Abstract
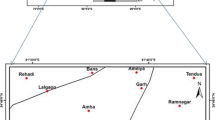
In arid regions, inherent climatic conditions and adverse terrain condition pose perpetual shortage of water. The dominant aeolian topography conceals older geological formations making it difficult to infer prospects of ground water and tapping the same. A ground water prospect map has been prepared for a part of Jodhpur district in western Rajasthan through integrated analysis of four major controlling factors: geology, geomorphology, structure and hydrology. Through visual interpretation of satellite data and using Geographical Information System, twenty-five hydro-geomorphic units (prospect units) have been delineated and mapped. Potential of each prospect unit have been discussed in reference to hydro-geomorphic units, their influence and well inventory like well yield, water table level and quality of drinking water. 34 % of the area was classified to have high groundwater potential and 5.8 % area was classified into low potential categories. Most of the area (60.2 %) is of moderate ground water potential.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chatterji, P.C., Singh, S. and Qureshi, Z.H. (1979). Hydrogeomorphology of the central Luni basin, western Rajasthan (India).Geoforum,9(3): 211–224.
Ghose, B., Singh, S. and Aamal Kar (1975). Geomorphology of prior and present drainage networks and their control on groundwater in Dyana tehsil-Annual Report, CAZRI, Jodhpur.
Lokesha, N., Gopalakrishna Gowda, H.H., Gupta, A.K. (2005). Delineation of ground water potential zones in a hard rock terrain in Mysore district, Karnataka using IRS data and GIS techniques.J. Indian Soc. Remote Sensing,33(3): 405–412.
NRSA (1995). Integrated Mission for Sustainable Development -Technical Guidelines, National Remote Sensing Agency, Dept. of Space, Hyderabad.
NRSA (2000).Technical guidelines for preparation of groundwater prospects map. Rajiv Gandhi National Drinking Water Mission, National Remote Sensing Agency, Hyderabad.
Purohit, M.L. (1997). Impact of recent spurt in human and livestock population on arid ecosystem. In:Desertification control in the arid ecosystem of India for sustainable development (Eds. Surendra Singh and Amal Kar), Agro Botanical Publishers (India), Bikaner, pp. 198–210
Rao, Y. Srinivasa and Jugran, D. K. (2003). Delineation of groundwater potential zones and zones of groundwater quality suitable for domestic purposes using remote sensing and GIS.Hydrological Sciences,48(5): 821–833.
Reddy, P.R., Kumar, K.V. and Seshadri, K. (1996). Use of IRS-1C data in groundwater studies.Current Science,70(7): 600–605.
SAC (1986).Report on ground water potential maps of Rajasthan (Based on visual interpretation of landsat thematic Mapper Data) Space Application Centre, Ahmedabad.
Sahai, B. (1993). Remote Sensing of deserts, the Indian experience.Journal of Arid Environments,25(1): 173–185.
Shankarnarayan, K.A., Chatterji, P.C. and Singh, S. (1983). Role of remote sensing in ground water extraction for problem villages and habitants of hard rock regions of western Rajasthan.Proceedings Und All India Conference on Drilling Equipment for Ground Water Extraction held at New Delhi—pp. 1/3–-1/25.
Venkateswarlu, J., Sen, A.K., Dubey, J.C., Joshi, N.L. and Kar, A. (1990).Water 2000 AD- the scenario for Arid Rajasthan, CAZRI, Jodhpur, 49p.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, M.A., Narain, P. & Moharana, P.C. Prospecting ground water resources using RS-GIS—A case study from arid western rajasthan of India. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 34, 171–179 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02991822
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02991822