Abstract
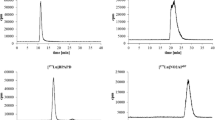
Objective: Disodium cycloheptylaminomethylenediphosphonate monohydrate (incadronate disodium) is a third-generation bisphosphonate compound which potently inhibits bone resorption, and a highly effective drug in the treatment of metastatic bone disease. We first labeled incadronate disodium with99Tc, and examined its biodistribution and bone uptake after intravenous injection in rats to assess its potential for clinical use as a bone-seeking agent for judgment of the therapeutic effect of incadronate on bone metastases. Bone scan with99mTc-labeled incadronate (99mTc-incadronate) may yield important information prior to the use of incadronate for treatment of bone metastases.Methods: Synthesis of99mTc-incadronate was carried out by reduction of99mTc-pertechnetate in the presence of SnCl2 and N2 gas. Normal rats were injected with 18.5 MBq (0.5 mCi)99mTc-incadronate in a volume of 0.1 ml intravenously and then sacrificed at 15 min, 30 min, 1 h or 2 h (six rats at each time point) after injection. Samples of muscle, stomach, small intestine, kidney, liver and bone (femur) were taken and weighed. In addition, a 1-ml sample of blood was drawn from the heart, and urine was taken from the urinary bladder immediately after sacrifice. Samples were measured for radioactivity and expressed as percent uptake of injected dose per gram or per milliliter (% ID/g or ml). Bone-to-blood and bone-to-muscle uptake ratios were determined from the % ID/g or ml values for these organs.Results: The greatest accumulation of99m Tc-incadronate was found in bone. Radioactivity in bone was as high as 3.22±0.68% ID/g at 2 hours after injection. Scintigraphic images of99mTc-incadronate in normal rats revealed highly selective skeletal uptake.Conclusion:99mTc-incadronate exhibited high uptake in bone, and relatively low uptake in soft tissue, suggesting that it may be useful as a bone-seeking agent for judgment of the therapeutic effect of incadronate on bone metastases, by determining the degree of its accumulation in metastatic bone lesions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fleisch H, Russell RGG, Francis MD. Diphosphonates inhibit hydroxyapatite dissolutionin vitro and bone resorption in tissue culture andin vivo.Science 1969; 165: 1262–1264.
Reynolds JJ, Minkin C, Morgan DB, Spycher D, Fleisch H. The effect of two diphosphonates on the resorption of mouse calvariain vitro.Calcif Tissue Res 1972; 10: 302–313.
Fleisch H. Bisphosphonates—History and experimental basis.Bone 1987; 8 (Suppl 1): S23-S28.
Flanagan AM, Chambers TJ: Dichloromethylenebisphosphonate (Cl2MBP) inhibits bone resorption through injury to osteoclasts that resorb Cl2MBP-coated bone.Bone Mineral 1989; 6: 33–43.
Russell RGG, Fleisch H. Pyrophosphate and diphosphonates in skeletal metabolism.Clin Orthop 1975; 108: 241–263.
Shinoda H, Adamek G, Felix R, Fleisch H, Schenk R, Hagan P. Structure-activity relationships of various bisphosphonates.Calcif Tissue Int 1983; 35: 87–99.
Schenk R, Eggli P, Fleisch H, Rosini S. Quantitative morphometric evaluation of the inhibitory activity of new aminobisphosphonates on bone resorption in the rat.Calcif Tissue Int 1986; 38: 342–349.
Pluijm GVD, Binderup L, Bramm E, Wee-Pals LVD, Groot HD, Binderup E, et al. Disodium 1-hydroxy-3-(1-pyrrolidinyl)-propylidene-1, 1-bisphosphonate (EB-1053) is a potent inhibitor of bone resorptionin vitro andin vivo.J Bone Min Res 1992; 7: 981–986.
Sato M, Grasser W. Effects of bisphosphonates on isolated rat osteoclasts as examined by reflected light microscopy.J Bone Min Res 1990; 5: 31–40.
Kawamuki K, Kudo M, Ouchi N, Abe T. Inhibitory effect of YM175 on bone resorptionin vitro.Basic Clinical Rep 1994; 28: 2895–2904. (in Japanese)
Takahashi K, Fukushima S, Kokubo S, Teramura K, Tanaka T. Effect of YM175 on hypercalcemia induced by human squamous cell carcinoma of oral cavity.Basic Clinical Rep 1994; 28: 2905–2919. (in Japanese)
Takeuchi M, Sakamoto S, Yoshida M, Abe T, Isomura Y. Studies on novel bone resorption inhibitors. I. Synthesis and pharmacological activities of aminomethylenebisphosphonate derivatives.Chem Pharm Bull 1993; 41: 688–693.
Hamdy NAT, Papapoulos SE. The palliative management of skeletal metastases in prostate cancer: use of boneseeking radionuclides and bisphosphonates.Semin Nucl Med 2001; 31: 62–68.
Bevan JA, Tofe AJ, Benedict JJ, Francis MD, Barnett BL. Tc-99m HMDP (hydroxymethylene diphosphonate): a radiopharmaceutical for skeletal and acute myocardial infarct imaging. I. Synthesis and distribution in animals.J Nucl Med 1980; 21: 961–966.
Subramanian G, McAfee JG, Blair RJ, Kallfelz FA, Thomas FD. Technetium-99m-methylene diphosphonate— a superior agent for skeletal imaging: Comparison with other technetium complexes.J Nucl Med 1975; 16: 744–755.
Lin WY, Lin CP, Yeh SJ, Hsieh BT, Tsai ZT, Ting G, et al. Rhenium-188 hydroxyethylidene diphosphonate: A new generator-produced radiotherapeutic drug of potential value for the treatment of bone metastases.Eur J Nucl Med 1997; 24: 590–595.
Deutsch E, Libson K, Vanderheyden JV, Ketring AR, Maxon HR. The chemistry of rhenium and technetium as related to the use of isotopes of these elements in therapeutic and diagnostic nuclear medicine.Nucl Med Biol 1986; 13: 465–477.
Rudd TG, Allen DR, Hartnett DE. Tc-99m methylene diphosphonate versus Tc-99m pyrophosphate: biologic and clinical comparison.J Nucl Med 1977; 18: 872–876.
Lin WY, Wang SJ. The influence of two bone agents (Tc-99m pyrophosphate and Tc-99m methylenediphosphonate) on quantitative sacroiliac joint scintigraphy.Nucl Med Commun 1996; 17: 1035–1038.
Imanishi Y, Mitogawa Y, Takizawa M, Konno S, Samura H, Ohsawa A, et al. Relapsing polychondritis diagnosed by Tc-99m MDP bone scintigraphy.Clin Nucl Med 1999; 24: 511–513.
Fukumoto S, Matsumoto T, Takebe K, Onaya T, Eto S, Nawata H, et al. Treatment of malignancy-associated hypercalcemia with YM175, a new bisphosphonate: Elevated threshold for parathyroid hormone secretion in hypercalcemic patients.J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1994; 79: 165–170.
Tsunematsu R, Saito T, Iguchi H, Fukuda T, Tsukamoto N. Hypercalcemia due to parathyroid hormone-related protein produced by primary ovarian clear cell adenocarcinoma: Case report.Gynecol Oncol 2000; 76: 218–222.
Koizumi M, Kobayashi M, Furukawa M, Yamashita T, Ogawa E. The bisphosphonate incadronate for bone metastases of breast cancer.Int J Clin Oncol 2000; 5: 241–246.
Wang TST, Fawwaz RA, Johnson LJ, Mojdehi GE, Johnson PM. Bone-seeking properties of Tc-99m carbonyl diphosphonic acid and monohydroxy-methylene phosphonic acid: concise communication.J Nucl Med 1980; 21: 767–770.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shigematsu, M., Shiomi, S., Iwao, H. et al. New bone-seeking agent: Animal study of Tc-99m-incadronate. Ann Nucl Med 16, 55–59 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02995292
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02995292