Abstract
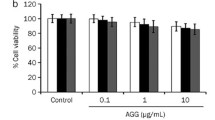
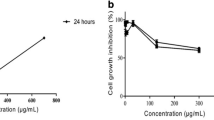
Mistletoe lectin has been reported to induce apoptosis in different cancer cell linesin vitro and to show antitumor activity against a variety of tumors in animal models. We previously demonstrated the Korean mistletoe lectin (Viscum album var.coloratum, VCA)-induced apoptosis by down-regulation of Bcl-2 and telomerase activity and by up-regulation of Bax through p53- and p21-independent pathway in hepatoma cells. In the present study, we observed the induction of apoptotic cell death through activation of caspase-3 and the inhibition of telomerase activity through transcriptional down-regulation of hTERT in the VCA-treated A253 cells. We also observed the inhibition of telomerase activity and induction of apoptosis resulted from dephosphorylation of Akt in the survival signaling pathways. In addition, combining VCA with the inhibitors of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3-kinase) upstream of Akt, wortmannin and LY294002 showed an additive inhibitory effect of telomerase activity. In contrast, the inhibitor of protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A), okadaic acid inhibited VCA-induced dephosphorylation of Akt and inhibition of telomerase activity. Taken together, VCA induces apoptotic cell death through Akt signaling pathway in correlated with the inhibition of telomerase activity and the activation of caspase-3. From these results, together with our previous studies, we suggest that VCA triggers molecular changes that resulting in the inhibition of cell growth and the induction of apoptotic cell death of cancer cells, which suggest that VCA may be useful as chemotherapeutic agent for cancer cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akiyama M., Hideshima T., Hayashi T., Tai Y. T., Mitsiades C. S., Mitsiades N., Chauhan D., Richardson P., Munshi N. C., and Anderson K. C., Nuclear factor-kappaB p65 mediates tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced nuclear translocation of telomerase reverse transcriptase protein.Cancer Res., 63, 18–21 (2003).
Bantel, H., Engels, I. H., Voelter, W., Schulze-Osthoff, K., and Wesselborg, S., Mistletoe lectin activates caspase-8/FLICE independently of death receptor signaling and enhances anticancer drug-induced apoptosis.Cancer Res., 59, 2083–2090 (1999).
Bellacosa, A., Chan, T. O., Ahmed, N. N., Datta, K., Malsrom, S., Stokoe, D., McCormick, F., Feng, J., and Tsichlis, P., Akt activation by growth factors is a multiple-step process: The role of the PH domain.Oncogene, 17, 313–325 (1998).
Breitschopf, K., Zeiher, A. M., and Dimmeler, S., Pro-atherogenic factors induce telomerase inactivation in endothelial cells through an Akt-dependent mechanism.FEBS Lett., 493, 21–25 (2001).
Brunet, A., Bonni, A., Zigmond, M. J., Lin, M. Z., Juo, P., Hu, L. S., Anderson, M. J., Arden, K. C., Blenis, J., and Greenberg, M. E., Akt promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead transcription factor.Cell, 96, 857–868 (1999).
Bussing, A., Suzar, K., Bergmann, J., Pfüller, U., Schietzel, M., and Schweizer, K., Induction of apoptosis in human lymphocytes treated withViscum album L. is mediated by the mistletoe lectins.Cancer Lett., 99, 59–72 (1996).
Bussing, A., Multani, A. S., Pathak, S., Pfüller, U., and Schietzel, M., Induction of apoptosis by theN-acetylgalactosamine-specific toxic lectin fromViscum album L is associated with a decrease of nuclear p53 and Bcl-2 proteins and induction otelomeric associations.Cancer Lett., 130, 57–68 (1998).
Bussing, A., Biological and pharmacological properties ofViscum album L; From tissue flask to man. In A. Büssing (eds.), Mistletoe, genus Viscum & other genera, Medicinal and aromatic plantslndustrial profiles. Harwood Academic Publishers, Netherland, pp 45–60 (2000).
Cardone, M. H., Roy, N., Stennicke, H. R., Salvesen, G. S., Franke, T. F., Stanbridge, E., Frisch, S., and Reed, J. C., Regulation of cell death protease caspase-9 by phosphorylation.Science, 282, 318–321 (1998).
Choi, S. H., Kang, H. K., Im, E. O., Kim, Y. J., Bae, Y. T., Choi, Y. H., Lee, K. H., Chung, H. Y., Chang, H. K., and Kim, N. D., Inhibition of cell growth and telomerase activity of breast cancer cellsin vitro by retinoic acids.Int. J. Oncol., 17, 971–976 (2000).
Counter, C. M., Avilion, A. A., LeFeuvre, C. E., Stewart, N. G., Greider, C. W., Harley, C. B., and Bacchetti, S., Telomere shortening associated with chromosome instability in immortal cells which express telomerase activity.EMBO J., 11, 1921–1929 (1992).
Datta, S. R., Dudek, H., Tao, X., Masters, S., Fu, H., Gotoh, Y., and Greenberg, M. E., Akt phosphorylation of Bad couples survival signals to the cell-intrinsic death machinery.Cell, 91, 231–241 (1997).
Datta, S. R., Brunet, A., and Greenberg, M. E., Cellular survival: a play in three Akts.Genes Dev., 13, 2905–2927 (1999).
Gjertsen, B. T. and Doskeland, S. O., Protein phosphorylation in apoptosis.Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1269, 187–199 (1995).
Herbert, B. S., Pitts, A. E., Baker, S. I., Hamilton, S. E., Wright, W. E., Shay, J. W., and Corey, D. R., Inhibition of human telomerase in immortal human cells leads to progressive telomere shortening and cell death.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 96, 14276–14281 (1999).
Kang, S. S., Kwon, T. G., Kwon, D. Y., and Do, S. I., Akt protein kinase enhances human telomerase activity through phosphorylation of telomerase reverse transcriptase subunit.J. Biol. Chem., 274, 13085–13090 (1999).
Kennedy, S. G., Wagner, A. J., Conzen, S. D., Jordan, J., Belacosa, A., Tsichlis, P. N., and Hay, N., The PI3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway delivers an anti-apoptotic signal.Genes Dev., 11, 701–713 (1997).
Kim, N. W., Piatyszek, M. A., Prowse, K. R., Harley, C. B., West, M. D., Ho, P. L., Coviello, G. M., Wright, W. E., Weinrich, S. L., and Shay, J. W., Specific association of human telomerase activity with immortal cells and cancer.Science, 266, 2011–2015 (1994).
Kim, M. S., So, H. S., Lee, K. M., Park, J. S., Lee, J. H., Moon, S. K., Ryu, D. G., Chung, S. Y., Jung, B. H., Kim, Y. K., Moon, G., and Park, R., Activation of caspase cascades in Korean mistletoe (Viscum album var.coloratum) lectin-ll-induced apoptosis of human myeloeukemic U937 cells.Gen. Pharmacol., 34, 349–355 (2000).
Kondo, Y., Kondo, S., Tanaka, Y., Haqqi, T., barna, B. P., and Cowell, J. K., Inhibition of telomerase increases the susceptibility of human malignant glioblastoma cells to cisplatin-induced apoptosis.Oncogene, 16, 2243–2248 (1998).
Lyu, S. Y., Park, S. M., Choung, B. Y., and Park, W. B., Comparative study of Korean (Viscum album, var.coloratum) and European mistletoes (Viscum album).Arch. Pharm. Res., 23, 592–598 (2000).
Lyu, S. Y., Park, W. B., Choi, K. H., and Kim, W. H., Involvement of caspase-3 in apoptosis induced byViscum album var.coloratum agglutinin in HL-60 cells.Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem., 65, 534–541 (2001).
Lyu, S. Y., Choi S. H., and Park W. B., Korean mistletoe lectin-induced apoptosis in hepatocarcinoma cells is associated with inhibition of telomerasevia mitochondrial controlled pathway independent of p53.Arch. Pharm. Res., 25, 93–101 (2002).
Meier, R., Alessic, D. R., Cron, P., Andjelkovic, M., and Hemings, B. A., Mitogenic activation, phosphorylation, and nuclear translocation of protein kinase B beta.J. Biol. Chem., 272, 30491–30497 (1997).
Pae, H. O., Seo, W. G., Oh, G. S., Shin, M. K., Lee, H. S., Kim, S. B., and Chung, H. T., Potentiation of tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced apoptosis by mistletoe lectin.Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol., 22, 697–709 (2000).
Pae, H. O., Ohm, G. S., Kim, N. Y., Shin, M. K., Lee, H. S., Yun, Y. G., Oh, H., Kim, Y. M., and Chung, H. T., Roles of extracellular signal-regulated kinase and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in apoptosis of human monoblastic leukemia U937 cells by lectin-ll isolated from Korean mistletoe.In vitro Mol. Toxicol., 14, 99–106 (2001).
Ribereau-Gayon, G., Jung, M., Frantz, M., and Anton, R., Modulation of cytotoxicity and enhancement of cytokine release induced byViscum album L. extracts or mistletoe lectins.Anticancer Drugs, 8, S3–8 (1997).
Song, Q. and Lavin, M., Calyculin A., A potent inhibitor of phosphatasse-1 and 2A, prevenets apoptosis.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 190, 47–55 (1993).
Stein, G. M., Pfuller, U., Schietzel, M., and Bussing, A., Intracellular expression of IL-4 and inhibition of IFN-gamma by extracts from European mistletoe is related to induction of apoptosis.Anticancer Res., 20, 2987–2994 (2000).
Walzel, H., Blach, M., Neels, P., Schulz, U., Wollenhaupt, K., and Brock, J., The B-chain of mistletoe lectin I efficiently stimulates calcium signaling in human Jurkat T-cells.Immunol. Lett., 78, 57–66 (2001).
Yao, R. and Cooper, G. M., Requirement for phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase in the prevention of apoptosis by the nerve growth factor.Science, 267, 2003–2005 (1995).
Zha, J., Harada, H., Yang, E., Jockel, J., and Korsmeyer, S. J., Serine phosphorylation of death agonist Bad in response to survival factor results in binding to 14-3-3 not Bcl-xL.Cell, 87, 619–628 (1996).
Zhang, X., Mar, V., Zhou, W., Harrington, L., and Robinson, M. O., Telomere shortening and apoptosis in telomerase-inhibited human tumor cells.Genes Dev., 13, 2388–2399 (1999).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, S.H., Lyu, S.Y. & Park, W.B. Mistletoe lectin induces apoptosis and telomerase inhibition in human A253 cancer cells through dephosphorylation of akt. Arch Pharm Res 27, 68–76 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02980049
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02980049