Abstract
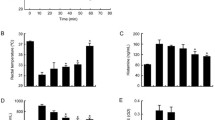
We studied the effect of aqueous extract ofMagnolia officinalis bark (Magnoliaceae) (MOAE) on the immediate hypersensitivity reaction. MOAE (0.01 to 1 g/kg) dose-depen-dently inhibited compound 48/80 induced systemic anaphylaxis in rats. MOAE (0.1 and 1 g/kg) also significantly inhibited local immunoglobulin E (IgE)-mediated passive cutaneous anaphylactic reaction. When MOAE was pretreated at concentrations ranging from 0.01 to 1 g/kg, the levels of plasma histamine were reduced in a dose-dependent manner. MOAE (0.001 to 1 mg/ml) dose-dependently inhibited the histamine release from rat peritoneal mast cells (RPMC) activated by compound 48/80 or anti-dinitrophenyl (DNP) lgE. The level of cyclic AMP (cAMP) in RPMC, when MOAE was added, significantly increased compared with that of the normal control. Moreover, MOAE (0.01 to 1 mg/ml) had a significant inhibitory effect on anti-DNP lgE-induced tumor necrosis factor-α production from RPMC. These results indicate that MOAE inhibits immediate hypersensitivity reactionin vivo andin vitro.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alber, G., Miller, L., Jelsema, C., Varin-Blank, N. and Metzger, H., Structure/function relationships in the mast cell high-affinity receptor for IgE (FcεRI): Role of cytoplasmic domains.J. Biol. Chem., 266, 22613–22620 (1991).
Allansmith, M. R., Baird, R. S., Ross, R. N., Barney, N. P. and Bloch, K. J., Ocular anaphylaxis induced in the rat by topical application of compound 48/80. Dose response and time course study.Acta Ohpthalmol., 67, 145–153 (1989).
Bueb, J. L., Mousli, M. C., Bronner, C., Rouot, B. and Landry, Y., Activation of Gi-like proteins, a receptor-independent effect of kinins in mast cells.Mol. Pharmacol., 38, 816–822 (1990).
Burd, P. R., Rogers, H. W., Cordon, J. R., Martin, C. A., Jayaraman, S., Wilson, S. D., Dvorak, A. M., Galli, S. J. and Dorf, M. E., Interleukin 3-dependent and independent mast cells stimulated with IgE and antigen express multiple cytokines.J. Exp. Med., 170, 245–257 (1989).
Chang, H. M. and But, P. P. H. (Eds).Pharmacology and applications of Chinese materia medica. World Scientific Publishing, Singapore, pp. 878–880 (1987).
Ennis, M., Pearce, F. L., and Weston, P. M., Some studies on the release of histamine from mast cells stimulated with polylysine.Br. J. Pharmacol., 70, 329–334 (1980).
Galli, S. J., Gorden, J. R., and Wershil, B. K., Cytokine production by mast cells and basophils.Cur. Opin. lmmunol., 3, 865–872 (1991).
Gorden, J. R. and Galli, S. J., Mast cell as a source of both preformed and immunologically inducible TNF-α/ cachectin.Nature, 346, 274–276 (1990).
Gurish, M. F., Ghildyal, N., Arm, J., Austen, K. F., Avraham, S., Reynolds, D. S., and Stevens, R. L., Cytokine mRNA are preferentially increased relative to secretory granule protein mRNA in mouse bone marrow-derived mast cells that have undergone IgE-mediated activation and degranulation.J. Immunol., 146, 1527–1533 (1991).
Hayashi, H., Ichikawa, A., Saito, T., and Tomita, K., Inhibitory role of cyclic adenosine 3′,5′-monophosphate in histamine release from rat peritoneal mast cellsin vitro.Biochem. Pharmac., 25, 1907–1913 (1976).
Inagaki, N., Miura, T., Daikoku, M., Nagai, H., and Koda, A., Inhibitory effect of β-adrenergic stimulants on increased vascular permeability caused by passive cutaneous anaphylaxis, allergic mediators and mediator releasers in rats.Pharmacol., 39, 19–27 (1989).
Inagaki, N., Miura, T., Ohira, K., Nagai, H., Xu, W., and Koda, A., Effect of CV-3988, a specific antagonist against platelet activation factor, on homologous passive cutaneous anaphylaxis in the mouse ear.J. Pharmacobiodyn., 13, 272–277 (1990).
Ishizaka, T., Chang, T. H., Taggart, M., and Ishizaka, K., Histamine release from rat mast cells by antibodies against rat basophilic leukemia cell membrane.J. Immunol., 119, 1589–1596 (1977).
Kanemoto, T. J., Kasugai, T., Yamatodani, A., Ushio, H., Mochizuki, T., Tohya, K., Kimura, M., Nishimura, M., and Kitamura, Y., Supernormal histamine release and normal cytotoxic activity of Biege rat mast cells with giant granules.Int. Arch. Allergy Immuniol., 100, 99–106 (1993).
Katayama, S., Shionoya, H. and Ohtake, S., A new method for extraction of extravasated dye in the skin and the influence of fasting stress on passive cutaneous anaphylaxis in guinea pigs and rats.Microbiol. Immunol., 22, 89–101 (1978).
Kim, H. M., Yi, J. M., and Lim, K. S., Magnoliae Flos inhibits mast cell-dependent immediate-type allergic reaction.Pharmacal. Res., 39, 107–111 (1999).
Makino, H., Saijo, T., Ashida, Y., Kuriki, H. H., and Maki, Y., Mechanism of action of an antiallergic agent: Amlexanox(AA-673), in inhibiting histamine release from mast cells.Int, Arch. Allergy Immunol., 82, 66–71 (1987).
Metzger, H., Alcaraz, G., Hohman, R., Kinet, J. P., Pribluda, V., and Quarto, R., The receptor with high affinity for immunoglobulin E.Annu. Rev. Immunol., 4, 419–470 (1986).
Mousli, M. C., Bronner, C., Bockaert, J., Rouot, B., and Landry, Y., Interaction of substance P, compound 48/80 and mastoparan with α-subunit C-terminal of G protein.Immunol. Lett., 25, 355–358 (1990a).
Mousli, M. C., Bronner, C., Landry, Y., Bockaert, J., and Rouot, B., Direct activation of GTP-binding regulatory proteins (G proteins) by substance P and compound 48/80.FEBS Lett., 259, 260–262 (1990b).
Peachell, P. T., MacGlashan, D. W., Lichtenstein, L. M., and Schleimer, R. P., Regulation of human basophil and lung mast cell function by cyclic adenosine monophosphate.J. Immunol., 140, 571–579 (1988).
Plaut, M., Pierce, J. H., Watson, C. J., Hanley-Hyde, J., Nordon, R. P., and Paul, W. E., Mast cell lines produce limphokines in response to cross-linkage of FcεRI or to calcium ionophores.Nature, 339, 64–67 (1989).
Rafferty, P. and Holgate, S. T., Histamine and its antagonists in asthma.J. Allergy Clin. Immunol., 84, 144–151 (1989).
Rimmer, S. J. and Church, M. K., The pharmacology and mechanisms of action of histamine H1-antagonists.Clin. Exp. Allergy, 20, 3–17 (1990).
Saito, H. and Nomura, Y., Screening methods for drug evaluation 3. In: Suzuki, L., Tanaka, H., Yajima, H.et al. (Eds).Pharmaceutical research and development. Hirokawa, Japan, pp.22 (1989).
Segal, D. M., Taurog, J., and Metzger, H., Dimeric immunoglobulin E serves as a unit signal for mast cell degranulation.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., USA, 74, 2993–2997 (1977).
Shin, T. Y., Park, J. H., and Kim, H. M., Effect of Cryptotympana atrata extract on compound 48/80-induced anaphylactic reactions.J. Ethnopharmacol., 66, 319–325 (1999).
Shore, P. A., Burkhalter, A., and Cohn, V. H., A method for fluorometric assay of histamine in tissues.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 127, 182–186 (1959).
Sullivan, T. J., Parker, K. L., Stenson, W., and Parker, C. W., Modulation of cyclic AMP in purified rat mast cells I: responses to pharmacologic, metabolic, and physical stimuli.J. Immunol., 114, 1473–1479 (1975).
Taniguchi, C., Homma, M., Takano, O., Hirano, T., Oka, K., Aoyagi, Y., Niitsuma, T., and Hayashi, T., Pharmacological effects of urinary products obtained after treatment with Saiboku-To, a herbal medicine for bronchial asthma, on type IV allergic reaction.Planta Med., 66, 607–611 (2000).
Tsai, S. K., Huang, S. S., and Hong, C. Y., Myocardial protective effect of honokiol: an active component in Magnolia officinalis.Planta Med., 62, 503–506 (1996).
Tsuruga, T., Ebizuka, Y., Nakajima, J., Chun, Y. T., Noguchi, H., Litaka, Y., and Sankawa, U., Biologically active constituents of Magnolia salicifolia: inhibitors of induced histamine release from rat mast cells.Chem. Pharm. Bull., 39, 3265–3271 (1991).
Wang, J. P., Ho, T. F., Chang, L. C., and Chen, C. C., Antiinflammatory effect of magnolol, isolated from Magnolia officinalis, on A23187-induced pleurisy in mice.J. Pharm. Pharmacol., 47, 857–860 (1995).
Watanabe, K., Watanabe, H., Goto, Y., Yamaguchi, M., Yamamoto, N., and Hagino, K., Pharmacological properties of magnolol and honokiol extracted from Magnolia officinalis: central depressant effects.Planta Med., 49, 103–108 (1983).
Wershil, B. K., Mekori, Y. A., Murakami, T., and Galli, S. J.,125l-fibrin deposition in IgE-dependent immediate hypersensitivity reactions in mouse skin: demonstration of the role of mast cells using genetically mast cell-deficient mice locally reconstituted with cultured mast cells.Immunol., 139, 2605–2614 (1987).
Wodnar-Filipowicz, A., Heusser, C. H., and Moroni, C., Production of the haemopoietic growth factors GM-CSF and interleukin-3 by mast cells in response to lgE receptor-mediated activation.Nature, 339, 150–152 (1989).
Yurt, R. W., Leid, R. W., and Austen, K. F., Native heparin from rat peritoneal mast cells.J. Biol. Chem., 252, 518–521 (1997).
Zhou, Y. and Xu, R., Antioxidative effect of Chinese drugs.Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi, 17, 368–369 (1992).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shin, T.Y., Kim, D.K., Chae, B.S. et al. Antiallergic action of Magnolia officinalis on immediate hypersensitivity reaction. Arch Pharm Res 24, 249–255 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02978266
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02978266