact injury in rats, possible role in spatial memory deficits.Brain Res. 739, 120–131.
Colicos MA, CE Dixon and PK Dash (1996b) Delayed, selective neuronal death following experimental cortical impact injury in rats, possible role in memory deficits.Brain Res. 739, 111–119.
Conti AC, R Raghupathi, JQ Trojanowski and TK McIntosh (1998) Experimental brain injury induces regionally distinct apoptosis during the acute and delayed post-traumatic period.J. Neurosci. 18, 5663–5672.
Danielson P, S Forss-Petter, MA Brow, L Calavetta, J Douglass, RH Milner and JG Sutcliffe (1988) p1B15, a cDNA clone of the rat mRNA encoding cyclophilin.DNA Cell Biol. 7, 261–267.
de Bilbao F and M Dubois-Dauphin (1996) Time course of axoto-my-induced apoptotic cell death in facial motoneurons of neonatal wild type and bcl-2 transgenic mice.Neuroscience 71, 1111–1119.
Deckwerth TL, JL Elliott, CM Knudson, EM Johnson Jr, WD Snider and SJ Korsmeyer (1996) BAX is required for neuronal death after trophic factor deprivation and during development.Neuron 17, 401–411.
Dietrich WD, O Alonso and M Halley (1994) Early microvascular and neuronal consequences of traumatic brain injury, a light and electron microscopic study in rats.J. Neurotrauma 11, 289–301.
Dixon C, G Clifton, J Lighthall, A Yaghmai and R Hayes (1991) A controlled cortical impact model of traumatic brain injury in the rat.J. Neurosci. Methods 39, 253–262.
Fox GB, L Fan, RA Levasseur and AI Faden (1998) Sustained sensory/motor and cognitive deficits with neuronal apoptosis following controlled cortical impact brain injury in the mouse.J. Neurotrauma 15, 599–614.
Gillardon F, H Wickert and M Zimmermann (1995) Up-regulation of bax and down-regulation of bcl-2 is associated with kainate-induced apoptosis in mouse brain.Neurosci. Lett. 192, 85–88.
Gillardon F, L Klimaschewski, H Wickert, S Krajewski, JC Reed and M Zimmerman (1996a) Expression pattern of candidate cell death effector proteins Bax, Bcl-2, Bcl-x and c-Jun in sensory and motor neurons following sciatic nerve transection in the rat.Brain Res. 739, 244–250.
Gillardon F, C Lenz, KF Waschke, S Krajewski, JC Reed, M Zimmermann and W Kuschinsky (1996b) Altered Expression of Bcl-2, Bcl-X, Bax and c-Fos colocalizes with DNA fragmentation and ischemic cell damage following middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats.Mol. Brain Res. 40, 254–260.
Graham DI, K Horsburgh, JA Nicoll and GM Teasdale (1999) Apolipoprotein E and the response of the brain to injury.Acta Neurochirurgica - Suppl.73, 89–92.
Hamm RJ, CE Dixon, DM Gbadebo, AK Singha, LW Jenkins, BG Lyeth and RL Hayes (1992) Cognitive deficits following traumatic brain injury produced by controlled cortical impact.J. Neurotrauma 9, 11–20.
Hassouna I, H Wickert, M Zimmerman and F Gillardon (1996) Increase in bax expression in substantia nigra following 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) treatment of mice.Neurosci. Lett. 204, 85–88.
Hicks RR, HD Soares, DH Smith and TK Mcintosh (1996) Temporal and spatial characterization of neuronal injury following lateral fluid-percussion brain injury in the rat.Acta Neuropathol. 91, 236–246.
Honkaniemi J, SM Massa, M Breckinridge and FR Sharp (1996) Global ischemia induces apoptosis-associated genes in hippocampus.Mol. Brain Res. 42, 79–88.
Irving EA, J Nicoll, DI Graham and D Dewar (1996) Increased tau immunoreactivity in oligodendrocytes following human stroke and head injury.Neurosci. Lett. 213, 189–192.
Jellinger KA, W Paulus, C Wrocklage and I Litvan (2001) Effects of closed traumatic brain injury and genetic factors on the development of Alzheimer’s disease.Eur. J. Neurol. 8, 707–710.
Kay AD, A Petzold, M Kerr, G Keir, E Thompson and JA Nicoll (2003) Alterations in cerebrospinal fluid apolipoprotein E and amyloid beta-protein after traumatic brain injury.J. Neurotrauma 20, 943–952.
Kaya SS, A Mahmood, Y Li, E Yavuz, M Goksel and M Chopp (1999) Apoptosis and expression of p53 response proteins and cyclin D1 after cortical impact in rat brain.Brain Res. 818, 23–33.
Korsmeyer SJ (1995) Regulators of cell death.Trends Genet. 11, 101–105.
Kotapka MJ, DI Graham, JH Adams and TA Gennarelli (1992) Hippocampal pathology in fatal non-missile human head injury.Acta Neuropathol. 83, 530–534.
Krajewski S, JK Mai, M Krajewska, M Sikorska, MJ Mossakowski and JC Reed (1995) Upregulation of Bax protein levels in neurons following cerebral ischemia.J. Neurosci. 15, 6364–6376.
Liu B, HM Gao and JS Hong (2003) Parkinson’s disease and exposure to infectious agents and pesticides and the occurrence of brain injuries, role of neuroinflammation.Env. Health Perspect. 111, 1065–1073.
Lye TC and EA Shores (2000) Traumatic brain injury as a risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease, a review.Neuropsychol. Rev. 10, 115–129.
McIntosh TK, R Vink, L Noble, I Yamakami, S Fernyak, H Soares and AL Faden (1989) Traumatic brain injury in the rat, characterization of a lateral fluid-percussion model.Neuroscience 28, 233–244.
McIntosh TK, M Juhler and T Wieloch (1998) Novel pharmacological strategies in the treatment of experimental brain injury.J. Neurotrauma 15, 731–769.
Nakamura M, R Raghupathi, DE Merry, U Scherbel, KE Saatman and TK McIntosh (1999) Overexpression of Bcl-2 is neuropro-tective after experimental brain injury in transgenic mice.J. Comp. Neurol. 412, 681–692.
Nemetz PN, C Leibson, JM Naessens, M Beard, E Kokmen, JF Annegers and LT Kurland (1999) Traumatic brain injury and time to onset of Alzheimer’s disease, a population-based study.Am. J. Epidemiol. 149, 32–40.
Newcomb JK, X Zhao, BR Pike and RL Hayes (1999) Temporal profile of apoptotic-like changes in neurons and astrocytes following controlled cortical impact injury in rats.Exp. Neurol. 158, 76–88.
Oltvai Z, C Milliman and S Korsmeyer (1993) Bcl-2 heterodimer-izesin vivo with a conserved homolog, Bax, that accelerates programmed cell death.Cell 74, 609–619.
Palkovits M (1973) Isolated removal of hypothalamic or other brain nuclei of the rat.Brain Res. 59, 449–450.
Paxinos G and C Watson (1986)The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates (Academic Press: San Diego, CA).
Pentland B, PA Jones, CW Roy and JD Miller (1986) Head injury in the elderly.Age Ageing 15, 193–202.
Raghupathi R, TK McIntosh and DH Smith (1995) Cellular responses to brain injury.Brain Pathol. 5, 437–442.
Raghupathi R, SC Fernandez, H Murai, SP Trusko, RW Scott, WK Nishioka and TK McIntosh (1998) BCL-2 overexpression attenuates cortical cell loss after traumatic brain injury in transgenic mice.J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 18, 1259–1269.
Raghupathi R, C Zhang, KI Strauss, S Krajewski, JC Reed and TK McIntosh (2003) Temporal alterations in cellular Bax, Bcl-2 ratio following traumatic brain injury in the rat.J. Neurotrauma 20, 421–435.
Reed JC (1998) Bcl-2 family proteins.Oncogene 17, 3225–3236.
Rink AD, KM Fung, JQ Trojanowski, VM-Y Lee, E Neugebauer and TK McIntosh (1995) Evidence of apoptotic cell death after experimental traumatic brain injury in the rat.Am. J. Pathol. 147, 1575–1583.
Ross DT, DI Graham and JH Adams (1993) Selective loss of neurons from the thalamic reticular nucleus following severe human head injury.J. Neurotrauma 10, 151–165.
Shiozaki T, H Akai, M Taneda, T Hayakata, M Aoki, J Oda, H Tanaka, A Hiraide, T Shimazu and H Sugimoto (2001) Delayed hemispheric neuronal loss in severely head-injured patients.J. Neurotrauma 18, 665–674.
Shiraiwa N, N Inohara, S Okada, M Yuzaki, S Shoji and S Ohta (1996) An additional form of rat Bcl-x, Bcl-xbeta, generated by an unspliced RNA, promotes apoptosis in promyeloid cells.J. Biol. Chem. 271, 13258–13265.
Strauss KI and DM Jacobowitz (1993) Quantitative measurement of calretinin and beta-actin mRNA in rat brain micropunches without prior isolation of RNA.Mol. Brain Res. 20, 229–239.
Sutton RL, L Lescaudron and DG Stein (1993) Unilateral cortical contusion injury in the rat, vascular disruption and temporal development of cortical necrosis.J. Neurotrauma 10, 135–149.
Wennersten A, S Holmin and T Mathiesen (2003) Characterization of Bax and Bcl-2 in apoptosis after experimental traumatic brain injury in the rat.Acta Neuropathologica 105, 281–288.
Xia Z, M Dickens, J Raingeaud, RJ Davis and ME Greenberg (1995) Opposing effects of ERK and JNK-p38 MAP kinases on apoptosis.Science 270, 1326–1331.
Yakovlev AG and AI Faden (1995) Molecular biology of CNS injury.J. Neurotrauma 12, 767–777.
Yakovlev AG, SM Knoblach, L Fan, GB Fox, R Goodnight and AI Faden (1997) Activation of CPP32-like caspases contributes to neuronal apoptosis and neurlogical dysfunction after traumatic brain injury.J. Neurosci. 17, 7415–7424.
Yin C, CM Knudson, SJ Korsmeyer and T Van Dyke (1997) Bax suppresses tumorigenesis and stimulates apoptosisin vivo.Nature 385, 637–640.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Strauss, K.I., Narayan, R.K. & Raghupathi, R. Common patterns of Bcl-2 family gene expression in two traumatic brain injury models. neurotox res 6, 333–342 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03033444
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03033444