Abstract
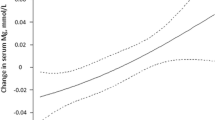
In a randomized, single-blind, controlled study (400 patients aged 25–63 yr; 374 males, 26 females), 206 subjects were administered a magnesium-rich diet, and 194 subjects their usual diet, for 6 wk. Age, sex, body weight, hypertension, hyperlipedemia, smoking, obesity, diuretic therapy, and diabetes were comparable between the two groups, as were laboratory data at entry to the study. Intervention-group A received a significantly higher amount of dietary magnesium and potassium compared to group B, which received its usual diet. After 6 wk, there was a significant fall in total serum cholesterol (228.5±46.2 mg/dL), LDL cholesterol 146.5±75.5 mg/dL), and triglyceride (143.8±40.5 mg/dL) in group A compared to serum cholesterol (242.5±58.2 mg/dL), LDL cholesterol (157.0±78.4 mg/dL), and triglyceride (156.5±60.0 mg/dL) at entry to study, but no such changes in group-B subjects. HDL cholesterol showed a marginal mean decrease of 0.8 mg/dL in group B and a 2.5 mg/dL increase in group A. The changes in blood lipids were consistent with an increased intake of magnesium and with a rise in serum levels. Although a general blood-lipid-reducing effect of such a diet cannot be excluded, it is possible that dietary magnesium may have contributed to the reduction of total serum cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, and triglyceride, and the marginal rise in HDL cholesterol. More studies with longer follow-up periods are needed to confirm this observation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. M. Altura, B. T. Altura, A. Gebrewold, W. Ising and T. Gunther, Magnesium deficiency and hypertension correlation between magnesium deficient diet and microcirculatory changes in Situ.Science 223, 1315–1317 (1984).
B. M. Altura, B. T. Altura, Magnesium electrolyte transport and coronary vascular tone.Drugs 28, 120–142 (1984).
B. M. Altura, and B. T. Altura, New perspective on the role of magnesium in the pathophysiology of cardiovascular system.Clin. Aspects, Magnesium 4, 226–244 (1985).
A. G. Arntzenius, D. Kromhout, I. D. Barth et al., Diet, lipoproteins and progression of coronary atherosclerosis.N. Engl. J. Med. 312, 805–808 (1985).
M. G. DeLos Rios, Serum magnesium and serum cholesterol changes in man.Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 9, 259–278 (1961).
E. M. Cindler, J. D. King, Determination of calcium in plasma.Am. J. Clin. Path. 58, 376–386 (1972).
M. Hathway, Magnesium in human nutrition.Home Econ. Res. Rep. USDA 19, (1962).
H. Karppanen, Epidemiological studies on the relationship between magnesium intake and cardiovascular disease.Artery 9, 190–199 (1981).
H. Khayam Bashi, T. J. Liu, and B. Walter, Determination of serum magnesium by calorimetric method.Clin. Chem. 23, 289–300
M. M. Mahfoux and F. A. Kummerow, Effect of magnesium deficiency on 6-desaturate activity and fatty acid composition of rat liver microsomes.Lipids 24, 727–732 (1989).
M. M. Mahfoux, T. L. Smith, F. A. Kummerow, Changes of linoleic acid metabolism and cellular phospholipid fatty acid composition in LLC-PK cells cultured at low magnesium concentrations.Biochem. Biophys. Acta 1006, 70–74 (1989).
J. R. Marier, Role of environmental magnesium in cardiovascular disease. InNutrition and Heart Disease, H. K. Wanto, ed. S P Medical and Scientific Books, New York, 1982, pp. 31–59.
B. S. Narsinga Rao, T. G. Deoschale, and K. C. Pant, Nutrient composition of Indian foods. National Institute of Nutrition, Hyderabad, India, 1989.
T. Rayssignier, New data on magnesium and lipids. Intermagnesium deficiency.Physiopathology and Treatment Implications, M. J. Halpern and J. Durlack, eds., 1986, pp. 122–131.
Y. Rayssiguier, E. Gueux, D. Cardot, G. Thomas, A. Robert, and G. Trugnan, Changes in free fatty acids in magnesium deficient rats.Nutr. Res. 6, 233–240 (1986).
I. Richmond, Determination of serum cholesterol in serum or plasma by enzymatic method.Clin. Chem. 19, 1350–1358 (1973).
R. B. Singh, Effect of dietary magensium supplmentation in the prevention of coronary heart disease and sudden cardiac death.Magnesium Trace Elem. 4, 143–151 (1990).
R. B. Singh, Multifactorial risk factor intervention for sudden cardiac death: The Indian diet-heart preliminary study.J. Adv. Med. 2, 475–485 (1989).
R. B. Singh, S. S. Rastogi, A. R. Sircar and R. Mody, Effect of dietary minerals on the incidence of sudden caridac death.Trace Elem. Med. 7, 19–24 (1990).
J. Sos, An investigation into the nutritional factors in cardiopathy.Electrolytes Cardiovas. Dis. I, 167–180 (1965).
H. Varley, A. H. Gowenlack, and M. Bell, Sodium potassium and chloride by flamephotometer,Prac Clin B. Biochemistry, William Heinman Medical Books, London, pp. 850–900 (1980).
E. Van Handel and B. D. Zilversmit, Micromethod in the direct estimation of serum triglyceride,J. Lab. Clin. Med. 60, 152–159 (1957).
J. J. Vitale, P. H. White, M. Nakamura, D. M. Hegstedt, N. Zamchkeck, E. E. Hellerstein, Interrelationships between experimental hypercholesterolemia, magensium requirement and experimental atherosclerosis.J. Exp. Med. 106, 757–766 (1957).
D. E. Wilson, M. J. Spiger A dual precipitation method for quantitative plasma lipoprotein mreasurement without ultracentrifugation.J. Lab. Clin. Med. 82, 473–482.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, R.B., Rastogi, S.S., Mani, U.V. et al. Does dietary magnesium modulate blood lipids?. Biol Trace Elem Res 30, 59–64 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02990342
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02990342