Abstract
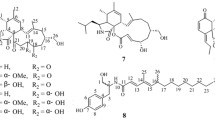
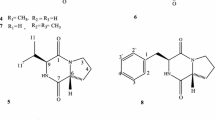
A novel phenazine derivative (1) together with six known compounds (2–7) were isolated by bioassay-guided fractionation from the culture broth of a bacterium,Bacillus sp., collected from a Pacific deep sea sediment sample (depth 5059 m). The structures of these compounds were determined using spectroscopic methods. Their cytotoxic effects on P388 and K562 cell lines were preliminarily examined using the sulforhodamine-B (SRB) assay.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carter R. E. and Richards J. H., The biogenesis of phenazine pigments.J. Am. Chem. Soc., 83, 495–496 (1961).
Chatterjee, S., Vijayakumar, E. K. S., Franco, C. M. M., Maurya, R., Blumbach, J., and Ganguli, B., Phencomycin, a new antibiotic from a Streptomyces species HIL Y-9031725.J. Antibio., 48, 1353–1354 (1995).
Chen, X. L., Zhang, Y. Zh., and Gao, P., Progress in deep-sea microbiology.J. Marine Sci., 28, 61–66 (2004).
Delong, E. F., Archaea in coastal marine environments.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 89, 5685–5689 (1992).
Eberhard, B. and Ulrich H., Carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance chemical shifts of substituted phenazines.J. Org. Chem., 41, 2104–2108 (1976).
Ge Y., Huang X., Wang S., Zhang X., and Xu Y., Phenazine-1- carboxylic acid is negatively regulated and pyoluteorin positively regulated bygacA inPseudomonas sp. M18.FEMS Microbio. Lett., 237, 41–47 (2004).
Gebhardt K., Schimana J., Krastel P., Dettner K., Rheinheimer J., Zeeck A., and Fiedler H., Endophenazines A-D, New Phenazine Antibiotics from the Arthropod Associated Endo- symbiontStreptomyces anulatus.I.Taxonomy, Fermentation, Isolation and Biological Activities.J. Antibio., 55, 794–800 (2002).
Faulkner, D. J., Marine natural products.J. Nat. Prod. Rep., 19, 1–48 (2002).
Fenical, W., Chemical studies of marine bacteria: developing a new resource.Chem. Rev., 93, 1673–1683 (1993).
Pusecker, K., Laatsch, H., Helmke, E., and Weyland, H., Dihy- drophencomycin methyl ester, a new phenazine derivative from a marineStreptomycete. J. Antibio., 50, 479–83 (1997).
Saitou, N. and Nei M., The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees.Mol. Biol. Evol., 4, 406–425 (1987).
Skehan, P., Storeng, R., Scudiero, D., Monks, A., McMahon, J., Vistica, D Warren, J. T., Bokesch, H., Kenney, S., and Boyd, M. R., New colorimetric cytotoxicity assay for anticancer drug screening.J. Natl Cancer Inst., 82, 1107- 1112(1990).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, D., Wang, F., Xiao, X. et al. a new cytotoxic phenazine derivative from a deep sea bacteriumBacillus sp.. Arch Pharm Res 30, 552–555 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02977647
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02977647