Abstract
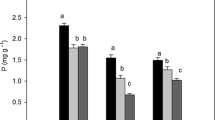
The allometry ofUrtica urens (small nettle), an important medicinal plant in many countries, growing in an area near pollution sources and an area away from pollution sources was determined. The allometric coefficients were determined for nonlinear relationships between plant height, stem width, root length, petiole length, leaf dry weight, petiole dry weight, leaf length, leaf width, leaf area and specific leaf area. The slopes of the linear equations were determined for the above parameters. The results showed that there is a difference in the allometry of different parts ofU. urens growing in these two areas. Air pollutants reduced the plant height, stem width, root length and petiole length and increased leaf parameters. The same pattern of growth was reflected by comparing the slopes of the straight lines of the parts of the plants growing in the two areas.
Similar content being viewed by others

Literature cited
Al-Esawi D (1996) Vegetation of Jordan: Fifty years. Unesco: Regional Office for Science and Technology for the Arab States, Cairo
Al-Hassan A (1995) Assessment of Air Quality in Al-Hash-imiyeh Town/Zarqa. Royal Scientific Society, Amman
Aqeel N, Elkarmi A, Assi R (1990) Monitoring Air Quality in the Areas near the Landfill Sites at Russaifeh. Royal Scientific Society, Amman
Chang J, Guan B, Ge Y, Chan Y (2004) Comparative studies on phynotypic plasticity of two herbs,Changium smyrniodes andAnthriscus sylvestris. J Zhejiang Univ Sci5: 656–662
Collins C, Cunningham N (2005) Modelling the fate of sulphur-35 in crops. 1. Calibration data. Environ Pollu133: 431–437
Commission of European Communities (1994) National soil map and land use project “The soils of Jordan”. Vol1: Main Report. Hunting Technical Series LTD in Association with Soil Survey and Land Research Center, Ministry of Agriculture, Jordan
Deepak S, Agrawal M (2001) Infuence of elevated CO2 on the sensitivity of two soybean cultivars to sulphur dioxide. Environ Exp Bot46: 81–91
Dilustro JJ, Day FP, Drake BG, Hinkle CR (2002) Abundance, production and mortality of fine roots under elevated atmospheric CO2 in oak-scrub ecosystem. Environ Exp Bot48: 149–159
Farooq M, Hans RK (1999) Metabolic effects of sulfur dioxide fumigation onMangifera indica Plants. Bull Environ Contamin Tox63: 774–781
Gimeno BS, Bermejo V, Sanz J, Torre D, Elvira S (2004) Growth response to ozone of annual species from Mediterranean pastures. Environ Pollu132: 297–306
Crantz D, Silva V, Toyota M, Ott N (2003) Ozone increases leaf CO2 assimilation in cotton and melon. J Exp Bot54: 2375–2384
Grantz D, Yang S (2000) Ozone impacts on allometry and root hydraulic conductance is not mediated by source limitation nor developmental age. J Exp Bot51: 919–927
Hamerlynck EP, Huxman TE, Charlet TN, Smith SD (2002) Effects of elevated CO2 (FACE) on the functional ecology of the drought-deciduous Mojave Desert shrub,Lycium andersonii. Environ Exp Bot48: 93–106
Huber H, Lukacs S, Watson MA (1999) Spatial structure of stoloniferous herbs: An interplay between structural blue-print, ontogeny and phenotypic plasticity. Plant Ecol141: 107–115
Jaggi M, Saurer M, Volk M, Fuhrer J (2005) Effects of elevated ozone on leaf d13-C and leaf conductance of plants grown in semi-natural grassland with or without irrigation. Environ Pollu134: 209–216
Kruse J, Hetzger I, Mai C, Polle A, Rennenberg H (2003) Elevated pCO2 affects N metabolism of young polar plants (Populus tremula xP. alba) differently at deficient and sufficient N-supply. New Phytol157: 65–81
Manning WJ, Cooley DR, Tuttle AF, Frenkel MA, Bergweiler CJ (2004) Assessing plant response to ambient ozone: Growth of young apple trees in open-top chambers and corresponding ambient air plots. Environ Pollu132: 503–508
Muzika RM, Guyette RP, Zielonka T, Liebhold AM (2004) The influence of O3, NO2 and SO2 on growth ofPicea abies andFagus sylvatica in the Carpathian Mountains. Environ Pollu130: 65–71
Nagashima H, Terashima I (1995) Relationships between height, diameter and weight distributions ofChenopodium album plants in stands: Effects of dimension and allometry. Annals Bot75: 181–188
Olszyk DM (1989) The Growth and Yield of Ambient Air Pollution on Valencia Orange Trees. Final Report to the California Air Resources Board Contract No. A733-087, Statewide Air Pollutant Research Center, University of California, Riverside
Paoletti E (2005) Ozone slows stomatal response to light and leaf wounding in a Mediterranean evergreen broadleaf,Arbutus unedo. Environ Pollu134: 439–445
Perez P, Morcuende R, Molino IMD, Martinez-Carrasco R (2005) Diurnal changes of Rubisco in response to elevated CO2, temperature and nitrogen in wheat grown under temperature gradient tunnels. Environ Exp Bot53: 13–27
Prietzel J, Mayer B, Legge AH (2004) Cumulative impact of 40 years of industrial sulfur emissions on a forest soil in west-central Alberta (Canada). Environ Pollu132: 129–144
Rakwal R, Agrawal G, Kubo A, Yonekura M, Tamogami S, Saji H, Iwahashi H (2003) Defense/stress responses elicited in rice seedlings exposed to the gaseous air pollutant sulfur dioxide, Environ Exp Bot49: 223–235
Ribas A, Penuelas J, Elvira S, Gimeno B (2005) Ozone exposure induces the activation of leaf senescence-related processes and morphological and growth changes in seedlings of Mediterranean tree species. Environ Pollu134: 291–300
Saad S, Al-Qadi A, Saleh A (1988) Medicinal, Aromatic and Toxic plants in Arab Countries. (in Arabic). Arabic Organization of Agricultural Development, Khartoum
Schoene K, Franz J-Th, Masuch G (2004) The effect of ozone on pollen development inLolium perenne L. Environ Pollu131: 347–354
Stuiver C, De Kok L (2001) Atmospheric H2S as sulfur source forBrassica oleracea: Kinetics of H2S uptake and activity of O-acetylserine (thiol)lyase as affected by sulfur nutrition. Environ Exp Bot46: 29–36
Tausz M, Weidner W, Wonisch A, De Kok L, Grill D (2003) Uptake and distribution of35S-sulfate in needles and roots of spruce seedlings as affected by exposure to SO2 and H2S. Environ Exp Bot50: 211–220
Vu CV (2005) Acclimation of peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) leaf photosynthesis to elevated growth CO2 and temperature. Environ Exp Bot53: 85–95
Xiong X, Allinson G, Stagnitti F, Murray F, Wang X, Liang R, Peterson J (2003) Effects of simultaneous exposure to atmospheric sulfur dioxide and heavy metals on the yield and metal content of soybean grain (Glycine max L. Merr.). Bullet Environ Contamin Tox71: 1005–1010
Zohary M (1972) Flora Palaestina. Vol2. The Israel Academy of Sciences and Humanities, Jerusalem
Zohary M (1973) Geobotanical Foundation of the Middle East. Swets and Zeitlinger, Amsterdam
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elkarmi, A., Eideh, R.A. Allometry ofUrtica urens in polluted and unpolluted habitats. J. Plant Biol. 49, 9–15 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03030783
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03030783