Abstract
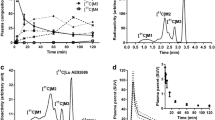
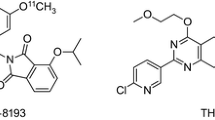
In previousin vivo studies with mice, rats, cats and monkeys, we have demonstrated that [7-methyl-11C]-(E)-8-(3,4,5-trimethoxystyryl)-1,3,7-trimethylxanthine ([11C]TMSX) is a potential radioligand for mapping adenosine A2A receptors of the brain by positron emission tomography (PET). In the present study, we studied the potential of [11C]TMSX for myocardial imaging. Uptake of radioactivity by the heart was high and gradually decreased after an intravenous injection of [11C]TMSX into mice. In metabolite analysis, 54% and 76% of the radioactivity in plasma and heart, respectively, were present as the unchanged form of [11C]TMSX 60 min postinjection. The myocardial uptake was reduced by carrier-loading and by co-injection of an adenosine A2A antagonist CSC, but not by co-injection of an adenosine A1 antagonist DPCPX. Pretreatment with a high dose of a non-selective antagonist theophylline also reduced the myocardial uptake of [11C]TMSX. These findings demonstrate the specific binding of [11C]TMSX to adenosine A2A receptors in the heart. Finally we successfully performed the myocardial imaging by PET with [11C]TMSX in a normal volunteer. A graphical analysis by Logan plot supported the receptormediated uptake of [11C]TMSX. Peripherally [11C]TMSX was very stable in human: >90% of the radioactivity in plasma was detected as the unchanged form in a 60-min study. We concluded that [11C]TMSX PET has the potential for myocardial imaging.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fredholm BB, Abbracchio MP, Burnstock G, Daly JW, Harden TK, Jacobson KA, et al. Nomenclature and classification of purinoceptors.Pharmacol Rev 1994; 46: 143–156.
Auchampach JA, Bolli R. Adenosine receptor subtypes in the heart: therapeutic opportunities and challenges.Am J Physiol 1999; 276: H1113-H1116.
Shryock JC, Belardinelli L. Adenosine and adenosine receptors in the cardiovascular system: biochemistry, physiology, and pharmacology.Am J Cardiol 1997; 79: 2–10.
Relevic V, Bumstock G. Receptors for purines and pyrimidines.Pharmacol Rev 1998; 50: 413–492.
Haas HL, Selbach O, Functions of neuronal adenosine receptors.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 2000; 362: 375–381.
Dunwiddie TV, Masino SA. The role and regulation of adenosine in the central nervous system.Ann Rev Neurosci 2001; 24: 31–55.
Svenningsson P, Hall H, Sedvall G, Fredholm BB. Distribution of adenosine receptors in the postmortem human brain: an extended autoradiographic study.Synapse 1997; 27: 322–335.
Johansson B, Fredholm B. Further characterization of the binding of the adenosine receptor agonist [3H]CGS 21680 to rat brain using autoradiography.Neuropharmacology 1995, 34: 393–403.
Schiffmann SN, Jacobs O, Vanderhaeghen JJ. Striatal restricted adenosine A2 receptor (RDC8) is expressed by enkephalin but not by substance P neurons: anin situ hybridization histochemistry study.J Neurochem 1991; 57: 1062–1067.
Augood SJ, Emson PC. Adenosine A2a receptor mRNA is expressed by enkephalin cells but not by somatostatin cells in rat striatum: a co-expression study.Mol Brain Res 1994; 22: 204–210.
Ishiwata K, Shimada J, Ishii K, Suzuki F. Assessment of the adenosine A2A receptors with PET as a new diagnostic tool for neurological disorders.Drugs Fut 2002; 27: 569–576.
Ishiwata K, Noguchi J, Toyama H, Sakiyama Y, Koike N, Ishii S, et al. Synthesis and preliminary evaluation of [11C]KF17837, a selective adenosine A2A antagonisnt.Appl Radiat Isot 1996; 47: 507–511.
Noguchi J, Ishiwata K, Wakabayashi S, Nariai T, Shumiya S, Ishii S, et al. Evaluation of carbon-11-labeled KF17837: a potential CNS adenosine A2a receptor ligand.J Nucl Med 1998; 39: 498–503.
Suzuki F, Ishiwata K. Selective adenosine antagonists for mapping central nervous system adenosine receptors with positron emission tomography: Carbon-11 labeled KF15372 (A1) and KF17837 (A2A).Drug Develop Res 1998; 45: 312–323.
Ishiwata K, Noguchi J, Wakabayashi S, Shimada J, Ogi N, Nariai T, et al.11C-labeled KF18446: a potential central nervous system adenosine A2a receptor ligand.J Nucl Med 2000; 41: 345–354.
Ishiwata K, Ogi N, Shimada J, Nonaka H, Tanaka A, Suzuki F, et al. Further characterization of a CNS adenosine A2a receptor ligand [11C]KF18446 within vitro autoradiography andin vivo tissue uptake.Ann Nucl Med 2000; 14: 81–89.
Ishiwata K, Shimada J, Wang WF, Harakawa H, Ishii S, Kiyosawa M, et al. Evaluation of iodinated and brominated [11C]styrylxanthine derivatives asin vivo radioligands mapping adenosine A2A receptor in the central nervous system.Ann Nucl Med 2000; 14: 247–253.
Wang WF, Ishiwata K, Nonaka H, Ishii S, Kiyosawa M, Shimada J, et al. Carbon-11-labeled KF21213: a highly selective ligand for mapping CNS adenosine A2A receptors with positron emission tomography.Nucl Med Biol 2000; 27: 541–546.
Ishiwata K, Ogi N, Nayakawa N, Oda K, Nagaoka T, Toyama H, et al. Adenosine A2A receptor imaging with [11C]KF18446 PET in the rat brain following quinolinic acid lesion: comparison with the dopamine receptor imaging.Ann Nucl Med 2002; 16: 467–475.
Ishiwata K, Sakiyama Y, Sakiyama T, Shimada J, Toyama H, Oda K, et al. Myocardial adenosine A2a receptor imaging of rabbit by PET with [11C]KF17837.Ann Nucl Med 1997; 11: 219–225.
Ishiwata K, Wang WF, Kimura Y, Kawamura K, Ishii K. Preclinical studies on [11C]TMSX for mapping adenosine A2A receptors by positron emission tomography.Ann Nucl Med 2003; 17: 205–211.
Shimada J, Suzuki F, Nonaka H, Ishii A, Ichikawa S. (E)-1,3-dialkyl-7-methyl-8-(3,4,5-trimethoxystyryl)xanthines: potent and selective adenosine A2 antagonists.J Med Chem 1992; 35: 2342–2345.
Jacobson KA, Gallo-Rodriguez C, Melman N, Fischer B, Maillard M, van Bergen A, et al. Structure-activity relationships of 8-styrylxanthines as A2-selective adenosine antagonists.J Med Chem 1993; 36: 1333–1342.
Logan J, Fowler JS, Volkow ND, Wolf AP, Dewey SL, Schlyer DJ, et al. Graphical analysis of reversible radioligand binding from time-activity measurements applied to [N-11C-methyl]-(-)-cocaine PET studies in human subjects.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1990; 10: 740–747.
Xu H, Stein B, Liang B. Characterization of a stimulatory adenosine A2a receptor in adult rat ventricular myocyte.Am J Physiol 1996; 270: H1655-H1661.
Norton GR, Woodiwiss AJ, McGinn RJ, Lorbar M, Chung ES, Honeyman TW, et al. Adenosine A2a receptor activation modulates A1 receptor-mediated antiadrenergic effects in the rat myocardium.Am J Physiol 1999; 276: H341-H349.
Kilpatrick EL, Narayan P, Mentzer RM Jr, Lasley RD. Cardiac myocyte adenosine A2a receptor activation fails to alter cAMP or contractility: role of receptor localization.Am J Physiol 2002; 282: H1035-H1040.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ishiwata, K., Kawamura, K., Kimura, Y. et al. Potential of an adenosine A2A receptor antagonist [11C]TMSX for myocardial imaging by positron emission tomography: a first human study. Ann Nucl Med 17, 457–462 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03006434
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03006434