Abstract
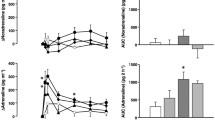
Central injection of porcine relaxin into the lateral ventricle of water-replete rats caused a marked drinking response. Relaxin in 2 µL 0.9% saline caused a dose-dependent (range 10–50 ng), significant (P<0.01) dipsogenesis compared with saline-treated controls. There was no drinking response to <10 ng relaxin. At 10 ng relaxin ICV rats drank 4.2 ± 0.2 mL water within 15 min of injection. The amount of water taken increased with increasing dose and plateaued at 50 ng ICV (10.2 ± 1.3 mL) thereafter; increasing the dose of relaxin did not significantly increase the total volume of water consumed. In contrast, there was no significant increase in water consumed in rats treated with a deactivated form of porcine relaxin, or with insulin. Rats appeared to compensate for the period of hyperdipsia, as there was no significant difference in the water consumed in control (saline-injected) and relaxin-treated rats in the 23 h period after testing.
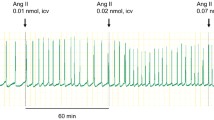
The effect of blocking the central action of angiotensin II on the dipsogenic effects of relaxin was tested by infusing of a specific angiotensin II receptor antagonist into the lateral ventricle before treatment with relaxin. Antagonism of the central angiotensin II system, confirmed by lack of a dipsogenic response to ICV exogenous angiotensin II (10 ng), completely blocked the dipsogenic response of relaxin (50 ng in 1 µL) in female rats.
These data demonstrate that exogenous porcine relaxin is dipsogenic in the rat and that the mechanism of action appears to be through the central angiotensin II system. It is possible that relaxin may affect water intake during pregnancy when relaxin levels are detectable in the plasma and the hormone may be implicated in the regulation of cardiovascular function in pregnancy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahokas, R.A., Sibai, B.M. & Anderson, G.D. (1989).Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol.,161, 618–622.
Bethea, C.L., Cronin, M.J., Haluska, G.J. & Novy, M.J. (1989).J. Clin. Endocrinol Metab.,69, 956–962.
Bradbury, M.W.B. (1985).Circ Res.,57, 213–222.
Denton, D. (1982).The Hunger for salt: an anthropological, physiological and medical analysis Spinger-Verlag: Berlin. pp. 446–447.
Downing, S.J. & Sherwood, O.D. (1989a).Endocrinology,116, 1215–1220.
Downing, S.J. & Sherwood, O.D. (1989b).Endocrinology,116, 1200–1205.
Durr, J.A., Stamoutsis, B. & Lindheimer, M.D. (1981).J. Clin. Invest.,68, 337–346.
Fitzsimons, J.T. & Thornton, S.N. (1992).J. Physiol.,446, 457P.
Geddes, B.J., Parry, L.J. & Summerlee, A.J.S. (1994).Endocrinology,134, 1188–1192.
Hwang, J.-J., Shanks, R.D. & Sherwood, O.D. (1989).Endocrinology,125, 260–266.
Hwang, J.-J., Lee, A.B., Fields, P.A., Haab, L.M., Mojonnier, L.E. & Sherwood. (1991).Endocrinology,129, 3034–3042.
Mumford, A.D., Parry, L.J. & Summerlee, A.J.S. (1989).J. Endocrinol.,122, 747–755.
Naito, Y., Fukata, J., Shindo, K., Ebisui, O., Murakami, N., Tominaga, T., Nakai, Y., Mori, K., Kasting, N.W. & Imura, H. (1991).Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm.,174, 1189–1195.
Oscheroff, P.L., Ling, V.T., Vandlen, R.L., Cronin, M.J. & Lofgren, J.A. (1990).J. Biol. Chem.,265, 9396–9401.
Parry, L.J. (1992). PhD Thesis, University of Guelph, ON, CAN
Parry, L.J. & Summerlee, A.J.S. (1991).Endocrinology,129, 47–52.
Parry, L.J., Poterski, R.S., Summerlee, A.J.S. & Jones, S.A. (1990).J. Neuroendocrinol.,2, 53–58.
Parry, L.J., Poterksi, R.S. & Summerlee, A.J.S. (1994).Biol. Reprod.,50, 622–628.
Pellegrino, L.T., Pellegrino, A.S. & Cashman, A.J. (1979).A stereotaxic atlas of the rat brain (2nd Edn). Plenum Press, New York.
Robertson, G.F. & Summerlee, A.J.S. (1991).Proc. Soc. Endocrinology, Abst 362.5
Robertson, G.F., Summerlee, A.J.S. & Chapman, H. (1991).3rd IBRO World Congress of Neuroscience, Montreal, CAN. Abst 219.
Rothwell, N. (1991).Trends in Pharmacol. Sci.,12, 430.
Saavedra, J.M. (1992).Endocrin Rev.,13, 329–380.
Sherwood, O.D. & O’Byrne, E.M. (1974).Arch Biochem Biophys.,160, 185–196.
Sherwood, O.D., Crnekovic, V.E., Gordon, W.L. & Rutherford, J.E. (1980).Endocrinology.107, 691–698.
Sortino, M.A., Cronin, M.J. & Wise, P.M. (1989).Endocrinology,124, 2013–2015.
St. Louis, J. & Massicotte, G. (1985).Life Sci.,37, 1351–1357.
Summerlee, A.J.S. & Wilson, B.C. (1994).Endocrinology,134, 2115–2120.
Summerlee, A.J.S., Mumford, A.D. & Smith, M.S. (1991).J. Neuroendocrinal,3, 1–7.
Summerlee, A.J.S., O’Byrne, K.T. & Jones, S.A. (1995).J. Endocrinol., in press.
Summerlee, A.J.S., O’Byrne, K.T., Jones, S.A. & Eltringham, L. (1987).J. Endocrinol.,115, 347–353.
Taverne, M.A.M., Bevers, M., Bradshaw, J.M.C., Dickman, S.J., Willemse, A.H. & Porter, D.G. (1982).J. Reprod. Fert.,65, 85–96.
Thornton, S.N. & Fitzsimons, J.T. (1989).Appetite,12, 242.
Way, S. & Leng, G. (1992).J. Endocrinol.,132, 149–158.
Wilson, B.C. & Summerlee, A.J.S. (1995).Biol. Reprod. (in press).
Weisinger, R.S., Burns, P., Eddie, L.W. & Wintour, E.M. (1993).J. Endocrinol.,137, 505–510.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Summerlee, A.J.S., Robertson, G.F. Central administration of porcine relaxin stimulates drinking behaviour in rats: an effect mediated by central angiotensin II. Endocr 3, 377–381 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03021422
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03021422