Abstract
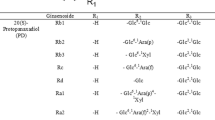
When ginseng water extract was incubated at 60°C in acidic conditions, its protopanaxadiol ginsenosides were transformed to ginsenoside Rg3 and ▵20-ginsenoside Rg3. However, protopanaxadiol glycoside ginsenosides Rb1, Rb2 and Rc isolated from ginseng were mostly not transformed to ginsenoside Rg3 by the incubation in neutral condition. The transformation of these ginsenosides to ginsenoside Rg3 and ▵20-ginsenoside Rg3 was increased by increasing incubation temperature and time in acidic condition: the optimal incubation time and temperature for this transformation was 5 h and 60°C resepectively. The transformed ginsenoside Rg3 and ▵20-ginsenoside Rg3 were metabolized to ginsenoside Rh2 and ▵20-ginsenoside Rh2, respectively, by human fecal microflora. Among the bacteria isolated from human fecal microflora,Bacteroides sp.,Bifidobacterium sp. andFusobacterium sp. potently transformed ginsenoside Rg3 to ginsenoside Rh2. Acid-treated ginseng (AG) extract, fermented AG extract, ginsenoside Rh2 and protopanaxadiol showed potent cytotoxicity against tumor cell lines. AG extract, fermented AG extract and protopanaxadiol potently inhibited the growth ofHelicobacter pylori.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akao, T., Kanaoka, M., and Kobashi, K., Appearance of compound K, a major metabolite of ginsenoside Rb1 by intestinal bacteria, in rat plasma after oral administrationmeasurement of compound K by enzyme immunoassay.Biol. Pharm. Bull., 21, 245–249 (1998).
Akao, T., Kida, H., Kanaoka, M., Hattori, M., and Kobashi, K., Intestinal bacterial hydrolysis is required for the appearance of compound K in rat plasma after oral administration of ginsenoside Rb1 from Panax ginseng.J. Pharm. Pharmacol., 50, 1155–1160 (1998).
Bae, E.-A., Park, S.-Y., and Kim, D.-H., Constitutive β-glucosidases hydrolyzing ginsenoside Rb1 and Rb2 from human intestinal bacteria.Biol. Pharm. Bull., 23, 1481–1485 (2000).
Bae, E. A., Han, M. J., Choo, M. K., Park, S. Y., and Kim, D. H., Metabolism of 20(S)- and 20(R)-ginsenoside Rg3 by human intestinal bacteria and its relation toin vitro biological activities.Biol. Pharm. Bull., 25, 58–63 (2002).
Carmichael, J., DeGreff, W. G., Gazdar, A. F., Minna, J. D., and Mitchell, J. B., Evaluation of a tetrazolium-based semiautomated colorimetric assay: Assessment of chemosensitivity testing.Cancer Res., 47, 936–940 (1987).
Han, B. H., Park, M. H., Han, Y. N., Woo, L. K., Sankawa, U., Yahara, S., and Tanaka, O., Degradation of ginseng saponins under mild acidic conditions.Planta Med., 44, 146–149 (1982).
Hasegawa, H., Sung, J.-H., and Benno, Y., Role of human intestinalPrevotella oris in hydrolyzing Ginseng saponins.Planta Med., 63, 436–440 (1997).
Kanaoka, M., Kato, H., Shimada, F., and Yano, S., Studies on the enzyme immunoassay of bioactive constituents contained in oriental medicinal drugs. VI. Enzyme immunoassay of ginsenoside Rb1 formPanax ginseng.Chem. Pharm. Bull., 40, 314–317 (1992).
Kanaoka, M., Akao, T., and Kobashi, K., Metabolism of ginseng saponins, ginsenosides, by human intestinal bacteria.J. Tradit. Med., 11, 241–245 (1994).
Karikura M., Miyaze T., Tanizawa H., Taniyzma T., and Takino Y., Studies on absorption, distribution, excretion and metabolism of ginseng saponins. VII. Comparison of the decomposition modes of ginsenoside Rb1 and Rb2 in the digestive tract of rats.Chem. Pharm. Bull., 39, 2357–2361 (1991).
Kitagawa, I., Yoshikawa, M., Yoshihara, M., Hayashi, T., and Taniyama, T., Chemical studies on crude drug precession. I. On the constituents of ginseng radix rubura (I).Yakugaku Zasshi, 103, 612–622 (1983).
Kown, S. W., Han, S. B., Park, I. H., Kim, J. M., Park, M. K., and Park, J. H., Liquid chromatographic determination of less polar ginsenosides in processed ginseng.J. Chromatogr. A, 921, 335–339 (2001)
Lee, S. J., Sung, J. H., Lee, S. J., Moon, C. K., and Lee, B. H., Antitumor activity of a novel ginseng saponin metabolite in human pulmonary adenocarcinoma cells resistant to cisplatin.Cancer Lett., 144, 39–43 (1999).
Mochizuki, M., Yoo, C. Y., Matsuzawa, K., Sato, K., Saiki, I., Tono-oka, S., Samukawa, K., and Azuma, I., Inhibitory effect of tumor metastasis in mice by saponins, ginsenoside Rb2, 20(R)- and 20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3, of Red ginseng.Biol. Pharm. Bull., 18, 1197–1202 (1995).
Sato, K., Mochizuki, M., Saiki, I., Yoo, Y. C., Samukawa K., and Azuma, I., Inhibition of tumor angiogenesis and metastasis by a saponin of Panax ginseng-ginsenoside Rb2.Biol. Pharm. Bull., 17, 635–639 (1994).
Shibata, S., Fujita, M., Itokawa, H., Tanaka, O., and Ishii, T., Panaxadiol, a sapogenin of ginseng roots (1).Chem. Pharm. Bull., 11, 759–764 (1963).
Tanaka, N., Tanaka, O., and Shibata, S., Chemical studies on the oriental plant drugs. XXVIII. Saponins and sapogenins of ginseng; Stereochemistry of sapogenin of ginsenoside Rb1, Rb2 and Rc.Chem. Pharm. Bull., 20, 1212–1216 (1972).
Wakabayashi, C., Hasegawa, H., Murata, J., and Saiki, I.,In vivo antimetastatic action of ginseng protopanaxadiol saponins is based on their intestinal bacterial metabolites after oral administration.Oncol. Res., 9, 411–417 (1998).
Wu, J. Y., Gardner, B. H., Murphy, C. I., Seals, J. R., Kensil, C. R., Recchia, J., Beltz, G. A., Newman, G. W., and Newman, M. J., Saponin adjuvant enhancement of antigen-specific immune responses to an experimental HIV-1 vaccine.J. Immunol., 148, 1519–1525 (1992).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bae, EA., Han, M.J., Kim, EJ. et al. Transformation of ginseng saponins to ginsenoside rh2 by acids and human intestinal bacteria and biological activities of their transformants. Arch Pharm Res 27, 61–67 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02980048
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02980048