Abstract
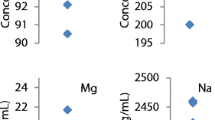
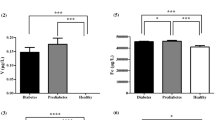
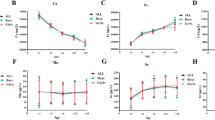
In this preliminary study, blood plasma samples from 32 insulintreated (ITDM),55 non-insulin-treated (NITDM) diabetic patients, and 30 nondiabetic individuals (C-NDM) (all fasting) from Oxford, England, were analyzed for Ag, Al, As, Ba, Br, Ca, Cd, Co, Cr, Cs, Cu, Fe, Hg, I, Mg, Mn, Mo, Ni, Pb, Rb, Sb, Sc, Se, Sn, V, and Zn. Neutron activation analysis and electrothermal atomic absorption methods were used. Analysis of a “pooled standard” blood plasma for 17 elements showed a good agreement with most coefficients of variation less than 15%, and recoveries of 92–102%. The elemental concentrations for healthy individuals and ITDM each obey an almost normal distribution, while those of NITDM deviate greatly from this. The NITDM group has a marked tendency to increased mean elemental values. Comparison between C-NDM and ITDM shows no significant relationship with relative periodic table position, biological essentiality or toxic behavior-and there is uniformly no increase in variability (as with NITDM). There is no significant difference in plasma chromium levels between the diabetic groups; however, each was significantly higher than the controls; ITDM (S**: probability less than 0.005) and NITDM (S*: probability between 0.05 and 0.01). Those diabetics on insulin treatment were significantly lower in plasma zinc compared with the other two groups.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. A, Pyke, C. G. Theophanicks, and R. B. Tattersall,Lancet 2, 464 (1976).
O. P. Ganda and S. S. Soeldner,Arch. Int. Med. 137, 461 (1977).
P. G. Nelson, D. A. Pyke, and D. R. Gamble,Brit. Med. J. 4, 249 (1975).
F. K. Jansen, H. Müntefering, and W. A. K. Schmidt,Diabetologia 13, 545 (1977).
G. F. Bottazzo and J. I. Mann,Brit. Med. J. 2, 165 (1978).
R. Chiks and M. Tzagournis,Diabetes 19, 458 (1978).
D. H. K. Lee,Metallic Contaminants in Human Health, Academic Press, New York, 1972.
T. H Maugh,Science 181, 253 (1973).
J. G. Reinhold,Clin. Chem. 21, 476 (1975).
A. S. Prasad,Trace Elements in Human Health and Disease., Vol. II, Essential and Toxic Elements., Academic Press, New York, 1976.
M. Kirchgessner, H. P. Roth, R. Spoerl, A. Schnegg, R. J. Keller, and E. Weigand,Nutr. Metab. 21, 119 (1977).
I. Lombeck and H. J. Bremer,Nutr. Metab. 21, 49 (1977).
E. J. Underwood,Trace Elements in Human and Animal Nutrition, 4th ed., Academic Press, New York, 1977.
L. R. Amspaugh,Chemical Elements in the Serum of Man in Health and Diabetes Mellitus, Thesis, California Univ., Berkeley, Lawrence Radiation Lab., Contract W-7405, 1963, pp. 48–78.
L. G. Kosenko,Vrach, Delv. 1, 60 (1965). (Russ.)
I. N. Boeriu, T. Fekete, N. Ghelberg, S. Nagy, and E. BodorClujul. Med. 51(2), 110 (1978). (Rom.)
M. Montagnani, R. Nuti, and M. Gallin,Boll. Soc. Hal. Biol. Spe. 54(2), 132 (1978). (Ital.)
A. M. Yusubova and A. N. Shevchenko,Azerb. Med. Zh. 55(5), 19 (1978). (Azerbaijani.)
H. M. Mather, J. A. Nisbet, G. H. Burton, G. J. Poston, J. M Bland, P. A. Bailey, and T. R. E. Pilkington,Clin. Chim. Acta 95, 235 (1979).
H. M. Mather, G. E. Levin, J. A. Nisbet, L. A. Hadley, N. W. Oakley, and T. R. E. Pilkington,Diabetologia 21, 131 (1981).
J. Matsuda,Chiba Hokkaidoritsu Eisei Kenkyushoho 31, 16 (1981).
K. Schwarz and W. Mertz,Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 72, 515 (1957).
W. H. Glinsmann and W. Mertz,Metab. Clin. Exp. 15, 510 (1966).
L. L. Hopkins, Jr. and M. G. Price,Western Hemisphere Nutr. Congr. 11, 40 (1968).
W. Mertz,Physiol. Rev. 49, 163 (1969).
W. Mertz, E. W. Toepfer, E. E. Roginski, and M. M. PolanskyFed. Proc. 33, 2275 (1974).
R. A. Anderson and W. Mertz,Trends Biochem. Sci. 2, 277 (1977).
W. W. Toepfer, W. Mertz, M. M. Polansky, E. E. Roginski, and W. R. WolfJ. Agri. Food Chem. 25, 162 (1977).
W. Mertz, E. E. Roginski, and H. A. Schroeder,J. Nutr. 81, 107 (1965).
H. A. Schroeder,J. Nutr. 88, 439 (1966).
I. W. F. Davidson and W. L. Blackwell,Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 127, 66 (1968).
R. W. Tuman, J. J. Bilbo, and R. J. Doisy,Diabetes 27, 49 (1978).
T. H. Maugh,Science 193, 220 (1976).
K. M. Hambidge,Proc. Nutr. Soc. 33, 249 (1974).
R. S. Doisy, D. H. P. Streeten, J. M. Freiberg, and A. S. Schneider, inTrace Elements in Human Health and Disease, A. Prasad, ed., Academic Press, New York, 1976, pp. 79–104.
W. Mertz,Med. Clin. North Am. 60, 739 (1976).
S. M. Freiberg, T. R. Schneider, D. H. P. Streeten, and A. S. Schneider Diabetes (Suppl. 2), 433 (1975).
V. J. K. Liu and J. S. Morris,Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 31, 972 (1978).
E. G. Offenbacher and F. X. Pi-Sunyer,Diabetes 29, 919 (1980).
N. I. Ward and D. E. Ryan,Anal. Chim. Acta 105, 185 (1979).
L. A. Currie,Anal. Chem. 40, 586 (1968).
N. I. Ward, R. Stephens, and D. E. Ryan,Anal. Chim Acta 110, 9 (1979).
O. Mickelsen, inNutrition, Physiology and Obesity, R. Schemmel, ed., CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, 1980, p. l67.
C E. Casey and K. M. Hambidge, inAdvances in Nutritional Research, Vol. 3, H. H. Draper, ed., Plenum, London, 1980, p. 23.
W. R. Beisel and R. S. Pekarek, inNeurology of the Trace Metals Zinc and Copper, C. C. Pfeiffer, ed., Academic Press, New York, 1972, p. 53.
W. F. Glinsmann, F. J. Feldman, and W. Mertz,Science 152, 114 (1966).
R. S. Pekarek, E. C. Hauer, E. J. Rayfield, R. W. Wannemacher, Jr., and W. R. Beisel,Diabetes 24, 350 (1975).
R. Riales and M. J. Albrink,Amer. J. Clin. Nutr. 34, 2670 (1981).
S. Tarui,Endocrinol. Jap. 10, 9 (1963).
H. G. Pidduck, P. J. J. Wren, and D. A. Price Evans,Diabetes 19, 234 (1970).
A. S. Prasad,Trace Elements in Human Health and Disease, Vol. I., Zinc and Copper, Academic Press, New York, 1976.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ward, M.I., Pim, B. Trace element concentrations in blood plasma from diabetic patients and normal individuals. Biol Trace Elem Res 6, 469–487 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02987202
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02987202
Index Entries
- Trace elements, levels in blood plasma, aluminum
- Antimony
- Arsenic
- Barium
- Cadmium
- Cesium
- Calcium
- Chromium
- cobalt
- copper
- iodine
- iron
- lead
- magnesium
- manganese
- mercury
- molybdenum
- nickel
- rubidium
- scandium
- selenium
- silver
- tin
- vanadium
- zinc
- in blood plasma
- neutron activation analysis
- electrothermal atomic absorption spectrophotometry, of trace elements
- in blood plasma
- insulin- and non-insulin-treated diabetics, of
- trace elements in blood plasma
- Oxford, England, trace elements in blood plasma