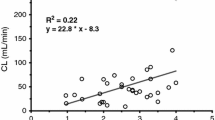
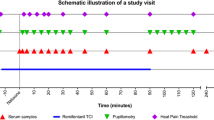
Abstract
The effects of epidural, subdural and intraperitoneal fentanyl were determined on the tail flick response of the rat using the response latency as a measure of analgesia. Dose-timeresponse curves were generated for incremental doses of fentanyl administered at constant injection volumes. Serum concentrations at varying doses were determined using a radioimmunoassay technique. It was found that serum concentrations for extradural, subdural and intraperitoneal fentanyl were similar at the low doses, but differed significantly at higher doses suggesting that pharmacokinetic differences may be concentration dependent. Extradural administration of naloxone (0.004 mg) was able to antagonize extradural fentanyl (8.0 μg), a dose eight-fold greater than the lowest maximally effective dose. The relationship between serum fentanyl concentrations and administered doses suggest that the analgesic properties of extradural and subdural fentanyl are in part dependent on centrally mediated actions.
Résumé
Les effets dufentanil administré en épidurale, en sousdurale et intrapéritonéale ont été déterminés chez des rats utilisant le temps de latence comme mesure du degré de l’analgésie. Des courbes de réponse dose-temps ont été créées pour des doses croissantes de fentanyl administrées à des volumes d’injection constants. Les concentrations plasmatiques ont été déterminées par radioimmunoessai. On a trouvé que les concentrations plasmatiques pour l’administration extradurale, sousdurale et intrapéritonéale de fentanyl, étaient similaires à des doses basses mais significativement différentes à des doses élevées suggérant des différences pharmacocinétiques dépendant de la concentration. Ladministration extradurale de naloxone (0,004 mg) antagonisait le fentanyl (8,0 μg) administré par voie extradurale, une dose huit fois plus grande que la plus basse dose efficace. La relation entre les concentrations plasmatiques de fentanyl et les doses administrées suggérent que les propriétés analgésiques de l’administration de fentanyl par voie extradurale et sousdurale était en d’origine centrale.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang JK, Nauss LA, Thomas JE. Pain relief by intrathecally applied morphine in man. Anesthesiology 1979; 50: 149–51.
Behar M, Magora F, Olshwang D, Davidson JT. Epidural morphine in treatment of pain. Lancet 1979; 1: 527–8.
Torda TA. Epidural analgesia with morphine. A preliminary communication. Anaesth Intensive Care 1979; 7: 367–70.
Glynn CJ, Mather LE, Cousins MJ, Graham JR, Wilson PR. Selective spinal analgesia in man following epidural administration of pethidine. Anaesth Intensive Care 1980; 8: 371.
Wolfe MJ, Davies GK. Analgesic action of extradural fentanyl. Br J Anaesth 1980; 52: 357–8.
Bilsback P, Roily G, Tampubolon O. Efficacy of the extradural administration of lofentanil, buprenorphine or saline in the management of postoperative pain. Br J Anaesth 1985; 57: 943–8.
Chauvin M, Salbaing J, Perrin D, Levron JC, Viars P. Clinical assessment and plasma pharmacokinetics associated with intramuscular or extradural alfentanil. Br J Anaesth 1985; 57: 886–91.
Donadoni R, Roily G, Noorduin H, Van Den Bussche G. Epidural sufentanil for postoperative pain relief. Anaesthesia 1985; 40: 634–8.
Kalia PK, Madan R, Saksena R, Batra RK, Gode GR. Epidural pentazocine for postoperative pain relief. Anesth Analg 1983; 62: 949–50.
Van Den Hoogen RHWM, Colpaert FC. Long-term catheterization of the lumbar epidural space in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 1981; 15: 515–6.
Bahar M, Rosen M, Vickers MD. Chronic cannulation of the intradural or extradural space in the rat. Br J Anaesth 1984; 56: 405–10.
Durant PAC, Yaksh TL. Epidural injections of bupivacaine, morphine, fentanyl, lofentanil and DADL in chronically implanted rats. A pharmacologic and pathologic study. Anesthesiology 1986; 64: 43–53.
Yaksh TL, Noueihed RY, Durant PAC. Studies of the pharmacology and pathology of intrathecally administered 4-anilinopiperidine analogues and morphine in the rat and cat. Anesthesiology 1986; 64: 54–66.
Janssen PAJ, Niemegeeres CJE, Dony JGH. The inhibitory effect of fentanyl and other morphine-like analgesics on the warm water induced tail withdrawal reflex in rats. Arzneimittel forschung. 1963; 13: 502–9.
Meert TF, Lu HR, van Craenndonck H, Janssen PAJ. Comparison between epidural fentanyl, sufentanil, carfentanil, lofentanil and alfentanil in the rat: analgesia and other in vivo effects. Eur J Anaesthesiol 1988; 5: 313–21.
Michiels M, Hendriks R, Heykants J. A sensitive radioimmunoassay for fentanyl. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 1977; 12: 153–58.
Schild HO. Drug antagonism and pAx. Pharmacol Rev 1957; 9: 242–6.
Takemori AE. Determination of pharmacological constants: use of narcotic antagonists to characterize analgesic receptors.In: Braude MCet al. (Eds.). Narcotic Antagonists, Advances in Biochemical Psychopharmacology. New York: Raven press, 1974; 8: 335–44.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Immelman, L., Roth, S., Sabourin, M.A. et al. Analgesia and serum concentrations of extradural, subdural and intraperitoneal fentanyl in a rat model. Can J Anesth 37, 63–68 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03007486
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03007486