Conclusion
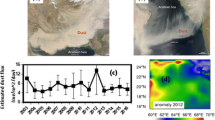
The present study clearly shows the influence of dust storms on chlorophyll bloom in the offshore region of the Arabian Sea, with a time lag of few days, during the pre-monsoon season. Various satellite derived parameters over the Arabian Sea, Himalayan and Tibet snow covered regions show large changes due to the influence of dust storms. The MODIS snow albedo gives unreliable values under the influence of dust storms due to increase in the aerosol loading over these regions and snow albedo product must be used in combination with snow pixel counts during the dust storm season. A detailed study is required for the quantitative evaluation of dust storms on the chlorophyll blooms in the Arabian Sea region and on the snow parameters in the Himalayan region.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker, A.R., Kelly, S.D., Biswas, K.F., Witt, M. and Jickells, T.D. (2003). Atmospheric deposition of nutrients to the Atlantic Ocean.Geophys. Res. Lett.,30(24), 2296, doi: 10.1029/2003GL018518.
Banzon, V.F., Evans, R.E., Gordon, H.R. and Chomko, R.M. (2004). SeaWiFS observations of the Arabian Sea southwest monsoon bloom for the year 2000. Deep Sea Research Part II:Topical Studies in Oceanography,51: 189–208.
Chauhan, P., Mohan, M., Sarangi, R.K., Kumari, B., Nayak, S. and Matondkar, S.G.P. (2002). Surface chlorophyll estimation in the Arabian Sea using IRS- P4 OCM Ocean color monitor satellite data.International Journal of Remote Sensing,23(8): 1663–1676.
Croop, R.A., Gabric, A.J., McTanish, G.H., Braddock, R.D. and Tindale, N. (2005). Coupling between ocean biota and atmospheric aerosols: Dust, dimethylsulphide, or artifact?, Global Biogeochem. Cycles,19, GB4002, doi:10.1029/2004GB002436.
Hall, D.K., Riggs, G.A. and Salomonson, V.V. (2006). Updated Daily. MODIS/Terra snow cover daily L3 global 500m grid v005 (April 1-30 2005). Boulder, Colorado USA: National Snow and Ice Data Center, Digital media.
Jickells, T.D., An, Z.S., Andersen, K.K., Baker, A.R., Bergametti, G., Brooks, N., Cao, J.J., Boyd, P.W., Duce, R.A., Hunter, K.A., Kawahata, H., Kubilay, N., laRoche. J., Liss, P.S., Mahowald, N., Prospero, J.M., Ridgwell, A.J., Tegen, I. and Torres, R. (2005). Global iron connections between desert dust, ocean biogeochemistry, and climate.Science,308 (5718): 67–71. doi: 10.1126/science. 1105959 Kang, S., Wake, C.P., Dahe, Q., Mayewski, P.A. and
Tandong, Y. (2000). Monsoon and dust signals recorded in Dasuopu glacier, Tibetan Plateau,Journal of Glaciology,46: 222–226.
Mahowald, N.M., Baker, A.R., Bergametti, G., Brooks, N., Duce, RA., Jickells, T.D., Kubilay, N., Prospero, J.M. and Tegen, I. (2005). Atmospheric global dust cycle and iron inputs to the ocean, Global Biogeochem. Cycles, 19, GB4025, doi: 10.1029/2004GB002402.
Meskhidze, N., Chameides, W.L. and Nenes, A. (2005). Dust and pollution: A recipe for enhanced ocean fertilization?,J. Geophys. Res.,110, D03301, doi: 10.1029/2004JD005082.
Middleton, N.J., Goudie, A.S. and Wells, GL. (1985). The frequency and source areas of dust storms. In Aeolian Geomorphology, edited by W.G. Nickling, 237–259. Allen & Unwin, Boston.
Prasad, A.K. and Singh, R.P. (2007a). Comparison of MISR-MODIS aerosol optical depth over the Indo- Gangetic basin during the winter and summer seasons (2000–2005).Remote Sens. Environ.,107: 109–119.
Prasad, A.K., Singh, S., Chauhan, S.S.. Srivastava, M.K., Singh, R.P, Singh, R. and Holben, B. (2007). Aerosol radiative forcing over the Indo-Gangetic plains during major dust storms. Atmospheric Environment. doi:10.1016/j.atmosenv.2007.03.060.
Prasad, A.K. and Singh, R.P. (2007b). Changes in aerosol parameters during major dust storm events (2001–2005) over the Indo-Gangetic basin using AERONET and MODIS data.J. Geophys. Res. (in press).
Wake, C.P., Mayewski, P.A., Zichu, X., Ping W. and Zhongqin, Li (1993). Regional Distribution of Monsoon and Desert Dust Signals Recorded in Asian Glaciers.Geophys. Res. Lett.,20(14): 1411- 1414.
Yadav, S. and Rajamani, V. (2004). Geochemistry of aerosols of northwestern part of India adjoining the Thar Desert.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta. 68(9): 1975–1988.
Yuan, W. and Zhang, J. (2006). High correlations between Asian dust events and biological productivity in the western North Pacific, Geophys. Res. Lett.,33, L07603, doi: 10.1029/2005GL025174.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Kayetha, V.K., Kumar J., S., Prasad, A.K. et al. Effect of dust storm on ocean color and snow parameters. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 35, 1–9 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02991828
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02991828