Abstract
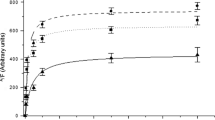
Na+,K+-ATPase activity, Na+-dependent phosphorylation, and [3H]ouabain binding in sarcolemma prepared from 4 week old spontaneously hypertensive rat(SHR) ventricles were compared to the same parameters in sarcolemma from age matched normotensive Wistar-Kyoto (WKY) rat ventricles to examine whether the reduced myocardial Na+-pump activity in SHR is an inherited enzymatic defect or a second phenomenon due to sustained hypertension. The total body weights, ventricular weights, and blood pressures were the same for SHR and WKY. No significant differences in sarcolemmal protein content and protein recovery were noted between the two groups. Sarcolemma isolated from SHR ventricles showed significantly less Na+, K+-ATPase activity and number of phosphorylation sites when, compared to sarcolemma from the WKY ventricles. Equilibrium binding of [3H]ouabain and the tumover number of myocardial Na+,K+-ATPase, however, were the same for both groups. These results indicate that the low affinity (α, or α1) isoform for ouabain is reduced in SHR compared to WKY but that the high affinity (α+, or α2) α isoform is the same in ventricles of SHR and WKY. The reduced amount of isoform of the Na+,K+-ATPase in, prehypertensive SHR ventricles may play some role in the development of hypertension.
Similar content being viewed by others
References Cited
Adams, R. J. and Schwartz, A., Comparative mechanisms for contraction of cardiac and skeletal muscle.Chest, 78(Suppl), 123–139 (1980).
Adams, R. J., Schwartz, A., Grupp, G., Grupp, I., Lee, S. W., Wallick, E. T., Powell, T., Twist, A. and Gatheram, P., High affinity ouabain binding site and low dose positive inotropic effect in rat myocardium.Nature, 296, 167–169 (1982).
Akera, T., Yamamoto, S., Temma, K., Kim, D.-H. and Brody, T., Is ouabain-sensitive rubidium or potassium uptake a measure of sodium pump activity in isolated cardiac muscle?Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 640, 779–790 (1981).
Blaustein, M. P., Intracellular electrolytes and arterial hypertension, Thieme Stratton, Inc., New York, 151–157 (1980).
Clough, D. L., Pamnani, M. B., Overbeck, H. W. and Haddy, F. J., Decreased Na+,K+-ATPase in right ventricular myocardium of rats with one-kidney Goldblatt hypertension.Physiologist, 20, 18 (1977).
David-Dufilho, M., Devynck, M.-A., Beugras, J. P. and Meyer, P., Quantitative changes in cardiac Na+,K+-adenosine triphosphatase of spontaneously hypertensive rats.J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol., 6, 273–280 (1984).
Erdmann, E., Philipp, G. and Scholtz, H., Cardiac giycoside receptor, Na+,K+-ATPase activity and force of contraction in rat heart.Biochem. Pharmacol., 29, 3219–3229 (1980).
Ferrario, C. M. and Page, I. H., Current views concerning cardiac output in the genesis of experimental hypertension.Cir. Res., 43, 821–831 (1978).
Friedman, M. and Freed, S. C., Microphonic manometer for indirect determination of systolic blood presure in the rat.Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med., 70, 670–672 (1949).
Ganguli, M. L. and Tobian, J., Cardiac output and peripheral resistance in strains of rats sensitive and resistant to NaCl hypertension.Hypertension 1, 3–7 (1979).
Gheyouche, R., Uzan, A., Le Fur, G. and Corgier, M., Decrease in [3H]ouabain binding sites in heart and brain from spontaneously hypertensive rats.Experientia 37, 492–493 (1981).
Gothberg, G., Jandhyala, B. and Folkow, B., Studies on the role of sodium potassiumactivated ATPase as determinant of vascular reactivity in Wistar-Kyoto and spontaneously hypertensive rats.Clin. Science, 59, 187S-189S (1980).
Haddy, F. J., Local control of vascular resistance as related to hypertension.Arch. Intern. Med., 133, 916–931 (1974).
Haddy, F. J., Potassium and blood vessels,Life Sci., 16, 1489–1498 (1975).
Haddy, F. J. and Overbeck, H. W., The role of humoral agents in volume expanded hypertension.Life Sci., 19, 935–948 (1976).
Haddy, F. J., Pamnani, M. B. and Clough, D. L., Pathophysiological role of cation transport and natriuretic factors in hypertension.Hypertension 10, I101–107 (1987).
Haddy, F. J. and Pamnani, M. B., Pharmacologic agents for the in vivo detection of vascular sodium transport defects in hypertension.Life Sci., 41(25), 2685–2696 (1987).
Hansen, O., Non-uniform populations of g-strophanthin binding sites (Na+,K+)-activated ATPase.Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 433, 388–392 (1976).
Huang, C. T., Cardona, P. and Michelakis, A. M., Existence of a new vasoactive factor in experimental hypertension.Am. J. Physiol., 234, E25-E31 (1978).
Jones, A. W., Altered ion transport in vascular smooth muscle spontaneously hypertensive rats. Influence of aldosterone, norepinephrine, and angiotensinCir. Res., 33, 563–572 (1973).
Jones, A. W., Altered ion transport in large and small arteries from spontaneously hypertensive rats and the influence of calcium.Cir. Res., 34 and 35 (Suppl I), I-117–I-122 (1974).
Kaloyanides, G. J., Balabanian, M. B. and Bowmann, R. L., Evidence that the brain participates in the humoral natriuretic mechanism of blood volume expansion in the dog.J. Clin. Invest., 62, 1288–1295 (1978).
Kaniike, K., Sasagawa, S. and Asano, Y., Na+,K+-ATPase activities in brain and kidney microsome of stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats.Jap. Heart J., 19, 595–596 (1978).
Kelly, R. A., Endogenous cardiac glycosidelike compounds.Hypertension 10, I 87–92 (1987).
Lee, S. W., Schwartz, A., Adams, R. J., Yamori, Y., Whitmer, K., Lane, L. K. and Wallick, E. T., Decrease in Na+,K+-ATPase activity and [3H]ouabain binding sites in sarcolemma prepared from hearts of spontaneously hypertensive rats.Hypertension 5, 682–688 (1983).
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, H. J., Farr, A. L. and Randall, R. J., Protein measurement with the Folin Phenol reagent.J. Biol. Chem., 193, 265–275 (1951).
Marin, J., Fernandez-Alfonso, M. S. and Sanchez-Ferrer, C. F., Sodium pump activity and contractile effect of ouabain in human placental veins.Eur. J. Pharmacol., 201, 75–82 (1991).
Matsuda, T., Iwata, H. and Cooper, J. R., Specific inactivation of α(+) molecular form of (Na+,K+)-ATPase by pyrithiamin.J. Biol. Chem., 259, 3858–3863 (1984).
Ng, Y. C. and Akera, T., Two classes of ouabain binding sites in ferret heart and two forms of Na+, K+-ATPase.Amer. J. Physiol., 252, H1016-H1022 (1987).
Overbeck, H. W., Pamnani M. B., Akera, T., Brody, T. M. and Haddy, F. J., Depressed function of a ouabain-sensitive sodium-potassium pump in blood vessels from renal hypertensive dogs.Circ Res., 38, 48–52 (1976).
Pamnani, M. B., Clough, D. L. and Haddy, F. J., Altered activity of the sodium potassium pump in arteries of rat with steroid hypertension.Clin. Sci. Molec. Med., 55, 41S-43S (1978).
Sakai, Y. and Inazu, M., Sodium pump activity and contraction of renal artery from spontaneously hypertensive rats.Eur. J. Pharmacol., 200, 227–231 (1991).
Schwartz, A., Allen, J. C. and Harigaya, S., Possible involvement of cardiac Na+,K+-adenosine triphosphatase in the mechanism of action of cardiac glycosides.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 168, 31–41 (1969).
Schwartz, A., Lindenmayer, G. E. and Allen, J. C., The sodium potassium adenosine triphosphatase: Pharmacological, Physiological, and biochemical aspects.Pharmacol. Rev., 27, 3–134 (1975).
Shull, G. E., Greeb, J. and Lingrel, J. B., Molecular cloning of three distinct froms of the Na+,K+-ATPase α-subunit from rat brain.Biochemistry 25, 8125–8132 (1986).
Sowers, J. R., Beck, F., Stern, N. and Raghaven, S. R. V., Reduced sodium potassium dependent ATPase and its possible role in the development of hypertension in spontaneously hypertensive rats.Clin. Exper. Hyper. Theory and Practice A(5(1), 71–86 (1983).
Sweadner, K. J., Enzymatic properties of separated isozymes of the Na+,K+-ATPase. Substrate affinities, kinetic cooperativity, and ion transport stoichiometry.J. Biol. Chem., 260, 11508–11513 (1985).
Sweadner, K. J. and Gilkeson, R. C., Two isozymes of the Na+,K+-ATPase have distinct antigenic determinants.J. Biol. Chem., 260, 9016–9022 (1985).
Van Alstyne, E., Burch, R. M., Knickelbein, R. G., Hungerford, R. T., Gower, F. J., Webb, J. G., Poe, S. L. and Lindenmayer, G. E., Isolation of sealed vesicles highly enriched with sarcolemma markers from canine ventricle.Biochim. Biophys. Acta., 602, 131–143 (1980).
Wallick, E. T., Anner, B. M., Ray, M. V. and Schwartz, A., Effect of temperature on phosphorylation and ouabain binding to N-ethylmaleimide treated Na+, K+-ATPase.J. Biol. Chem., 253, 8778–8786 (1978).
Wallick, E. T. and Schwartz, A., Nature of the transport ATPase digitalis complex. X. Thermodynamics of the rate of ouabain binding.J. Biol. Chem., 249, 5141–5147 (1974).
Wallick, E. T., Lane, L. K. and Schwartz, A., Biochemical mechanism of the sodium pump.Ann. Rev. Physiol., 41, 397–411 (1979).
Whitmer, K. R., Lee, J. H., Martin, A. F., Lane, L. K., Lee, S. W., Schwartz, A., Overbeck, H. W. and Wallick, E. T., Myocardial Na+,K+-ATPase in one-kidney, one-clip hypertensive rats.J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol., 18, 1085–1095 (1986).
Willems, W. J., Willems, M. W. and Stekiel, W. J., The effect of tetrodotoxin(TTX) upon mesenteric venous membrane potential and diameter in spontaneously hypertensive rats(SHR)(abstr.).Physiologist 18, 451 (1975).
Young, R. M. and Lingrel, J. B., Tissue distribution of mRNAs encoding the isoforms and subunit of rat Na+,K+-ATPase.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 145, 52–58 (1987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, S.W., Lee, J.S. & Wallick, E.T. Altered cardiac Na+,K+-ATPase activity in prehypertensive spontaneously hypertensive rat. Arch. Pharm. Res. 16, 305–311 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02977521
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02977521