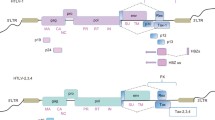
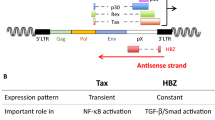
Abstract
Human T-cell leukemia/lymphoma virus type 1 (HTLV-1) causes neoplastic transformation of human T-cells in a small number of infected individuals several years from infection. Collective evidence from in vitro studies indicates that several viral proteins act in concert to increase the responsiveness of T-cells to extracellular stimulation, modulate proapoptotic and antiapoptotic gene signals, enhance T-cell survival, and avoid immune recognition of the infected T-cells. The virus promotes T-cell proliferation by usurping several signaling pathways central to immune T-cell function, such as antigen stimulation and receptor-ligand interaction, suggesting that extracellular signals are important for HTLV-1 oncogenesis. Environmental factors such as chronic antigen stimulation may therefore be of importance, as also suggested by epidemiological data. Thus genetic and environmental factors together with the virus contribute to disease development. This review focuses on current knowledge of the mechanisms regulating HTLV-1 replication and the T-cell pathways that are usurped by viral proteins to induce and maintain clonal proliferation of infected T-cells. The relevance of these laboratory findings is related to clonal T-cell proliferation and adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma development in vivo.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gallo RC. The first human retrovirus.Sci Am. 1986;255:88–98.
Poiesz BJ, Ruscetti FW, Gazdar AF, Bunn PA, Minna JD, Gallo RC. Detection and isolation of type C retrovirus particles from fresh and cultured lymphocytes of a patient with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980;77:7415–7419.
Yoshida M, Miyoshi I, Hinuma Y. Isolation and characterization of retrovirus from cell lines of human adult T-cell leukemia and its implication in the disease.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982;79:2031–2035.
Miyoshi I, Kubonishi I, Yoshimoto S, et al. Type C virus particles in a cord T-cell line derived by co-cultivating normal human cord leukocytes and human leukaemic T-cells.Nature. 1981;294:770–771.
Blattner WA, Kalyanaraman VS, Robert-Guroff M, et al. The human type-C retrovirus, HTLV, in Blacks from the Caribbean region, and relationship to adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma.Int J Cancer. 1982;30:257–264.
Catovsky D, Greaves MF, Rose M, et al. Adult T-cell lymphomaleukaemia in blacks from the West Indies.Lancet. 1982;1:639–643.
Hinuma Y, Nagata K, Hanaoka M, et al. Adult T-cell leukemia: antigen in an ATL cell line and detection of antibodies to the antigen in human sera.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981;78:6476–6480.
Robert-Guroff M, Ruscetti FW, Posner LE, Poiesz BJ, Gallo RC. Detection of the human T cell lymphoma virus p19 in cells of some patients with cutaneous T cell lymphoma and leukemia using a monoclonal antibody.J Exp Med. 1981;154:1957–1964.
Takatsuki K, Uchiayama T, Sagawa K, Yodoi J. Adult T-cell leukemia in Japan. In: Seno S, Takaku F, Irino S, eds.Topics in Hematology. Amsterdam: Excerpta Medicia; 1977:73.
Gessain A, Barin F, Vernant JC, et al. Antibodies to human T-lymphotropic virus type I in patients with tropical spastic paraparesis.Lancet. 1985;2:407–410.
Osame M, Usuku K, Izumo S, Ijichi N, Amitani H, Igata A. HTLV-I associated myelopathy, a new clinical entity.Lancet. 1986;1:1031–1032.
Rodgers-Johnson P, Gajdusek DC, Morgan OS, Zaninavic V, Sarin PS, Graham DS. HTLV-I and HTLV-III antibodies and tropical spastic paraparesis.Lancet. 1985;2:1247–1249.
Bangham CR. The immune response to HTLV-I.Curr Opin Immunol. 2000;12:397–402.
Hollsberg P, Hafler DA.What is the pathogenesis of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis?Ann Neurol. 1995;37:143–145.
Jacobson S, Shida H, McFarlin DE, Fauci AS, Koenig S. Circulating CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes specific for HTLV-I pX in patients with HTLV-I associated neurological disease.Nature. 1990;348:245–248.
Jacobson S. Immunopathogenesis of human T cell lymphotropic virus type I-associated neurologic disease.J Infect Dis. 2002;186(suppl 2):S187-S192.
Osame M. Pathological mechanisms of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I-associated myelopathy (HAM/TSP).J Neurovirol. 2002;8:359–364.
Blattner WA.Epidemiology of HTLV-I and Associated Diseases. New York: Raven; 1990.
Murphy EL, Hanchard B, Figueroa JP, et al. Modeling the risk of adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma in persons infected with human T-lymphotropic virus type I.Int J Cancer. 1989;43:250–253.
Yamaguchi K, Takatsuki K. Adult T cell leukaemia-lymphoma.Baillieres Clin Haematol. 1993;6:899–915.
de The G, Bomford R. An HTLV-I vaccine: why, how, for whom?AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1993;9:381–386.
Tajima K, Kuroishi T. Estimation of rate of incidence of ATL among ATLV (HTLV-I) carriers in Kyushu, Japan.Jpn J Clin Oncol. 1985;15:423–430.
Wong-Staal F, Hahn B, Manzari V, et al. A survey of human leukaemias for sequences of a human retrovirus.Nature. 1983;302:626–628.
Yoshida M, Seiki M, Yamaguchi K, Takatsuki K. Monoclonal integration of human T-cell leukemia provirus in all primary tumors of adult T-cell leukemia suggests causative role of human T-cell leukemia virus in the disease.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984;81:2534–2537.
Takatsuki K, Yamaguchi K, Kawano F, et al. Clinical diversity in adult T-cell leukemia-lymphoma.Cancer Res. 1985;45:4644s-4645s.
Yamaguchi K, Nishimura H, Kawano F, et al. A proposal for smoldering adult T-cell leukemia: diversity in clinical pictures of adult T-cell leukemia.Jpn J Clin Oncol. 1983;13:189–199.
Seiki M, Hattori S, Kirayama Y, Yoshida M. Human T-cell leukemia/lymphotropic virus: complete nucleotide sequence of the provirus genome integrated in leukemia cell DNA.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983;80:3618–3622.
Fields BN, Knipe DM, Howley PM.Fields Virology. Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven; 1996.
Bertola F, Manigand C, Picard P, Goetz M, Schmitter JM, Precigoux G. N-Terminal domain of HTLV-I integrase: complexation and conformational studies of the zinc finger.J Pept Sci. 2001;7:588–597.
Ha JJ, Gaul DA, Mariani VL, Ding YS, Ikeda RA, Shuker SB. HTLV-I protease cleavage of P19/24 substrates is not dependent on NaCl concentration.Bioorg Chem. 2002;30:138–144.
Heidecker G, Hill S, Lloyd PA, Derse D. A novel protease processing site in the transframe protein of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 PR76(gag-pro) defines the N terminus of RT.J Virol. 2002;76:13101–13105.
Kobayashi M, Ohi Y, Asano T, et al. Purification and characterization of human T-cell leukemia virus type I protease produced inEscherichia coli.FEBS Lett. 1991;293:106–110.
Le Blanc I, Prevost MC, Dokhelar MC, Rosenberg AR. The PPPY motif of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Gag protein is required early in the budding process.J Virol. 2002;76:10024–10029.
Mariani VL, Beckham SS. Identification of the RT-RH/IN cleavage site of HTLV-I.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003;300:268–270.
Muller B, Krausslich HG. Characterization of human T-cell leukemia virus type I integrase expressed inEscherichia coli.Eur J Biochem. 1999;259:79–87.
Trentin B, Rebeyrotte N, Mamoun RZ. Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 reverse transcriptase (RT) originates from the pro and pol open reading frames and requires the presence of RT-RNase H (RH) and RT-RH-integrase proteins for its activity.J Virol. 1998;72:6504–6510.
Ciminale V, Pavlakis GN, Derse D, Cunningham CP, Felber BK. Complex splicing in the human T-cell leukemia virus (HTLV) family of retroviruses: novel mRNAs and proteins produced by HTLV-I.J Virol. 1992;66:1737–1745.
Koralnik I, Gessain A, Klotman ME, Lo Monico A, Berneman ZN, Franchini G. Protein isoforms encoded by the pX region of the human T-cell leukemia/lymphotropic virus type I.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992;89:8813–8817.
Koralnik IJ, Fullen J, Franchini G. The p12I, p13II, and p30II proteins encoded by human T-cell leukemia/lymphotropic virus type I open reading frames I and II are localized in three different cellular compartments.J Virol. 1993;67:2360–2366.
Franchini G, Mulloy JC, Koralnik IJ, et al. The human T-cell leukemia/lymphotropic virus type I p12I protein cooperates with the E5 oncoprotein of bovine papillomavirus in cell transformation and binds the 16-kilodalton subunit of the vacuolar H+ ATPase.J Virol. 1993;67:7701–7704.
Ding W, Albrecht B, Kelley RE, et al. Human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 p12(I) expression increases cytoplasmic calcium to enhance the activation of nuclear factor of activated T cells.J Virol. 2002;76:10374–10382.
Albrecht B, D’souza CD, Ding W, Tridandapani S, Coggeshall KM, Lairmore MD. Activation of nuclear factor of activated T cells by human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 accessory protein p12(I).J Virol. 2002;76:3493–3501.
Johnson JM, Nicot C, Fullen J, et al. Free major histocompatibility complex class I heavy chain is preferentially targeted for degradation by human T-cell leukemia/lymphotropic virus type 1 p12(I) protein.J Virol. 2001;75:6086–6094.
Mulloy JC, Kislyakova T, Cereseto A, et al. Human T-cell lymphotropic/ leukemia virus type 1 Tax abrogates p53-induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis through its CREB/ATF functional domain.J Virol. 1998;72:8852–8860.
Nicot C, Mulloy JC, Ferrari MG, et al. HTLV-1 p12(I) protein enhances STAT5 activation and decreases the interleukin-2 requirement for proliferation of primary human peripheral blood mononuclear cells.Blood. 2001;98:823–829.
Nicot C, Dundr M, Johnson JM, Fukumoto R, Misteli T, Franchini G. A novel negative regulator of HTLV-1 replication. Unpublished manuscript.
Zhang W, Nisbet JW, Bartoe JT, Ding W, Lairmore MD. Human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 p30(II) functions as a transcription factor and differentially modulates CREB-responsive promoters.J Virol. 2000;74:11270–11277.
Zhang W, Nisbet JW, Albrecht B, et al. Human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 p30(II) regulates gene transcription by binding CREB binding protein/p300.J Virol. 2001;75:9885–9895.
Berneman ZN, Gartenhaus RB, Reitz MS Jr, et al. Expression of alternatively spliced human T-lymphotropic virus type I (HTLV-I) pX mRNA in infected cell lines and in primary uncultured cells from patients with adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma and healthy carriers.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992;89:3005–3009.
Ciminale V, Zotti L, D’Agostino DM, et al. Mitochondrial targeting of the p13II protein coded by the x-II ORF of human T-cell leukemia/lymphotropic virus type I (HTLV-I).Oncogene. 1999;18:4505–4514.
D’Agostino DM, Ranzato L, Arrigoni G, et al. Mitochondrial alterations induced by the p13II protein of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1: critical role of arginine residues.J Biol Chem. 2002;277:34424–34433.
Aldovini A, De Rossi A, Feinberg MB, Wong-Staal F, Franchini G. Molecular analysis of a deletion mutant provirus of type I human T-cell lymphotropic virus: evidence for a doubly spliced x-lor mRNA.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986;83:38–42.
Seiki M, Hikikoshi A, Taniguchi T, Yoshida M. Expression of the pX gene of HTLV-I: general splicing mechanism in the HTLV family.Science. 1985;228:1532–1534.
Wachsman W, Golde DW, Temple PA, Orr EC, Clark SC, Chen IS. HTLV x-gene product: requirement for the env methionine initiation codon.Science. 1985;228:1534–1537.
Felber BK. Regulation of mRNA expression in HIV-1 and other retroviruses. In: Harford JB, Morris DR, eds.mRNA Metabolism and Post-Transcriptional Gene Regulation. New York: Wiley-Liss; 1997:323–340.
Orita S, Saiga A, Takagi S, et al. A novel alternatively spliced viral mRNA transcribed in cells infected with human T cell leukemia virus type 1 is mainly responsible for expressing p21X protein.FEBS Lett. 1991;295:127–134.
Gaudray G, Gachon F, Basbous J, Biard-Piechaczyk M, Devaux C, Mesnard JM. The complementary strand of the human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 RNA genome encodes a bZIP transcription factor that down-regulates viral transcription.J Virol. 2002;76:12813–12822.
Larocca D, Chao LA, Seto MH, Brunck TK. Human T-cell leukemia virus minus strand transcription in infected T-cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989;163:1006–1013.
Ballard DW, Dohnlein E, Lowenthal JW, Wano Y, Franza BR, Greene WC. HTLV-I tax induces cellular proteins that activate the kappa B element in the IL-2 receptor alpha gene.Science. 1988;241:1652–1655.
Hiscott J, Kwon H, Genin P. Hostile takeovers: viral appropriation of the NF-kappaB pathway.J Clin Invest. 2001;107:143–151.
Jeang KT. Functional activities of the human T-cell leukemia virus type I Tax oncoprotein: cellular signaling through NF-kappa B.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2001;12:207–217.
Yoshida M, Suzuki T. HTLV-I oncoprotein Tax and cellular transcription factors.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1995;193:79–89.
Marriott SJ, Lemoine FJ, Jeang KT. Damaged DNA and miscounted chromosomes: human T cell leukemia virus type I tax oncoprotein and genetic lesions in transformed cells.J Biomed Sci. 2002;9:292–298.
Ding W, Albrecht B, Luo R, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum and cis-Golgi localization of human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 p12(I): association with calreticulin and calnexin.J Virol. 2001;75:7672–7682.
Albrecht B, Collins ND, Burniston MT, et al. Human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 open reading frame I p12(I) is required for efficient viral infectivity in primary lymphocytes.J Virol. 2000;74:9828–9835.
Derse D, Mikovits J, Ruscetti F. X-I and X-II open reading frames of HTLV-I are not required for virus replication or for immortalization of primary T-cells in vitro.Virology. 1997;237:123–128.
Robek MD, Wong FH, Ratner L. Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 pX-I and pX-II open reading frames are dispensable for the immortalization of primary lymphocytes.J Virol. 1998;72:4458–4462.
Collins ND, Newbound GC, Albrecht B, Beard JL, Ratner L, Lairmore MD. Selective ablation of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 p12I reduces viral infectivity in vivo.Blood. 1998;91:4701–4707.
Martins ML, Soares BC, Ribas JG, et al. Frequency of p12K and p12R alleles of HTLV Type 1 in HAM/TSP patients and in asymptomatic HTLV type 1 carriers.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2002;18:899–902.
Trovato R, Mulloy JC, Johnson JM, Takemoto S, de Oliveira MP, Franchini G. A lysine-to-arginine change found in natural alleles of the HTLV-I p12I protein greatly influences its stability.J Virol. 1999;73:6460–6467.
Franchini G. Molecular mechanisms of human T-cell leukemia/ lymphotropic virus type I infection.Blood. 1995;86:3619–3639.
Feller SM, Ren R, Hanafusa H, Baltimore D. SH2 and SH3 domains as molecular adhesives: the interactions of Crk and Abl.Trends Biochem Sci. 1994;19:453–458.
Mayer BJ. SH3 domains: complexity in moderation.J Cell Sci. 2001;114:1253–1263.
Koralnik I, Mulloy JC, Andresson T, Fullen J, Franchini G. Mapping of the intermolecular association of the human T-cell leukemia/ lymphotropic virus type 1 p12I and the vacuolar H+ATPase 16 kDa subunit protein.J Gen Virol. 1995;76:1909–1916.
Stevens TH, Forgac M. Structure, function and regulation of the vacuolar (H+)-ATPase.Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 1997;13:779–808.
Mulloy JC, Crowley RW, Fullen J, Leonard WJ, Franchini G. The human T-cell leukemia/lymphotropic virus type I p12I protein binds the interleukin-2 receptor β and βc chains and affects their expression on the cell surface.J Virol. 1996;70:3599–3605.
Lewis RS. Calcium signaling mechanisms in T lymphocytes.Annu Rev Immunol. 2001;19:497–521.
Rusnak F, Mertz P. Calcineurin: form and function.Physiol Rev. 2000;80:1483–1521.
Bonifacino JS, Klausner RD. Degradation of proteins retained in the endoplasmic reticulum. In: Ciechanover A, Schwartz AL, eds.Cellular Proteolytic Systems. New York:Wiley-Liss; 1994:137.
Plemper RK, Wolf DH. Retrograde protein translocation: ERADication of secretory proteins in health and disease.Trends Biochem Sci. 1999;24:266–270.
Nagai M, Usuku K, Matsumoto W, et al. Analysis of HTLV-I proviral load in 202 HAM/TSP patients and 243 asymptomatic HTLV-I carriers: high proviral load strongly predisposes to HAM/TSP.J Neurovirol. 1998;4:586–593.
D’Agostino DM, Zotti L, Ferro T, et al. Expression and functional properties of proteins encoded in the x-II ORF of HTLV-I.Virus Res. 2001;78:35–43.
Bartoe JT, Albrecht B, Collins ND, et al. Functional role of pX open reading frame II of human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 in maintenance of viral loads in vivo.J Virol. 2000;74:1094–1100.
D’Agostino DM, Ciminale V, Zotti L, Rosato A, Chieco-Bianchi L. The human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 Tof protein contains a bipartite nuclear localization signal that is able to functionally replace the amino-terminal domain of Rex.J Virol. 1997;71:75–83.
Hemelaar J, Bex F, Booth B, Cerundolo V, McMichael A, Daenke S. Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Tax protein binds to assembled nuclear proteasomes and enhances their proteolytic activity.J Virol. 2001;75:11106–11115.
Desagher S, Martinou JC. Mitochondria as the central control point of apoptosis.Trends Cell Biol. 2000;10:369–377.
Rojo G, Chamorro M, Salas ML, Vinuela E, Cuezva JM, Salas J. Migration of mitochondria to viral assembly sites in African swine fever virus-infected cells.J Virol. 1998;72:7583–7588.
Lefebvre L, Vanderplasschen A, Ciminale V, et al. Oncoviral bovine leukemia virus G4 and human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 p13(II) accessory proteins interact with farnesyl pyrophosphate synthetase.J Virol. 2002;76:1400–1414.
Rao KN. The significance of the cholesterol biosynthetic pathway in cell growth and carcinogenesis [review].Anticancer Res. 1995;15:309–314.
Kiyokawa T, Seiki M, Iwashita S, Imagawa K, Shimizu F, Yoshida M. p27x-III and p21x-III, proteins encoded by the pX sequence of human T-cell leukemia virus type I.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985;82:8359–8363.
Nagashima K, Yoshida M, Seiki M. A single species of pX mRNA of human T-cell leukemia virus type I encodes trans-activator p40x and two other phosphoproteins.J Virol. 1986;60:394–399.
Furukawa K, Furukawa K, Shiku H. Alternatively spliced mRNA of the pX region of human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 proviral genome.FEBS Lett. 1991;295:141–145.
Kubota S, Hatanaka M, Pomerantz RJ. Nucleo-cytoplasmic redistribution of the HTLV-I Rex protein: alterations by coexpression of the HTLV-I p21x protein.Virology. 1996;220:502–507.
Orita S, Takagi S, Saiga A, et al. Human T cell leukaemia virus type 1 p21X mRNA: constitutive expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with adult T cell leukaemia.J Gen Virol. 1992;73:2283–2289.
Hidaka M, Inoue J, Yoshida M, Seiki M. Post-transcriptional regulator (rex) of HTLV-1 initiates expression of viral structural proteins but suppresses expression of regulatory proteins.EMBO J. 1988;7:519–523.
Inoue J, Seiki M, Yoshida M. The second pX product p27 chi-III of HTLV-1 is required for gag gene expression.FEBS Lett. 1986;209:187–190.
Inoue J, Itoh M, Akizawa T, Toyoshima H, Yoshida M. HTLV-1 Rex protein accumulates unspliced RNA in the nucleus as well as in cytoplasm.Oncogene. 1991;6:1753–1757.
Nosaka T, Siomi H, Adachi Y, et al. Nucleolar targeting signal of human T-cell leukemia virus type I rex-encoded protein is essential for cytoplasmic accumulation of unspliced viral mRNA.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989;86:9798–9802.
Ohta M, Nyunoya H, Tanaka H, Okamoto T, Akagi T, Shimotohno K. Identification of a cis-regulatory element involved in accumulation of human T-cell leukemia virus type II genomic mRNA.J Virol. 1988;62:4445–4451.
Siomi H, Shida H, Nam SH, Nosaka T, Maki M, Hatanaka M. Sequence requirements for nucleolar localization of human T cell leukemia virus type I pX protein, which regulates viral RNA processing.Cell. 1988;55:197–209.
Smith MR, Greene WC. Type I human T cell leukemia virus tax protein transforms rat fibroblasts through the cyclic adenosine monophosphate response element binding protein/activating transcription factor pathway.J Clin Invest. 1991;88:1038–1042.
Ballaun C, Farrington GK, Dobrovnik M, Rusche J, Hauber J, Bohnlein E. Functional analysis of human T-cell leukemia virus type I rex-response element: direct RNA binding of Rex protein correlates with in vivo activity.J Virol. 1991;65:4408–4413.
Bar-Shira A, Panet A, Honigman A. An RNA secondary structure juxtaposes two remote genetic signals for human T-cell leukemia virus type I RNA 3′-end processing.J Virol. 1991;65:5165–5173.
Hanly SM, Rimsky LT, Malim MH, et al. Comparative analysis of the HTLV-I Rex and HIV-1 Rev trans-regulatory proteins and their RNA response elements.Genes Dev. 1989;3:1534–1544.
Seiki M, Inoue J, Hidaka M, Yoshida M. Two cis-acting elements responsible for posttranscriptional trans-regulation of gene expression of human T-cell leukemia virus type I.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988;85:7124–7128.
Unge T, Solomin L, Mellini M, Derse D, Felber BK, Pavlakis GN. The Rex regulatory protein of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I binds specifically to its target site within the viral RNA.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991;88:7145–7149.
Yoshida M, Seiki M. Recent advances in the molecular biology of HTLV-1: trans-activation of viral and cellular genes.Annu Rev Immunol. 1987;5:541–559.
Adachi Y, Copeland TD, Takahashi C, et al. Phosphorylation of the Rex protein of human T-cell leukemia virus type I.J Biol Chem. 1992;267:21977–21981.
Grone M, Koch C, Grassmann R. The HTLV-1 Rex protein induces nuclear accumulation of unspliced viral RNA by avoiding intron excision and degradation.Virology. 1996;218:316–325.
Kanamori H, Suzuki N, Siomi H, et al. HTLV-1 p27rex stabilizes human interleukin-2 receptor alpha chain mRNA.EMBO J. 1990;9:4161–4166.
McGuire KL, Curtiss VE, Larson EL, Haseltine WA. Influence of human T-cell leukemia virus type I tax and rex on interleukin-2 gene expression.J Virol. 1993;67:1590–1599.
Sodroski JG, Rosen CA, Haseltine WA. Transacting transcriptional activation of the long terminal repeat of human T lymphotropic viruses in infected cells.Science. 1984;225:381–385.
Cann AJ, Rosenblatt JD, Wachsman W, Shah NP, Chen IS. Identification of the gene responsible for human T-cell leukaemia virus transcriptional regulation.Nature. 1985;318:571–574.
Felber BK, Paskalis H, Wong-Staal F, Pavlakis GN. The pX protein of HTLV-I is a transcriptional activator of its long terminal repeats.Science. 1985;229:675–679.
Sodroski J, Rosen C, Goh WC, Haseltine W. A transcriptional activator protein encoded by the x-lor region of the human T-cell leukemia virus.Science. 1985;228:1430–1434.
Sodroski JG, Goh WC, Rosen CA, et al. trans-Activation of the human T-cell leukemia virus long terminal repeat correlates with expression of the x-lor protein.J Virol. 1985;55:831–835.
Stevenson M. Molecular mechanisms for the regulation of HIV replication, persistence and latency.AIDS. 1997;11(suppl A):S25-S33.
Kronke M, Leonard WJ, Depper JM, Greene WC. Deregulation of interleukin-2 receptor gene expression in HTLV-I-induced adult T-cell leukemia.Science. 1985;228:1215–1217.
Lando Z, Sarin P, Megson M, et al. Association of human T-cell leukaemia/lymphoma virus with the Tac antigen marker for the human T-cell growth factor receptor.Nature. 1983;305:733–736.
Greene WC, Leonard WJ, Wano Y, et al. Trans-activator gene of HTLV-II induces IL-2 receptor and IL-2 cellular gene expression.Science. 1986;232:877–880.
Cross SL, Feinberg MB, Wolf JB, Holbrook NJ, Wong-Staal F, Leonard WJ. Regulation of the human interleukin-2 receptor alpha chain promoter: activation of a nonfunctional promoter by the transactivator gene of HTLV-I.Cell. 1987;49:47–56.
Inoue J, Seiki M, Taniguchi T, Tsuru S, Yoshida M. Induction of interleukin 2 receptor gene expression by p40x encoded by human T-cell leukemia virus type 1.EMBO J. 1986;5:2883–2888.
Leung K, Nabel GJ. HTLV-1 transactivator induces interleukin-2 receptor expression through an NF-kappa B-like factor.Nature. 1988;333:776–778.
Maruyama M, Shibuya H, Harada H, et al. Evidence for aberrant activation of the interleukin-2 autocrine loop by HTLV-1-encoded p40x and T3/Ti complex triggering.Cell. 1987;48:343–350.
Ruben S, Poteat H, Tan TH, et al. Cellular transcription factors and regulation of IL-2 receptor gene expression by HTLV-I tax gene product.Science. 1988;241:89–92.
Siekevitz M, Feinberg MB, Holbrook N, Wong-Staal F, Greene WC. Activation of interleukin 2 and interleukin 2 receptor (Tac) promoter expression by the trans-activator (tat) gene product of human T-cell leukemia virus, type I.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987;84:5389–5393.
Baeuerle PA, Baltimore D. NF-kappa B: ten years after.Cell. 1996;87:13–20.
Alexandre C, Charnay P, Verrier B.Transactivation of Krox-20 and Krox-24 promoters by the HTLV-1 Tax protein through common regulatory elements.Oncogene. 1991;6:1851–1857.
Fujii M, Tsuchiya H, Chuhjo T, Akizawa T, Seiki M. Interaction of HTLV-1 Tax1 with p67SRF causes the aberrant induction of cellular immediate early genes through CArG boxes.Genes Dev. 1992;6:2066–2076.
Goodman RH, Smolik S. CBP/p300 in cell growth, transformation, and development.Genes Dev. 2000;14:1553–1577.
Yoshida M. Multiple viral strategies of HTLV-1 for dysregulation of cell growth control.Annu Rev Immunol. 2001;19:475–496.
Fujii M, Tsuchiya H, Chuhjo T, Minamino T, Miyamoto K, Seiki M. Serum response factor has functional roles both in indirect binding to the CArG box and in the transcriptional activation function of human T-cell leukemia virus type I Tax.J Virol. 1994;68:7275–7283.
Herdegen T, Leah JD. Inducible and constitutive transcription factors in the mammalian nervous system: control of gene expression by Jun, Fos and Krox, and CREB/ATF proteins.Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1998;28:370–490.
Suzuki T, Hirai H, Fujisawa J, Fujita K, Yoshida M. A trans-activator Tax of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 binds to NF-kappa B p50 and serum response factor (SRF) and associates with enhancer DNAs of the NF-kappa B site and CArG box.Oncogene. 1993;8:2391–2397.
Tsuchiya H, Fujii M, Niki T, Tokuhara M, Matsui M, Seiki M. Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Tax activates transcription of the human fra-1 gene through multiple cis elements responsive to transmembrane signals.J Virol. 1993;67:7001–7007.
Shuh M, Derse D. Ternary complex factors and cofactors are essential for human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 tax transactivation of the serum response element.J Virol. 2000;74:11394–11397.
Armstrong AP, Franklin AA, Uittenbogaard MN, Giebler HA, Nyborg JK. Pleiotropic effect of the human T-cell leukemia virus Tax protein on the DNA binding activity of eukaryotic transcription factors.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993;90:7303–7307.
Jin G, Howe PH. Regulation of clusterin gene expression by transforming growth factor beta.J Biol Chem. 1997;272:26620–26626.
Mori N, Fujii M, Iwai K, et al. Constitutive activation of transcription factor AP-1 in primary adult T-cell leukemia cells.Blood. 2000;95:3915–3921.
Jeang KT,Widen SG, Semmes OJ, IV, Wilson SH. HTLV-I transactivator protein, tax, is a trans-repressor of the human betapolymerase gene.Science. 1990;247:1082–1084.
Uittenbogaard MN, Armstrong AP, Chiaramello A, Nyborg JK. Human T-cell leukemia virus type I Tax protein represses gene expression through the basic helix-loop-helix family of transcription factors.J Biol Chem. 1994;269:22466–22469.
Lemasson I, Robert-Hebmann V, Hamaia S, Duc DM, Gazzolo L, Devaux C. Transrepression of lck gene expression by human T-cell leukemia virus type 1-encoded p40tax.J Virol. 1997;71:1975–1983.
Uittenbogaard MN, Giebler HA, Reisman D, Nyborg JK. Transcriptional repression of p53 by human T-cell leukemia virus type I Tax protein.J Biol Chem. 1995;270:28503–28506.
Suzuki T, Hirai H, Murakami T, Yoshida M. Tax protein of HTLV-1 destabilizes the complexes of NF-kappa B and I kappa B-alpha and induces nuclear translocation of NF-kappa B for transcriptional activation.Oncogene. 1995;10:1199–1207.
Suzuki T, Uchida-Toita M, Yoshida M. Tax protein of HTLV-1 inhibits CBP/p300-mediated transcription by interfering with recruitment of CBP/p300 onto DNA element of E-box or p53 binding site.Oncogene. 1999;18:4137–4143.
Brauweiler A, Garrus JE, Reed JC, Nyborg JK. Repression of bax gene expression by the HTLV-1 Tax protein: implications for suppression of apoptosis in virally infected cells.Virology. 1997;231:135–140.
Nicot C, Mahieux R, Opavsky R, et al. HTLV-I Tax transrepresses the human c-Myb promoter independently of its interaction with CBP or p300.Oncogene. 2000;19:2155–2164.
Nicot C, Opavsky R, Mahieux R, et al. Tax oncoprotein transrepresses the endogenous B-myb promoter activity in human T cells.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2000;16:1629–1632.
Nicot C, Mahieux R, Pise-Masison C, et al. Human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 Tax represses c-Myb-dependent transcription through activation of the NF-kappaB pathway and modulation of coactivator usage.Mol Cell Biol. 2001;21:7391–7402.
Arnulf B, Villemain A, Nicot C, et al. Human T-cell lymphotropic virus oncoprotein Tax represses TGF-beta 1 signaling in human T cells via c-Jun activation: a potential mechanism of HTLV-I leukemogenesis.Blood. 2002;100:4129–4138.
Lee DK, Kim BC, Brady JN, Jeang KT, Kim SJ. Human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 tax inhibits transforming growth factor-beta signaling by blocking the association of Smad proteins with Smadbinding element.J Biol Chem. 2002;277:33766–33775.
Mori N, Morishita M, Tsukazaki T, et al. Human T-cell leukemia virus type I oncoprotein Tax represses Smad-dependent transforming growth factor beta signaling through interaction with CREB-binding protein/p300.Blood. 2001;97:2137–2144.
Azimi N, Brown K, Bamford RN, Tagaya Y, Siebenlist U, Waldmann TA. Human T cell lymphotropic virus type I Tax protein trans-activates interleukin 15 gene transcription through an NFkappaB site.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998;95:2452–2457.
Azimi N, Nagai M, Jacobson S, Waldmann TA. IL-15 plays a major role in the persistence of Tax-specific CD8 cells in HAM/TSP patients.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98:14559–14564.
Mariner JM, Lantz V, Waldmann TA, Azimi N. Human T cell lymphotropic virus type I Tax activates IL-15Ralpha gene expression through an NF-kappaB site.J Immunol. 2001;166:2602–2609.
Kirken RA, Erwin RA, Wang L, Wang Y, Rui H, Farrar WL. Functional uncoupling of the Janus kinase 3-Stat5 pathway in malignant growth of human T cell leukemia virus type 1-transformed human T cells.J Immunol. 2000;165:5097–5104.
Li-Weber M, Giaisi M, Chlichlia K, Khazaie K, Krammer PH. Human T cell leukemia virus type I Tax enhances IL-4 gene expression in T cells.Eur J Immunol. 2001;31:2623–2632.
Mori N, Prager D. Transactivation of the interleukin-1alpha promoter by human T-cell leukemia virus type I and type II Tax proteins.Blood. 1996;87:3410–3417.
Mori N, Prager D. Interleukin-10 gene expression and adult T-cell leukemia.Leuk Lymphoma. 1998;29:239–248.
Mori N, Mukaida N, Ballard DW, Matsushima K, Yamamoto N. Human T-cell leukemia virus type I Tax transactivates human interleukin 8 gene through acting concurrently on AP-1 and nuclear factor-kappaB-like sites.Cancer Res. 1998;58:3993–4000.
Yamashita I, Katamine S, Moriuchi R, et al. Transactivation of the human interleukin-6 gene by human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 Tax protein.Blood. 1994;84:1573–1578.
Chieco-Bianchi L, Saggioro D, Del Mistro A, Montaldo A, Majone F, Levis AG. Chromosome damage induced in cord blood T-lymphocytes infected in vitro by HTLV-I.Leukemia. 1988;2:223S-232S.
Markham PD, Salahuddin SZ, Kalyanaraman VS, Popovic M, Sarin P, Gallo RC. Infection and transformation of fresh human umbilical cord blood cells by multiple sources of human T-cell leukemia-lymphoma virus (HTLV).Int J Cancer. 1983;31:413–420.
Popovic M, Lange-Wantzin G, Sarin PS, Mann D, Gallo RC. Transformation of human umbilical cord blood T-cells by human T-cell leukemia/lymphoma virus.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983;80:5402–5406.
Reid RL, Lindholm PF, Mireskandari A, Dittmer J, Brady JN. Stabilization of wild type p53 in human T-lymphocytes transformed by HTLV-I.Oncogene. 1993;8:3029–3036.
Yamato K, Oka T, Hiroi M, et al. Aberrant expression of the p53 tumor suppressor gene in adult T-cell leukemia and HTLV-Iinfected cells.Jpn J Cancer Res. 1993;84:4–8.
Cereseto A, Diella F, Mulloy JC, et al. p53 functional impairment and high p21waf1/cip1 expression in human T-cell lymphotropic/ leukemia virus type I-transformed T-cells.Blood. 1996;88:1551–1560.
Akagi T, Ono H, Shimotohno K. Expression of cell-cycle regulatory genes in HTLV-I infected T-cell lines: possible involvement of Tax1 in the altered expression of cyclin D2, p18Ink4 and p21waf1/ cip1/sdi1.Oncogene. 1996;12:1645–1652.
Schmitt I, Rosin O, Rohwer P, Gossen M, Grassmann R. Stimulation of cyclin-dependent kinase activity and G1- to S-phase transition in human lymphocytes by the human T-cell leukemia/lymphotropic virus type 1 Tax protein.J Virol. 1998;72:633–640.
Pise-Masison CA, Choi KS, Radonovich M, Dittmer J, Kim SJ, Brady JN. Inhibition of p53 transactivation function by the human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 Tax protein.J Virol. 1998;72:1165–1170.
Akagi T, Ono H, Tsuchida N, Shimotohno K. Aberrant expression and function of p53 in T-cells immortalized by HTLV-I Tax 1.FEBS Lett. 1997;406:263–266.
Pise-Masison CA, Radonovich M, Sakaguchi K, Appella E, Brady JN. Phosphorylation of p53: a novel pathway for p53 inactivation in human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1-transformed cells.J Virol. 1998;72:6348–6355.
Pise-Masison CA, Mahieux R, Radonovich MF, Jiang H, Brady JN. Human T-lymphotropic virus type I Tax protein utilizes distinct pathways for p53 inhibition that are cell type-dependent.J Biol Chem. 2001;276:200–205.
Van PL, Yim KW, Jin DY, Dapolito G, Kurimasa A, Jeang KT. Genetic evidence of a role for ATM in functional interaction between human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Tax and p53.J Virol. 2001;75:396–407.
Chaudhry S, Freebern WJ, Smith JL, Butscher WG, Haggerty CM, Gardner K. Cross-regulation of T cell growth factor expression by p53 and the tax oncogene.J Immunol. 2002;169:6767–6778.
Pise-Masison CA, Mahieux R, Jiang H, et al. Inactivation of p53 by human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 Tax requires activation of the NF-kappaB pathway and is dependent on p53 phosphorylation.Mol Cell Biol. 2000;20:3377–3386.
Ariumi Y, Kaida A, Lin JY, et al. HTLV-1 tax oncoprotein represses the p53-mediated trans-activation function through coactivator CBP sequestration.Oncogene. 2000;19:1491–1499.
Livengood JA, Scoggin KE, Van Orden K, et al. p53 Transcriptional activity is mediated through the SRC1-interacting domain of CBP/p300.J Biol Chem. 2002;277:9054–9061.
Van Orden K, Giebler HA, Lemasson I, Gonzales M, Nyborg JK. Binding of p53 to the KIX domain of CREB binding protein: a potential link to human T-cell leukemia virus, type I-associated leukemogenesis.J Biol Chem. 1999;274:26321–26328.
Kaida A, Ariumi Y, Ueda Y, et al. Functional impairment of p73 and p51, the p53-related proteins, by the human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Tax oncoprotein.Oncogene. 2000;19:827–830.
Lemasson I, Nyborg JK. Human T-cell leukemia virus type I tax repression of p73beta is mediated through competition for the C/H1 domain of CBP.J Biol Chem. 2001;276:15720–15727.
Lu H, Pise-Masison CA, Fletcher TM, et al. Acetylation of nucleosomal histones by p300 facilitates transcription from tax-responsive human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 chromatin template.Mol Cell Biol. 2002;22:4450–4462.
Cheng H, Cenciarelli C, Shao Z, et al. Human T cell leukemia virus type 1 Tax associates with a molecular chaperone complex containing hTid-1 and Hsp70.Curr Biol. 2001;11:1771–1775.
Schilling B, De Medina T, Syken J, Vidal M, Munger K. A novel human DnaJ protein, hTid-1, a homolog of theDrosophila tumor suppressor protein Tid56, can interact with the human papillomavirus type 16 E7 oncoprotein.Virology. 1998;247:74–85.
Lemoine FJ, Marriott SJ. Accelerated G(1) phase progression induced by the human T cell leukemia virus type I (HTLV-I) Tax oncoprotein.J Biol Chem. 2001;276:31851–31857.
Hinds PW, Weinberg RA. Tumor suppressor genes.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1994;4:135–141.
Nevins JR. E2F: a link between the Rb tumor suppressor protein and viral oncoproteins.Science. 1992;258:424–429.
Morgan DO. Principles of CDK regulation.Nature. 1995;374:131–134.
Peter M, Herskowitz I. Joining the complex: cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitory proteins and the cell cycle.Cell. 1994;79:181–184.
Sherr CJ, Roberts JM. Inhibitors of mammalian G1 cyclin-dependent kinases.Genes Dev. 1995;9:1149–1163.
Harper JW, Adami GR, Wei N, Keyomarsi K, Elledge SJ. The p21 Cdk-interacting protein Cip1 is a potent inhibitor of G1 cyclindependent kinases.Cell. 1993;75:805–816.
Cereseto A, Washington-Parks R, Rivadeneira E, Franchini G. Limiting amounts of p27kip1 correlates with constitutive activation of cyclin E-CDK2 complex in HTLV-I-transformed T-cells.Oncogene. 1999;18:2441–2450.
el-Deiry WS, Tokino T, Velculescu VE, et al. WAF1, a potential mediator of p53 tumor suppression.Cell. 1993;75:817–825.
Haller K, Ruckes T, Schmitt I, Saul D, Derow E, Grassmann R. Taxdependent stimulation of G1 phase-specific cyclin-dependent kinases and increased expression of signal transduction genes characterize HTLV type 1-transformed T cells.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2000;16:1683–1688.
Low KG, Dorner LF, Fernando DB, Grossman J, Jeang KT, Comb MJ. Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 tax releases cell cycle arrest induced by p16INK4a.J Virol. 1997;71:1956–1962.
Suzuki T, Kitao S, Matsushime H, Yoshida M. HTLV-I Tax protein interacts with cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p16ink4a and counteracts its inhibitory activity towards CDK4.EMBO J. 1996;15:1607–1614.
Suzuki T, Narita T, Uchida-Toita M, Yoshida M. Down-regulation of the INK4 family of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors by tax protein of HTLV-1 through two distinct mechanisms.Virology. 1999;259:384–391.
Mori N, Fujii M, Hinz M, et al. Activation of cyclin D1 and D2 promoters by human T-cell leukemia virus type I tax protein is associated with IL-2-independent growth of T cells.Int J Cancer. 2002;99:378–385.
Santiago F, Clark E, Chong S, et al. Transcriptional up-regulation of the cyclin D2 gene and acquisition of new cyclin-dependent kinase partners in human T-cell leukemia virus type 1-infected cells.J Virol. 1999;73:9917–9927.
Huang Y, Ohtani K, Iwanaga R, Matsumura Y, Nakamura M. Direct trans-activation of the human cyclin D2 gene by the oncogene product Tax of human T-cell leukemia virus type I.Oncogene. 2001;20:1094–1102.
Mori N, Fujii M, Cheng G, et al. Human T-cell leukemia virus type I tax protein induces the expression of anti-apoptotic gene Bcl-xL in human T-cells through nuclear factor-kappaB and c-AMP responsive element binding protein pathways.Virus Genes. 2001;22:279–287.
Lemasson I, Thebault S, Sardet C, Devaux C, Mesnard JM. Activation of E2F-mediated transcription by human T-cell leukemia virus type I Tax protein in a p16(INK4A)-negative T-cell line.J Biol Chem. 1998;273:23598–23604.
Macleod KF, Sherry N, Hannon G, et al. p53 dependent and independent expression of p21 during cell growth, differentiation, and DNA damage.Genes Dev. 1995;9:935–944.
Zhang H, Hannon J, Beach D. p21-containing cyclin kinases exist in both active and inactive states.Genes Dev. 1994;8:1750–1758.
de La Fuente C, Deng L, Santiago F, Arce L, Wang L, Kashanchi F. Gene expression array of HTLV type 1-infected T cells: up-regulation of transcription factors and cell cycle genes.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2000;16:1695–1700.
Iwanaga R, Ohtani K, Hayashi T, Nakamura M. Molecular mechanism of cell cycle progression induced by the oncogene product Tax of human T-cell leukemia virus type I.Oncogene. 2001;20:2055–2067.
Kao SY, Marriott SJ. Disruption of nucleotide excision repair by the human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Tax protein.J Virol. 1999;73:4299–4304.
Kao SY, Lemoine FJ, Marriott SJ. Suppression of DNA repair by human T cell leukemia virus type 1 Tax is rescued by a functional p53 signaling pathway.J Biol Chem. 2000;275:35926–35931.
Lemoine FJ, Kao SY, Marriott SJ. Suppression of DNA repair by HTLV type 1 tax correlates with tax trans-activation of proliferating cell nuclear antigen gene expression.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2000;16:1623–1627.
Li Y, Jenkins CW, Nichols MA, Xiong Y. Cell cycle expression and p53 regulation of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21.Oncogene. 1994;9:2261–2268.
Mozzherin DJ, McConnell M, Jasko MV, et al. Proliferating cell nuclear antigen promotes misincorporation catalyzed by calf thymus DNA polymerase delta.J Biol Chem. 1996;271:31711–31717.
de La Fuente C, Santiago F, Chong SY, et al. Overexpression of p21(waf1) in human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1-infected cells and its association with cyclin A/cdk2.J Virol. 2000;74:7270–7283.
Suzuki T, Uchida-Toita M, Andoh T, Yoshida M. HTLV-1 tax oncoprotein binds to DNA topoisomerase I and inhibits its catalytic activity.Virology. 2000;270:291–298.
Yoshida M, Suzuki T. HTLV type 1 Tax oncoprotein binds to DNA topoisomerase I and inhibits its catalytic activity.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2000;16:1639–1645.
Lemoine FJ, Marriott SJ. Genomic instability driven by the human T-cell leukemia virus type I (HTLV-I) oncoprotein,Tax.Oncogene. 2002;21:7230–7234.
Miyake H, Suzuki T, Hirai H, Yoshida M. Trans-activator Tax of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 enhances mutation frequency of the cellular genome.Virology. 1999;253:155–161.
Poiesz BJ, Ruscetti FW, Mier JW, Woods AM, Gallo RC. T-cell lines established from human T-lymphocytic neoplasias by direct response to T-cell growth factor.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980;77:6815–6819.
Uchiyama T, Yodoi J, Sagawa K, Takatsuki K, Uchino H. Adult T-cell leukemia: clinical and hematologic features of 16 cases.Blood. 1977;50:481–492.
Fu DX, Kuo YL, Liu BY, Jeang KT, Giam CZ. Human T-lymphotropic virus type I tax activates I-kappa B kinase by inhibiting IKKgamma-associated serine/threonine protein phosphatase 2A.J Biol Chem. 2002;278:1487–1493.
Hardwick KG, Murray AW. Mad1p, a phosphoprotein component of the spindle assembly checkpoint in budding yeast.J Cell Biol. 1995;131:709–720.
Jin DY, Spencer F, Jeang KT. Human T cell leukemia virus type 1 oncoprotein Tax targets the human mitotic checkpoint protein MAD1.Cell. 1998;93:81–91.
Majone F, Semmes OJ, Jeang KT. Induction of micronuclei by HTLV-I Tax: a cellular assay for function.Virology. 1993;193:456–459.
Saggioro D, Majone F, Forino M, Turchetto L, Leszl A, Chieco-Bianchi L. Tax protein of human T-lymphotropic virus type I triggers DNA damage.Leuk Lymphoma. 1994;12:281–286.
Semmes OJ, Majone F, Cantemir C, Turchetto L, Hjelle B, Jeang KT. HTLV-I and HTLV-II Tax: differences in induction of micronuclei in cells and transcriptional activation of viral LTRs.Virology. 1996;217:373–379.
Campbell MS, Chan GK, Yen TJ. Mitotic checkpoint proteins HsMAD1 and HsMAD2 are associated with nuclear pore complexes in interphase.J Cell Sci. 2001;114:953–963.
Cereseto A, Kislyakova T, Washington-Parks R, Franchini G. Differential response to genotoxic stress in immortalized or transformed HTLV-I-infected T-cells.J Gen Virol. 1999;80:1575–1581.
Chlichlia K, Busslinger M, Peter ME, et al. ICE-proteases mediate HTLV-I Tax-induced apoptotic T-cell death.Oncogene. 1997;14:2265–2272.
Hall AP, Irvine J, Blyth K, Cameron ER, Onions DE, Campbell ME. Tumours derived from HTLV-I tax transgenic mice are characterized by enhanced levels of apoptosis and oncogene expression.J Pathol. 1998;186:209–214.
Kao SY, Lemoine FJ, Mariott SJ. HTLV-1 Tax protein sensitizes cells to apoptotic cell death induced by DNA damaging agents.Oncogene. 2000;19:2240–2248.
Kao SY, Lemoine FJ, Marriott SJ. p53-Independent induction of apoptosis by the HTLV-I tax protein following UV irradiation.Virology. 2001;291:292–298.
Los M, Khazaie K, Schulze-Osthoff K, Baeuerle PA, Schirrmacher V, Chlichlia K. Human T cell leukemia virus-I (HTLV-I) Tax-mediated apoptosis in activated T cells requires an enhanced intracellular prooxidant state.J Immunol. 1998;161:3050–3055.
Nicot C, Harrod R. Distinct p300-responsive mechanisms promote caspase-dependent apoptosis by human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1.Mol Cell Biol. 2000;20:8580–8589.
Yamada T, Yamaoka S, Goto T, Nakai M, Tsujimoto Y, Hatanaka M. The human T-cell leukemia virus type I Tax protein induces apoptosis which is blocked by the Bcl-2 protein.J Virol. 1994;68:3374–3379.
Arai M, Kannagi M, Matsuoka M, Sato T, Yamamoto N, Fujii M. Expression of FAP-1 (Fas-associated phosphatase) and resistance to Fas-mediated apoptosis in T cell lines derived from human T cell leukemia virus type 1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis patients.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1998;14:261–267.
Kasai T, Iwanaga Y, Iha H, Jeang KT. Prevalent loss of mitotic spindle checkpoint in adult T-cell leukemia confers resistance to microtubule inhibitors.J Biol Chem. 2002;277:5187–5193.
Kishi S, Saijyo S, Arai M, et al. Resistance to Fas-mediated apoptosis of peripheral T cells in human T lymphocyte virus type I (HTLV-I) transgenic mice with autoimmune arthropathy.J Exp Med. 1997;186:57–64.
Nicot C, Astier-Gin T, Guillemain B. Activation of Bcl-2 expression in human endothelial cells chronically expressing the human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I.Virology. 1997;236:47–53.
Ruckes T, Saul D, Van Snick J, Hermine O, Grassmann R. Autocrine antiapoptotic stimulation of cultured adult T-cell leukemia cells by overexpression of the chemokine I-309.Blood. 2001;98:1150–1159.
Tsukahara T, Kannagi M, Ohashi T, et al. Induction of Bcl-x(L) expression by human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Tax through NFkappaB in apoptosis-resistant T-cell transfectants with Tax.J Virol. 1999;73:7981–7987.
Yamada Y, Sugahara K, Tsuruda K, et al. Fas-resistance in ATL cell lines not associated with HTLV-I or FAP-1 production.Cancer Lett. 1999;147:215–219.
Nicot C, Mahieux R, Takemoto S, Franchini G. Bcl-XL is upregulated by HTLV type I and type II in vitro and in ex vivo ATLL samples.Blood. 2000;96:275–281.
Rivera-Walsh I, Waterfield M, Xiao G, Fong A, Sun SC. NF-kappaB signaling pathway governs TRAIL gene expression and human T-cell leukemia virus-I Tax-induced T-cell death.J Biol Chem. 2001;276:40385–40388.
Rivera I, Harhaj EW, Sun SC. Involvement of NF-AT in type I human T-cell leukemia virus Tax-mediated Fas ligand promoter transactivation.J Biol Chem. 1998;273:22382–22388.
Rock KL, Gramm C, Rothstein L, et al. Inhibitors of the proteasome block the degradation of most cell proteins and the generation of peptides presented on MHC class I molecules.Cell. 1994;78:761–771.
Beraud C, Greene WC. Interaction of HTLV-I Tax with the human proteasome: implications for NF-kappa B induction.J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr Hum Retrovirol. 1996;13(suppl 1):S76-S84.
Petropoulos L, Hiscott J. Association between HTLV-1 Tax and I kappa B alpha is dependent on the I kappa B alpha phosphorylation state.Virology. 1998;252:189–199.
Rousset R, Desbois C, Bantignies F, Jalinot P. Effects on NF-kappa B1/p105 processing of the interaction between the HTLV-1 transactivator Tax and the proteasome.Nature. 1996;381:328–331.
Tan C, Waldmann TA. Proteasome inhibitor PS-341, a potential therapeutic agent for adult T-cell leukemia.Cancer Res. 2002;62:1083–1086.
Lomas M, Hanon E, Tanaka Y, Bangham CR, Gould KG. Presentation of a new H-2D(k)-restricted epitope in the Tax protein of human T-lymphotropic virus type I is enhanced by the proteasome inhibitor lactacystin.J Gen Virol. 2002;83:641–650.
Morgan DC, Ruscetti FW, Gallo RC. Selective in vitro growth of T lymphocytes from normal human bone marrows.Science. 1976;193:1007–1008.
Tsukasaki K, Krebs J, Nagai K, et al. Comparative genomic hybridization analysis in adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma: correlation with clinical course.Blood. 2001;97:3875–3881.
Migone TS, Lin JX, Cereseto A, et al. Constitutively activated JAKSTAT pathway in T-cells transformed with HTLV-I.Science. 1995;269:79–81.
Mulloy JC, Migone TS, Ross TM, et al. Human and simian T-cell leukemia viruses type 2 (HTLV-2 and STLV-2pan-p) transform T-cells independently of Jak/STAT activation.J Virol. 1998;72:4408–4412.
Xu XN, Screaton GR, Gotch FM, et al. Evasion of cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) responses by nef-dependent induction of Fas ligand (CD95L) expression on simian immunodeficiency virus-infected cells.J Exp Med. 1997;186:7–16.
Migone TS, Cacalano NA, Taylor N, Yi T, Waldmann TA, Johnston JA. Recruitment of SH2-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1 to the interleukin 2 receptor: loss of SHP-1 expression in human T-lymphotropic virus type I-transformed T cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998;95:3845–3850.
Grassmann R, Dengler C, Muller-Fleckenstein I, et al. Transformation to continuous growth of primary human T lymphocytes by human T-cell leukemia virus type I X-region genes transduced by a herpesvirus saimiri vector.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989;86:3351–3355.
Iwanaga Y, Tsukahara T, Ohashi T, et al. Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 tax protein abrogates interleukin-2 dependence in a mouse T-cell line.J Virol. 1999;73:1271–1277.
Tanaka Y, Yoshida A, Tozawa H, Shida H, Nyunoya H, Shimotohno K. Production of a recombinant human T-cell leukemia virus type-I trans-activator (tax1) antigen and its utilization for generation of monoclonal antibodies against various epitopes on the tax1 antigen.Int J Cancer. 1991;48:623–630.
Kelly K, Davis P, Mitsuya H, et al. A high proportion of early response genes are constitutively activated in T cells by HTLV-I.Oncogene. 1992;7:1463–1470.
Robek MD, Ratner L. Immortalization of CD4(+) and CD8(+) T lymphocytes by human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Tax mutants expressed in a functional molecular clone.J Virol. 1999;73:4856–4865.
Rosin O, Koch C, Schmitt I, Semmes OJ, Jeang KT, Grassmann R. A human T-cell leukemia virus Tax variant incapable of activating NF-kappaB retains its immortalizing potential for primary T-lymphocytes.J Biol Chem. 1998;273:6698–6703.
Sallusto F, Lenig D, Forster R, Lipp M, Lanzavecchia A. Two subsets of memory T lymphocytes with distinct homing potentials and effector functions.Nature. 1999;401:708–712.
Nagai M, Brennan MB, Sakai JA, Mora CA, Jacobson S. CD8(+) T cells are an in vivo reservoir for human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I.Blood. 2001;98:1858–1861.
Richardson JH, Edwards AJ, Cruickshank JK, Rudge P, Dalgleish AG. In vivo cellular tropism of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1.J Virol. 1990;64:5682–5687.
Kazanji M, Ureta-Vidal A, Ozden S, et al. Lymphoid organs as a major reservoir for human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 in experimentally infected squirrel monkeys (Saimiri sciureus): provirus expression, persistence, and humoral and cellular immune responses.J Virol. 2000;74:4860–4867.
Gessain A, Louie A, Gout O, Gallo RC, Franchini G. Human T-cell leukemia-lymphoma virus type I (HTLV-I) expression in fresh peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with tropical spastic paraparesis/HTLV-I-associated myelopathy.J Virol. 1991;65:1628–1633.
Gabet AS, Mortreux F, Talarmin A, et al. High circulating proviral load with oligoclonal expansion of HTLV-1 bearing T cells in HTLV-1 carriers with strongyloidiasis.Oncogene. 2000;19:4954–4960.
Cavrois M, Leclercq I, Gout O, Gessain A, Wain-Hobson S, Wattel E. Persistent oligoclonal expansion of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1-infected circulating cells in patients with tropical spastic paraparesis/HTLV-1 associated myelopathy.Oncogene. 1998;17:77–82.
Hayashi J, Kishihara Y, Yoshimura E, et al. Correlation between human T cell lymphotropic virus type-1 andStrongyloides stercoralis infections and serum immunoglobulin E responses in residents of Okinawa, Japan.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1997;56:71–75.
Clarke MF, Trainor CD, Mann DL, Gallo RC, Reitz MS. Methylation of human T-cell leukemia virus proviral DNA and viral RNA expression in short- and long-term cultures of infected cells.Virology. 1984;135:97–104.
Datta S, Kothari NH, Fan H. Induction of Tax i expression in MT-4 cells by 5-azacytidine leads to protein binding in the HTLV-1 LTR in vivo.Virology. 2001;283:207–214.
Koiwa T, Hamano-Usami A, Ishida T, et al. 5′-long terminal repeatselective CpG methylation of latent human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 provirus in vitro and in vivo.J Virol. 2002;76:9389–9397.
Goon PK, Hanon E, Igakura T, et al. High frequencies of Th1-type CD4(+) T cells specific to HTLV-1 Env and Tax proteins in patients with HTLV-1-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis.Blood. 2002;99:3335–3341.
Hanon E, Hall S, Taylor GP, et al. Abundant tax protein expression in CD4+ T cells infected with human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I (HTLV-I) is prevented by cytotoxic T lymphocytes.Blood. 2000;95:1386–1392.
Jacobson S, Raine CS, Mingioli ES, McFarlin DE. Isolation of an HTLV-1-like retrovirus from patients with tropical spastic paraparesis.Nature. 1988;331:540–543.
Nagai M, Kubota R, Greten TF, Schneck JP, Leist TP, Jacobson S. Increased activated human T cell lymphotropic virus type I (HTLV-I) Tax11-19-specific memory and effector CD8+ cells in patients with HTLV-I-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis: correlation with HTLV-I provirus load.J Infect Dis. 2001;183:197–205.
Asquith B, Hanon E, Taylor GP, Bangham CR. Is human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I really silent?Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2000;355:1013–1019.
Hanon E, Stinchcombe JC, Saito M, et al. Fratricide among CD8(+) T lymphocytes naturally infected with human T cell lymphotropic virus type I.Immunity. 2000;13:657–664.
Hanon E, Asquith RE, Taylor GP, Tanaka Y, Weber JN, Bangham CR. High frequency of viral protein expression in human T cell lymphotropic virus type 1-infected peripheral blood mononuclear cells.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2000;16:1711–1715.
Kubota R, Furukawa Y, Izumo S, Usuku K, Osame M. Degenerate specificity of HTLV-I-specific CD8+ T cells during viral replication in patients with HTLV-I-associated myelopathy (HAM/TSP).Blood. 2003;101:3074–3081.
Lim DG, Bieganowska BK, Freeman GJ, Hafler DA. Examination of CD8+ T cell function in humans using MHC class I tetramers: similar cytotoxicity but variable proliferation and cytokine production among different clonal CD8+ T cells specific to a single viral epitope.J Immunol. 2000;165:6214–6220.
Feuerstein N, Firestein R, Aiyar N, He X, Murasko D, Cristofalo V. Late induction of CREB/ATF binding and a concomitant increase in cAMP levels in T and B lymphocytes stimulated via the antigen receptor.J Immunol. 1996;156:4582–4593.
Ego T, Ariumi Y, Shimotohno K. The interaction of HTLV-1 Tax with HDAC1 negatively regulates the viral gene expression.Oncogene. 2002;21:7241–7246.
Sasada T, Nakamura H, Masutani H, et al. Thioredoxin-mediated redox control of human T cell lymphotropic virus type I (HTLV-I) gene expression.Mol Immunol. 2002;38:723–732.
Kamada N, Sakurai M, Miyamoto K, et al. Chromosome abnormalities in adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma: a karyotype review committee report.Cancer Res. 1992;52:1481–1493.
Mortreux F, Leclercq I, Gabet AS, et al. Somatic mutation in human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 provirus and flanking cellular sequences during clonal expansion in vivo.J Natl Cancer Inst. 2001;93:367–377.
Tsukasaki K. Genetic instability of adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma by comparative genomic hybridization analysis.J Clin Immunol. 2002;22:57–63.
Niewiesk S, Daenke S, Parker CE, et al. The transactivator gene of human T-cell leukemia virus type I is more variable within and between healthy carriers than patients with tropical spastic paraparesis.J Virol. 1994;68:6778–6781.
Furukawa Y, Kubota R, Tara M, Izumo S, Osame M. Existence of escape mutant in HTLV-I tax during the development of adult T-cell leukemia.Blood. 2001;97:987–993.
Morozov VA, Lagaye S, Taylor GP, Matutes E, Weiss RA. Chimeric matrix proteins encoded by defective proviruses with large internal deletions in human T-cell leukemia virus type 1-infected humans.J Virol. 2000;74:3933–3940.
Ohshima K, Kikuchi M, Masuda Y, et al. Defective provirus form of human T-cell leukemia virus type I in adult T-cell leukemia/ lymphoma: clinicopathological features.Cancer Res. 1991;51:4639–4642.
Okazaki S, Moriuchi R, Yosizuka N, et al. HTLV-1 proviruses encoding non-functional TAX in adult T-cell leukemia.Virus Genes. 2001;23:123–135.
Tamiya S, Matsuoka M, Etoh K, et al. Two types of defective human T-lymphotropic virus type I provirus in adult T-cell leukemia.Blood. 1996;88:3065–3073.
Drexler HG. Review of alterations of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors INK4 family genes p15, p16, p18 and p19 in human leukemia-lymphoma cells.Leukemia. 1998;12:845–859.
Fujiwara H, Arima N, Hashimoto-Tamaoki T, et al. Alteration of p16 (CDKN2) gene is associated with interleukin-2-induced tumor cell growth in adult T cell leukemia.Exp Hematol. 1999;27:1004–1009.
Hatta Y, Hirama T, Miller CW, Yamada Y, Tomonaga M, Koeffler HP. Homozygous deletions of p15 (MTS2) and p16 (CDKN2/MTS1) genes in adult T-cell leukemia.Blood. 1995;85:2699–2704.
Hatta Y, Koeffler HP. Role of tumor suppressor genes in the development of adult T cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATLL).Leukemia. 2002;16:1069–1085.
Hoffman PM, Dhib-Jalbut S, Mikovits JA, et al. Human T-cell leukemia virus type I infection of monocytes and microglial cells in primary human cultures.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992;89:11784–11788.
Nosaka K, Maeda M, Tamiya S, Sakai T, Mitsuya H, Matsuoka M. Increasing methylation of the CDKN2A gene is associated with the progression of adult T-cell leukemia.Cancer Res. 2000;60:1043–1048.
Pombo-de-Oliveira MS, Dobbin JA, Loureiro P, et al. Genetic mutation and early onset of T-cell leukemia in pediatric patients infected at birth with HTLV-I.Leuk Res. 2002;26:155–161.
Trovato R, Cereseto A, Takemoto S, et al. Deletion of the p16INK4A gene inex vivo acute ATLL cells and methylation of p16INK4A promoter in HTLV-I-infected T-cell lines.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2000;16:709–713.
Hatta Y, Yamada M, Tomonaga M, Koeffler HP. Extensive analysis of the retinoblastoma gene in adult T cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATL).Leukemia. 1997;11:984–989.
Sakashita A, Hattori T, Miller CW, et al. Mutations of the p53 gene in adult T-cell leukemia.Blood. 1992;79:477–480.
Takemoto S, Trovato R, Cereseto A, et al. p53 stabilization and functional impairment in the absence of genetic mutation or the alteration of the p14(ARF)-MDM2 loop in ex vivo and cultured adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma cells.Blood. 2000;95:3939–3944.
Ohshima K, Haraoka S, Yoshioka S, et al. Mutation analysis of mitotic checkpoint genes (hBUB1 and hBUBR1) and microsatellite instability in adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma.Cancer Lett. 2000;158:141–150.
Mori N, Yamada Y, Hata T, et al. Expression of survivin in HTLVI- infected T-cell lines and primary ATL cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001;282:1110–1113.
Mori N, Inoue H, Yoshida T, Tanabe T, Yamamoto N. Constitutive expression of the cyclooxygenase-2 gene in T-cell lines infected with human T cell leukemia virus type I.Int J Cancer. 2001;94:813–819.
Takemoto S, Mulloy JC, Cereseto A, et al. Proliferation of adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma cells is associated with the constitutive activation of JAK/STAT proteins.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997;94:13897–13902.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Franchini, G., Fukumoto, R. & Fullen, J.R. T-Cell Control by Human T-Cell Leukemia/Lymphoma Virus Type 1. Int J Hematol 78, 280–296 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02983552
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02983552