Abstract
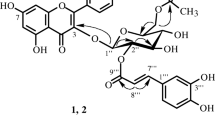
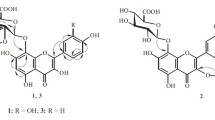
From the EtOAc fraction of the MeOH extract ofAlbizzia julibrissin (Leguminosae), a rare 5-deoxyflavone (geraldone,1), isookanin (2), luteolin (3), an isoflavone (daidzein,4), five preny-lated flavonoids [sophbflavescenol (5), kurarinone (6), kurarinol (7), kuraridin (8) and kuraridinol (9)], a cerebroside (soya-cerebroside I,10), and (-)-syringaresinol-4-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (11) were isolated and characterized on the basis of spectral data. Compounds2, 3, and11, showed 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl radical scavenging activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrawal, P. K. and Bansal, M. C., Isoflavonoids, in Agrawal, P. K. (ed.),Carbon-13 NMR of flavonoids. Elsevier, New York, pp. 184–214 (1989).
Blois, M. S., Antioxidant determination by the use of a stable free radical.Nature, 181, 1199–1200 (1958).
Clark-Lewis, J. W. and Porter, L. J., Phytochemical survey of the heartwood flavonoids ofAcacia species from arid zones of Austalia.Aust. J. Chem., 25, 1943–1945 (1972).
Foo, L. Y., Configuration and conformation of dihydroflavonols fromAcacia melanoxylon.Phytochemistry, 26, 813–817 (1987).
Higuchi, H., Kinjo, J., and Nohara, T., An arrhythmic-inducing glycoside fromAlbizzia julibrissin Durazz. IV.Chem. Pharm. Bull., 40, 829–831 (1992).
Inagaki, M., Harada, Y., Yamada, K., Isobe, R., Higuchi, R., Matsuua, H., and Itakura, Y., Isolation and structure determination of cerebrosides from garlic, the bulbs ofAllium sativum L.Chem. Pharm. Bull., 46, 1153–1156 (1998).
Inoue, T., Sakurai, N., Nagai, S., and Nagai, M., Studies on the constituents of Aceraceae plants (X). Isolation of flavonoids glycosides and a cerebroside from the leaves of Acer negundo.Shoyakugaku Zasshi, 46, 26–264 (1992).
Ito, S., Ohnishi, M., and Fujino, Y., Investigation of sphingolipids in pea seeds.Agric. Biol. Chem., 49, 539–540 (1985).
Jung, J. H., Lee, C.-O., Kim, Y. C., and Kang, S. S., New bioactive cerebrosides fromArisaema amurense.J. Nat. Prod., 59, 319–322 (1996).
Jung, M. J., Chung, H. Y., and Choi, J. S., Antioxidant activity of roasted defattedPerilla seed.Nat. Prod. Sci., 7, 72–75 (2001).
Jung, M. J., Chung, H. Y., Kang, S. S., Choi, J. H., Bae, K. S., and Choi, J. S., Antioxidant activity from the stem bark ofAlbizzia julibrissin.Arch. Pharm. Res., 26, 458–462 (2003).
Kang, S. S., Kim, J. S., Son, K. H., Kim, H. P., and Chang, H. W., Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitory cerebrosides from Phytolaccae radix.Chem. Pharm. Bull., 49, 321–323 (2001).
Kim, J. S., Byun, J. H., and Kang, S. S., Isolation of soya-cerebroside I from the roots ofTrichosanthes kirilowii.Nat. Prod. Sci., 7, 27–32 (2001).
Kim, T. J.,Korean Resources Plants. II. Seoul National University Press, Korea, pp. 194–195 (1996).
Kinjo, J., Fukui, K., Higuchi, H., and Nohara, T., The first isolation of lignan tri-and tetra-glycosides.Chem. Pharm. Bull., 39, 1623–1625 (1991a).
Kinjo, J., Higuchi, H., Fukui, K., and Nohara, T., Lignoids from Albizziae cortex. II. A biodegradation pathway of syringaresinol.Chem. Pharm. Bull., 39, 2952–2955 (1991b).
Kyogoku, K., Hatayama, K., and Komatsu, M., Constituents of Chinese crude drug “Kushen” (the root ofSophora flavescens Ait.). Isolation of five new flavonoids and formononetin.Chem. Pharm. Bull., 21, 2733–2738 (1973).
Lopes, J. L. C., Lopes, J. N. C., and Leitao Filho, H. F., 5-Deoxyflavones from the Vochysiaceae.Phytochemistry, 18, 362 (1979).
Mabry, T. J., Markham, K. R., and Thomas, M.,The systematic identification of flavonoids. Springer, Berlin (1970).
Markham, K. R.,Techniques of flavonoid identification. Academic press, London, (1982).
Ngadjui, B. T., Dongo, E., Abegaz, B. M., Fotso, S., and Tamboue, H., Dinklagins A, B and C: three prenylated flavonoids and other constituents from the twigs ofDorstenia dinklagei.Phytochemistry, 61, 99–104 (2002).
Ohnishi, M. and Fujino, Y., Chemical composition of ceramide and cerebroside in Azuki bean seeds.Agric. Biol. Chem., 45, 1283–1284 (1981).
Okuyama, E. and Yamazaki, M., The principles ofTetragonia tetragonoides having anti-ulcerogenic activity. II. Isolation and structure of cerebrosides.Chem. Pharm. Bull., 31, 2209–2219 (1983).
Ryu, S. Y., Lee, H. S., Kim, Y. K., and Kim, S. H., Determination of isoprenyl and lavandulyl positions of flavonoids from Sophora flavescens by NMR experiment.Arch. Pharm. Res., 20, 491–495 (1997).
Ryu, S. Y., Kim, S.-K., No, Z., and Ahn, J. W., A novel flavonoid fromSophora flavescens.Planta Med., 62, 361–363 (1996).
Shibuya, H., Kawashima, K., Sakagami, M., Kawanishi, H., Shimomura, M., Ohashi, K., and Kitagawa, I., Sphingolipids and glycerolipids. I. Chemical structures and ionophoretic activities of soya-cerebrosides I and II from soybean.Chem. Pharm. Bull., 38, 2933–2938 (1990).
Voutquenne, L., Lavaud, C., Massiot, G., Sevenet, T., and Hadi, H. A., Cytotoxic polyisoprenes and glycosides of long-chain fatty alcohols fromDimocarpus fumatus.Phytochemistry, 50, 63–69 (1999).
Watanabe, M., Antioxidative phenolic compounds from Japanese barnyard millet (Echinochloa utilis) grains.J. Agric. Food Chem., 47, 4500–4505 (1999).
Wong, E. and Francis, C. M., Flavonoids in genotypes ofTrifolium subterraneum L.Phytochemistry, 7, 2123–2129 (1968).
Woo, E. R., Kwak, J. H., Kim, H. J., and Park, H. K., A new prenylated flavonol from the roots ofSophora flavescens.J. Nat. Prod., 61, 1552–1554 (1998).
Xiao, Z.-Y., Chen, K.-H., and Si, J.-Y., Studies on the chemical constituents fromMomordica charantia. Chin. Trad.Herbal Drug (Zhongcaoyao), 31, 571–573 (2000).
Yoshioka, A., Etoh, H., Yagi, A., Sakata, K., and Ina, K., Isolation of flavonoids and cerebrosides from the bark ofPrunus jamasakura as repellents against the blue mussel,Mytilus edulis.Agric. Biol. Chem., 54, 3355–3356 (1990).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jung, M.J., Kang, S.S., Jung, H.A. et al. Isolation of flavonoids and a cerebroside from the stem bark ofAlbizzia julibrissin . Arch Pharm Res 27, 593–599 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02980155
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02980155