Abstract
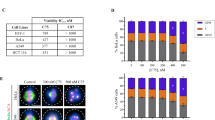
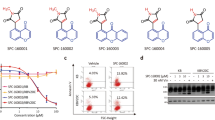
SJ compounds (SJ8002 and related compounds) are a group of novel anticancer agents (Cho, Chung, Lee, Kwon, Kang, Joo, and Oh. PCT/KR02/00392). To explore the anticancer mechanism of these compounds, we examined the effect of SJ8002 on microtubules of six human cell lines. At a high concentration (2 μg/mL), SJ8002 effectively disrupted microtubules of the six cell lines within 1 h. At lower concentrations (0.05~1.0 μg/mL), the antimicrotubule activity of SJ8002 varied defending on cell lines. The inhibition ofin vitro polymerization of pure tubulin by SJ8002 suggested that SJ8002 acts on free tubulin, inhibits the polymerization of tubulin dimer into microtubules, and hence induces the depolymerization of microtubules.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barbier, P., Gregoire, C., Devred, F., Sarrazin, M., and Peyrot, V.,In vitro effect of cryptophycin 52 on microtubule assembly and tubulin: Molecular modeling of the mechanism of action of a new antimitotic drug.Biochemisry, 40, 13510–13519 (2001).
Cho, E.-H., Chung, S. G., Lee, S. H., Kwon, H. S., Kang, D. W., Joo, J. H., and Oh, J. W., 9-Anminoacridine derivatives and process for the preparation Thereof. PCT/KR02/00392, March, 2002.
Choudhury, G. G., Maity, S., Bhattacharyya, B., and Biswas, B. B., B-ring of colchicines and its role in taxol-induced tubulin polymerization.FEBS Lett., 197, 31–34 (1986).
Combeau, C., Provost, J., Lancerin, F., Toumoux, Y., Prodhomme, F., Herman, F., Lavelle, F., Leboul, J., and Vuilhorgne, M., RPR112378 and RPR115781: Two representatives of a new family of microtubule assembly inhibitors.Mol. Pharm., 57, 553–563 (2000).
Gottsman, M. M., Fojo, T., and Bates, S. E., Multidrug resistance in cancer: role of ATP-dependent transporters.Nat. Rev. Cancer, 2, 48–58 (2002).
Gottsman, M. M., Pastan, I., and Ambudkar, S. V., P-glycoprotein and multidrug resistance.Curr. Op. Genet. Dev., 6, 610–617 (1996).
Hartley-Asp, B. and Gunnarsson, P. O., Growth and cell survival following treatment with estramucin, nor-nitrogen mustard, esteadiol and testosterone of a human prostate cancer cell line (DU145).J. Urol., 127, 818–822 (1982).
Jordan, A., Hadfield, J. A., Lawrence, N. J., and McGown, A. T., Tubulin as a target for anticancer drugs: Agents which interact with the mitotic spindle.Med. Res. Rev., 18, 259–296 (1998).
Jordan, M. A. and Wilson, L., Microtubules and actin filaments: dynamic targets for cancer chemotherapy.Curr. Op. Cell Biol., 10, 123–130 (1998).
Kruczynski, A. and Hill, B. T., Vinflunine, the latest Vinca alkaloid in clinical development. A review of its preclinical anticancer properties.Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol., 40, 159–173 (2001).
Meyer, T. U., Kapoor, T. M., Haggarty, S. J., King, R. W., Schreiber, S. L., and Mitchison, T. J., Small molecule inhibitor of mitotic spindle bipolarity identified in a phenotype-based screen.Science, 286, 913–914 (1999).
Murphy, D. B., Punction of tubulin isoforms.Curr. Op. Cell Biol., 3, 43–51 (1991).
Nogales, E., Structral insights into microtubule function.Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct., 30, 397–420 (2001).
Raff, E. C., The role of multiple tubulin isoforms in cellular microtubule function. Microtubules, pp 85–109, Modern Cell Biology Vol. 13. Hyams J. S. and Lloyd C. W. (Ed). Wiley-Liss, Inc. New York (1994).
Sakowicz, R., Berdelis, M. S., Ray, K., Blackburn, C. L., Hopmann, C., Faulkner, D. J., and Goldstein, L. S. B., A marine natural product inhibitor of kinesin motors.Science, 280, 292–295 (1998).
Shan, B., Medina, J. C., Santha, E., Frankmoelle, W. P., Chou, T.-C., Learned, R. M., Narbut, M. R., Stott, D., Wu, P., Jaen, J. C., Rosen, T., Timmermans, P. B. M. W. M., and Beckmann, H., Selective, covalent modification of -tubulin residue Cys-239 by T138067, an antitumor agent within vivo efficacy against multidrug-resistant tumors.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 96, 5686–5691 (1999).
Smith, C. D. and Zhang, X., Mechanism of action of cryptophycin.J. Biol. Chem., 271, 6192–6198 (1996).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, J.H., Kang, D.W., Kwon, H.S. et al. Microtubule inhibitory effects of various SJ compounds on tissue culture cells. Arch Pharm Res 27, 436–441 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02980086
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02980086