Abstract
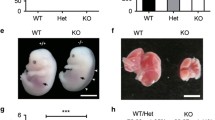
Mouse embryos homozygous for a targeted disruption in theFli-1 gene show hemorrhage into the neural tube and brain on embryonic day (E)11.0 and die shortly thereafter. Livers from the mutant embryos contain drastically reduced numbers of pronormoblasts, basophilic normoblasts, and colony-forming cells.To determine the nature of impaired hematopoiesis, we carried out cell culture studies of mutant embryonic stem (ES) cells and cells from the aorta-gonad-mesonephros (AGM) region of E10.0 mutant embryos. There was a striking reduction in the number of megakaryocytes in cultures of mutant AGM cells compared with cultures of AGM cells from wild-type or heterozygous embryos. Furthermore,Fli-1 mutant ES cells failed to produce megakaryocyte colonies and multilineage colonies containing megakaryocytes. Consistent with the observed defect in megakaryopoiesis, we also demonstrated the down-regulation of c-mpl in the AGM of mutant embryos. The percentages of pronormoblasts and basophilic normoblasts were significantly reduced in cultures of mutant AGM embryos, which contained primarily polychromatophilic and orthochromatic normoblasts. These results provide further evidence for the role ofFli-1 in the regulation of hematopoiesis and for c-mpl as aFli-1 target gene.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Watson DK, Smyth FE, Thompson DM, et al. The ERGB/Fli-1 gene: isolation and characterization of a new member of the family of human ETS transcription factors.Cell Growth Differ. 1992;3:705–713.
Seth A, Robinson L, Thompson DM, Watson DK, Papas TS. Trans-activation of GATA-1 promoter with ETS1, ETS2 and ERGB/Hu-FLI-1 proteins: stabilization of the ETS1 protein binding on GATA-1 promoter sequences by monoclonal antibody.Oncogene. 1993;8:1783–1790.
Seth A, Robinson L, Panayiotakis A, et al. The EndoA enhancer contains multiple ETS binding site repeats and is regulated by ETS proteins.Oncogene. 1994;9:469–477.
Deveaux S, Filipe A, Lemarchandel V, Ghysdael J, Romeo PH, Mignotte V. Analysis of the thrombopoietin receptor (MPL) promoter implicated GATA and Ets proteins in the coregulation of megakaryocyte-specific genes.Blood. 1996;87:4678–4685.
Lemarchandel V, Ghysdael J, Mignotte V, Rahuel C, Romeo PH. GATA and Ets cis-acting sequences mediate megakaryocyte-specific expression.Mol Cell Biol. 1993;13:668–676.
Zhang L, Lemarchandel V, Romeo PH, Ben-David Y, Greer P, Bernstein A. The Fli-1 proto-oncogene, involved in ery-throleukemia and Ewing’s sarcoma, encodes a transcriptional activator with DNA-binding specificities distinct from other Ets family members.Oncogene. 1993;8:1621–1630.
Seth A, Hodge DR, Thompson DM, et al. ETS family proteins activate transcription from HIV-1 long terminal repeat.Aids Res Hum Retroviruses. 1993;9:1017–1023.
Athanasiou M, Clausen PA, Mavrothalassitis GJ, Zhang XK, Watson DK, Blair DG. Increased expression of the ETS-related transcription factor FLI-1/ERGB correlates with and can induce the megakaryocytic phenotype.Cell Growth Differ. 1996;7:1525–1534.
Ben-David Y, Giddens EB, Letwin K, Bernstein A. Erythroleukemia induction by Friend murine leukemia virus: insertional activation of a new member of the ets gene family, Fli-1, closely linked to c-ets-1.Genes Dev. 1991;5:908–918.
Ott DE, Keller J, Rein A. 10A1 MuLV induces a murine leukemia that expresses hematopoietic stem cells markers by a mechanism that includes fli-1 integration.Virology. 1994;205:563–568.
Bergeron D, Houde J, Poliquin L, Barbeau B, Rassart E. Expression and DNA rearrangement of proto-oncogenes in Cas-Br-E-induced non-T-, non-B-cell leukemias.Leukemia. 1993;7:954–962.
Zhang L, Eddy A, Teng Y-T, et al. An immunological renal disease in transgenic mice that overexpress Fli-1, a member of theets family of transcription factor genes.Mol Cell Biol. 1995;15:6961–6970.
Georgiou P, Maroulakou IG, Green JE, et al. Expression of ets family of genes in systemic lupus erythematosus and Sjogren’s syndrome.Int J Oncol. 1996;9:9–18.
Spyropoulos DD, Pharr PN, Lavenburg KR, et al. Hemorrhage, impaired hematopoiesis and lethality in mouse embryos carrying a targeted disruption of the Fli1 transcription factor.Mol Cell Biol. 2000;20:5643–5652.
Hart A, Melet F, Grossfeld P, et al. Fli-1 regulates murine vascular and megakaryocytic development and is hemizygously deleted in patients with thrombocytopenia.Immunity. 2000;13:167–177.
Melet F, Motro B, Rossi DJ, Zhang L, Bernstein A. Generation of a novel Fli-1 protein by gene targeting leads to a defect in thymus development and a delay in Friend virus-induced erythroleukemia.Mol Cell Biol. 1996;16:2708–2718.
Jackson CW. Cholinesterase as a possible marker for early cells of the megakaryocytic series.Blood. 1973;42:413–421.
Williams RL, Hilton DJ, Pease S, et al. Myeloid leukemia inhibitory factor maintains the developmental potential of embryonic stem cells.Nature. 1988;336:684–687.
Abbondanzo SJ, Gadi I, Stewart CL. Derivation of embryonic stem cell lines.Methods Enzymol. 1993;225:803–823.
Wiles MV. Embryonic stem cell differentiation in vitro.Methods Enzymol. 1993;225:900–918.
Alexander, WS, Dunn, AR. Structure and transcription of the genomic locus encoding murine c-Mpl, a receptor for thrombopoietin.Oncogene. 1995;10:795–803.
Lemarchandel V, Ghysdaek J, Mignotte V, Rahuel C, Romeo PH. GATA and Ets cis-acting sequences mediate megakaryocyte-specific expression.Mol Cell Biol. 1993;13:668–676.
Hashimoto Y, Ware J. Identification of essential GATA and Ets binding motifs within the promoter of the platelet glycopotein Ib alpha gene.J Biol Chem. 1995;270:24532–24539.
Bastian LS, Kwiatkowshi BA, Breininger J, Danner S, Roth G. Regulation of the megakaryocytic glycoprotein IX promoter by the oncogenic Ets transcription factor Fli-1.Blood. 1999;93:2637–2644.
Minami T, Tachibana K, Imanishi T, Doi T. Both Ets-1 and GATA-1 are essential for positive regulation of platelet factor 4 gene expression.Eur J Biochem. 1998;258:879–889.
Skoda R, Seldin D, Chiang M-K, Peichel C, Vogt T, Leder P. Murine c-mpl: a member of the hematopoietic growth factor receptor superfamily that transduces a proliferative signal.EMBO J. 1993;12:2645–2653.
Bartley T, Bogenberger J, Hunt P, et al. Identification and cloning of a megakaryocyte growth and development factor that is a ligand for the cytokine receptor mpl.Cell. 1994;77:1117–1124.
deSauvage F, Hass P, Spencer S, et al. Stimulation of megakaryocy-topoiesis and thrombopoiesis by the c-Mpl ligand.Nature. 1994;369:533–538.
Lok S, Kaushansky K, Holly R, et al. Cloning and expression of murine thrombopoietin cDNA and stimulation of platelet production in vivo.Nature. 1994;369:565–571.
Solar GP, Kerr WG, Zeigler FC, et al. Role of c-mpl in early hematopoiesis.Blood. 1998;92:4–10.
Debili N, Wendling F, Cosman D, et al. The mpl receptor is expressed in the megakaryocytic lineage from late progenitors to platelets.Blood. 1995;85:391–401.
Gurney A, Carver-Moore K, deSauvage F, Moore M. Thrombocy-topenia in c-mpl-deficient mice.Science. 1994;265:1445–1447.
Pereira R, Quang CT, Lesault I, Dolznig H, Beug H, Ghysdael J. Fli-1 inhibits differentiation and induces proliferation of primary erythroblasts.Oncogene. 1999;18:1597–1608.
Starck J, Doubeikovski A, Sarrazin S, et al. Spi-1/PU.1 is a positive regulator of Fli-1 gene involved in inhibition of erythroid differentiation in Friend erythroleukemic cell lines.Mol Cell Biol. 1999;19:121–135.
Athanasiou M, Mavrothalassitis G, Sun-Hoffman L, Blair DG. Fli-1 is a suppressor of erythroid differentiation in human hemato-poietic cells.Leukemia. 2000;14:439–445.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Kawada, H., Ito, T., Pharr, P.N. et al. Defective Megakaryopoiesis and Abnormal Erythroid Development inFli-1 Gene-Targeted Mice. Int J Hematol 73, 463–468 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02994008
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02994008