Abstract
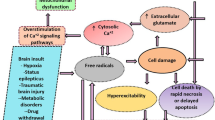
The inhibitory effects of the constituents ofGastrodia elata Bl. (GE) on glutamate-induced apoptosis in human neuronal cells were investigated using IMR32 human neuroblastoma cells. Glutamate (GLU) induced DNA fragmentation, a hallmark of apoptosis, in a dose-dependent manner. GLU also induced a slow and sustained increase in intracellular Ca2+ concentration. Treatment with EGTA, an extracellular Ca2+ chelator, in a nominal Ca2+-free buffer solution abolished the GLU-induced intracellular Ca2+ increase, indicating that GLU stimulated Ca2+ influx pathway in the IMR32 cells. BAPTA, an intracellular Ca2+ chelator, significantly inhibited the GLU-induced apoptosis assessed by the flow cytometry measuring hypodiploid DNA content indicative of apoptosis, implying that intracellular Ca2+ rise may mediate the apoptotic action of GLU. Vanillin (VAN) and p-hydroxybenzaldehyde(p-HB), known constituents of GE, significantly inhibited both intracellular Ca2+ rise and apoptosis induced by GLU. These results suggest that the apoptosis-inhibitory actions of the constituents of GE may account, at least in part, for the basis of their antiepileptic activities. These results further suggest that intracellular Ca2+ signaling pathway may be a molecular target of the constituents of GE.
Similar content being viewed by others
References Cited
Andersson, M., Bergendorff, O., Nielsen, M., Sterner, O., Witt, R., Ai, J., Lu, A. and Wang, A. M., Inhibi-tion of kainic acid binding to glutamate receptors by extracts ofGastrodia.Phytochemistry, 38, 835–836 (1995).
Bengzon, J., Kokaia, Z., Elmer, E., Nanobashvili, A., Kokaia, M. and Lindvall, O., Apoptosis and proliferation of dentate gyrus neurons after single and intermittent limbic seizures.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 94, 10432–10437 (1997).
Bittigau, P, and Ikonomidou, C., Glutamate in neuro-logic diseases.J. Child. Neurol., 12, 471–485 (1997).
Bombeli, T., Karsan, A., Tait, J. F. and Harlan, J. M., Apoptotic vascular endothelial cells become procoagulant.Blood, 89, 2429–2442 (1997).
Carriedo, S. G., Yin, H. Z., Sensi, S. L. and Weiss, J. H., Rapid Ca2+ entry through Ca2+-permeable AMPA/Kainate channels triggers marked intracellular Ca2+ rises and consequent oxygen radical production.J. Neurosci., 18, 7727–7738 (1998).
Choi, D. W., Methods for antagonizing glutamate neurotoxicity.Cerebrovasc. Brain Metab. Rev., 2, 105–147 (1990).
Du, Y., Bales, K. R., Dodel, R. C., Hamilton-Byrd, E., Horn, J. W., Czilli, D. L., Simmons, L. K., Ni, B. and Paul, S. M., Activation of a caspase 3-related cys-teine protease is required for glutamate-mediated apoptosis of cultured cerebellar granule neurons.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 94, 11657–11662 (1997).
Erdelyi, L., Vanillin modulates the fast outward and calcium currents in Helix neurons.Acta Biol. Hung., 43, 15–24 (1992).
Facchinetti, F., Dawson, V. L. and Dawson, T. M., Free radicals as mediators of neuronal injury.Cell. Mol. Neurobiol., 18, 667–682 (1998).
Friedman LK., Selective reduction of GluR2 protein in adult hippocampal CA3 neurons following status epilepticus but prior to cell loss.Hippocampus, 8, 511–525 (1998).
Grynkiewicz, G., Poene, M. and Tsien, R. Y., A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties.J. Biol. Chem., 260, 3440–3450 (1985).
Hockenbery, D., Nunez, G., Milliman, C., Schreiber, R. D. and Korsmeyer, S. J., Bcl-2 is an inner mitochondrial membrane protein that blocks programmed cell death.Nature 348, 334–336 (1990).
Hoyal, C. R., Thomas, A. P. and Forman, H. J., Hydroperoxide-induced increases in intracellular calcium due to annexin VI translocation and in-activation of plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase.J. Biol. Chem., 271, 29205–29210 (1996).
Hsieh, M. T., Wu, C. R. and Chen, C. F., Gastrodin and p-hydroxybenzyl alcohol facilitate memory consoli-dation and retrieval, but not acquisition, on the passive avoidance task in rats.J. Ethnopharmacol., 56, 45–54 (1997).
Huh, K., Kim, J.-S., Kwon, T.-H., Kim, J.-A., Yong, C.-S., Ha, J.-H. and Lee, D.-U., The mechanism of anticonvulsive effect on the rhizoma ofGastrodia elata in pentylenetetrazole treated rats.Yakhak Hoeji, 42, 330–335 (1998).
Kabuto, H., Yokoi, I. and Ogawa, N., Melatonin inhibits iron-induced epileptic discharges in rats by suppressing peroxidation.Epilepsia, 39, 237–243 (1998).
Kidd, V. J., Proteolytic activities that mediate apoptosis.Annu. Rev. Physiol., 60, 533–573 (1998).
Kim, J.-A., Kang, Y. S., Kim, Y. O., Lee, S. H. and Lee, Y. S., Role of Ca2+ influx in the tert-hydroperoxide-induced apoptosis of HepG2 human hepatoblastoma cells.Exp. Mol. Med., 30, 137–144 (1998).
Kim, J.-A., Huh, K. and Lee, Y. S., The mechanism of oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in IMR32 human neuroblastoma cells.Kor. J. Physiol. Pharmacol., 3, 19–27 (1999).
Lasley, S. M. and Yan, Q. S., Diminished potassium-stimulated GABA release in vivo in genetically epilepsyprone rats.Neurosci. Lett., 175, 145–148 (1994).
Leist, M. and Nicotera, P., Calcium and neuronal death.Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol., 132, 79–125 (1998).
Liu, J. and Mori, A., Antioxidant and free radical scavenging activities ofGastrodia elata Bl. andUncaria rhynchophylla (Miq.) Jacks.Neuropharmacology, 31, 1287–1298 (1992).
Liu, J. and Mori, A., Antioxidant and pro-oxidant activities of p-hydroxybenzyl alcohol and vanillin: effects on free radicals, brain peroxidation and degradation of benzoate, deoxyribose, amino acids and DNA.Neuropharmacology, 32, 659–669 (1993).
Lores Arnaiz, S., Travacio, M., Llesuy, S. and Rodriguez de Lores Arnaiz, G., Regional vulnerability to oxidative stress in a model of experimental epilepsy.Neurochem. Res., 23, 1477–1483 (1998).
McConkey, D. J. and Orrenius, S., The role of calcium in the regulation of apoptosis.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 239, 357–366 (1997).
Meldrum, B. S., Excitotoxicity and selective, neuronal loss in epilepsy.Brain Pathol., 3, 405–412 (1993).
Morimoto, K., Sato, H., Yamamoto, Y., Watanabe, T. and Suwaki, H., Antiepileptic effects of tiagabine, a selective GABA uptake inhibitor, in the rat kindling model of temporal lobe epilepsy.Epilepsia, 38, 966–974 (1997).
Petroff, O. A., Hyder, F., Mattson, R. H. and Rothman, D. L., Topiramate increases brain GABA, homocarno-sine, and pyrrolidinone in patients with epilepsy.Neurology, 52, 473–478 (1999).
Pollard, H., Charriaut-Marlangue, C., Cantagrel, S., Represa, A., Robain, O., Moreau, J. and Ben-Ari, Y., Kainate-induced apoptotic cell death in hippocampal neurons.Neuroscience, 63, 7–18 (1994).
Sigel, E., Baur, R., Netzer, R. and Rundfeldt C., The antiepileptic drug AWD 131–138 stimulates different recombinant isoforms of the rat GABA(A) receptor through the benzodiazepine binding site.Neurosci. Lett., 245, 85–88 (1998).
Tan, S., Sagara, Y., Liu, Y., Maher, P. and Schubert, D., The regulation of reactive oxygen species production during programmed cell death.J. Cell. Biol., 141, 1423–1432 (1998).
Troyer, M. D., Blanton, M. G. and Kriegstein, A. R., Abnormal action-potential bursts and synchronized, GABA-mediated inhibitory potentials in an in vitro model of focal epilepsy.Epilepsia, 33, 199–212 (1992).
Wu, H. Q., Xie, L., Jin, X. N., Ge, Q., Jin, H. and Liu, G. Q., The effect of vanillin on the fully amygdala-kindled seizures in the rat.Yao Hsueh Hsueh Pao 24, 482–486 (1989).
Wyllie, A. H., Morris, R. G., Smith, A. L. and Dunlop, D., Chromatin cleavage in apoptosis: Association with condensed chromatin morphology and dependence on macromolecular synthesis.J. Pathol., 142, 67–67 (1984).
Yun-Choi, H. S., Pyo, M. K. and Park, K. M., Isolation of 3-O-(4′-hydroxybenzyl)-beta-sitosterol and 4-[4′-(4″-hydroxybenzyloxy)benzyloxy]benzyl methyl ether from fresh tubers of Gastrodia elata.Arch. Pharm. Res., 21, 457–360 (1998).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, Y.S., Ha, JH., Yong, C.S. et al. Inhibitory effects of constituents ofGastrodia elata Bl. on glutamate-induced apoptosis in IMR-32 human neuroblastoma cells. Arch Pharm Res 22, 404–409 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02979066
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02979066