Abstract
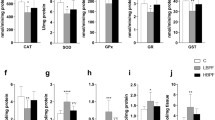
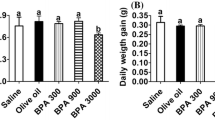
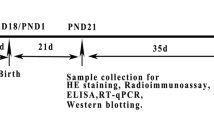
Bisphenol A (BPA) is an environmental endocrine disrupter that is known to be transferred to the fetus via the placenta and to the neonate via milk. In this study, we investigated BPA-induced alterations of the activities of murine peritoneal macrophages in dams and 7 week old offspring of dams exposed to BPA from gestational day 7 until lactation on day 21 after delivery, i.e. 34-36 days. BPA was administered in drinking water at three doses, 15, 75, and 300 mg/L. Dams were sacrificed 21 days after delivery and offspring at the age of 7 weeks. Peritoneal macrophages were cultured in the presence of LPS or LPS plus IFN-γ for 2 or 4 days. We found that nitric oxide (NO) production by maternal macrophages was significantly decreased in a BPA-dose dependent manner. However, while a significant reduction of NO production by macrophages in the offspring was observed at BPA concentrations of 75 mg/L and 300 mg/L in drinking water, this effect was not seen at the lowest concentration of 15 mg/L. Similar inhibition of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) production was observed with macrophages from both BPA-exposed dams and offspring. Thus, our results suggest that exposure to BPA during gestation and lactation induces downregulation of the activities of macrophages in both dams and offspring.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blaylock, B. L, Ahmed, S. A., and Holladay S. D., Perinatal immuno-toxicant exposure and autoimmune disease: In S.D. Holladay (Ed.) Developmental immunotoxicology. CRC Press, New York., p.219(2005).
Byun, J., Heo, Y., Kim, Y., and Pyo, M. Y., Bisphenol A-induced downregulation of murine macrophage activities in vitro and ex vivo.Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology., 19, 19–24(2005).
Chung, H-T., Pae, H-C., Choi, B-M., Billiar, T. R., Kim, Y-M., Nitric oxide as a bioregulator of apoptosis.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 282,1075–1079 (2001).
Green, L. C., Wagner, D. A., Glogowski, J. S., Skipper, P. L., and Wishnok, J. S., Tannenbaum, S. R., Analysis of nitrate, nitrite and [15N] nitrite in biological fluids.Analyt. Biochem., 126,131–138(1992).
Hilfiker-Kleiner, D., Hilfiker, A., Schieffer, B., Engel, D., Mann, D. L, Wollert, K. C., and Drexler, H., TNFalpha decreases alpha MHC expression by a NO mediated pathway: role of E-box transcription factors for cardiomyocyte specific gene regulation.Cardiovasc. Res., 53,460–469 (2002).
Holladay, S. D. and Smialowicz, R. J., Development of the murine and human immune system: differential effects of immuno-toxicants depend on time of exposure.Environ. Health Perspect 108 Suppl., 3,463–473 (2000).
Inoue, H., Tsuruta, A., Kudo, S., Ishii, T., Fukushima, Y., Iwano, H., Yokota, H., and Kato, S., Bisphenol a glucuronidation and excretion in liver of pregnant and nonpregnant female rats.Drug Metab. Dispos., 33, 55–59 (2005).
Khurana, S., Ranmal, S., and Ben-Jonathan, N., Exposure of newborn male and female rats to environmental estrogens: delayed and sustained hyperprolactinemia and alteration in estrogen receptor expression.Endocrinology, 141, 4512–4517(2002).
Kiekens, R. C. M., Thepen, T., Ossting, A. J., Bihari, I. C., van de Winkel, J. G. J., Bruijnzeel-Koomen, C. A. F. M., and Knol, E. F., Hetero-geneity within tissue-specific macrophage and dendritic cell populations during cutaneous inflammation in atopic dermatitis.Br. J. Dermatol., 145, 957–965 (2001).
Kim, Y. H., Kim, C. S., Park, S., Han, S. Y., Pyo, M.Y., and Yang, M., Gender differences in the levels of bisphenol A metabolites in urine.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 312, 441–448(2003).
Kim, Y. M., Talanian, R. V., Li, J., and Billiar, T. R., Nitric oxide inhibits apoptosis by preventing increases in caspase-3-like activity via two distinct mechanisms.J. Biol. Chem., 272, 31138–31148(1997).
Kolb, H. and Kolb-Bachofen, V., Nitric oxide in autoimmune disease: Cytotoxic or regulatory mediator.Immunol. Today., 19,556–561 (1998).
MacMicking, J., Xie, Q., and Nathan, C., Nitric oxide and macrophage function.Annu. Rev. Immunol., 15, 323–350 (1997).
Matejuk, A., Adlard, K., Zamora, A., Silverman, M., Vandenbark, A. A., and Offner, H., 17β-estradiol inhibits cytokine, chemokine, and chemokine receptor mRNA expression in the central nerveous system of female mice with experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.J. Neurosci., 65, 529–542 (2001).
Mishell, B. B. and Shiigi, S. M., Selected methods in cellular immunology.W. H. Freeman and Company, p. 14 (1980).
Morrissey, R. E., George, J. D., Price, C. J., Tyl, R. W., Marr, M. C., and Kimmel, C. A., The developmental toxicity of bisphenol A in rats and mice.Fund. Appl. Toxicol., 8, 571–582 (1987).
Palanza, P. L., Howdeshell, K. L, Parmigiani, S., and vom Saal, F. S., Exposure to a low dose of bisphenol A during fetal life or in adulthood alters maternal behavior in mice.Environ. Health Perspect., 110 suppl. 3,415–422 (2002).
Raghupathy, R., Pregnancy: success and failure within the Th1/ Th2/Th3 paradigm.Seminars Immuno., 13,219–227 (2001).
Ruh, M. F., Bi, Y., Cox, D., Berk, D., Howlett, A. C., and Bellone, C. J., Effect of environmental estrogens on IL-1beta promoter activity in a macrophage cell line.Endocrine., 9, 207–211 (1998).
Salem, M. L., Hossain, M. S., and Nomoto, K., Mediation of the immunomodulatory effect of beta-estradiol on inflammatory reponse by inhibition of recruitment and activation of inflammatory cells and their gene expression of TNF-alpha and IFN-gamma.Int. Arch. Allergy Immuno., 121, 235–245 (2000).
Shin, B. SA., Yoo, S. D., Cho, C. Y., Jung, J. H., Lee, B. M., Kim, J. H., Lee, K. C., Han, S. Y., Kim, H. S., and Park, K. L., Maternal-fetal disposition of bisphenol a in pregnant Sprague-Dawley rats.J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A., 65, 395–406 (2002).
Stefano, G B., Prevot, V., Beauvillain, J. C., Fimiani, C., Welters, I., Cadet, P., Breton, C., Pestel, J., Salzet, M., and Bilfinger, T. V., Estradiol coupling to human monocytes nitric oxide release is dependent on intracellular calcium transients: Evidence for an estrogen surface receptor.J. Immunol., 163, 3758–5763(1999).
Takal, Y., Tsutsumi, O., Ikezuki, Y., Kamei, Y., Osuga, Y., Yano, T., and Taketan, Y., Preimplantation exposure to bisphenol A advances postnatal development.Reprodactive Toxicology, 15(1), 71–74(2001).
Thomas, P. S., Tumor necrosis factor-a: The role of this multifunctional cytokine in asthma.Immunol. Cell. Biol., 79, 132–140,(2001).
Underhill, D. M. and Ozinsky, A., Phagocytosis of microbes: Complexity in action.Annu. Rev. Immunol., 20, 825–852, (2002).
Vegeto, E., Bonincontro, C., Pollio, G., Sala, A., Viappiani, S., Nardi, F., Brusadelli, A., Viviani, B., Ciana, P., and Maggi, A., Estrogen prevents the lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in microglia.J. Neurosci., 21,1809–1818 (2001).
Washington, W., Hubert, L., Jones, D., and Gray, W. G., Bisphenol A binds to the low-affinity estrogen binding site.In Vitro Mol. Toxicol., 14,43–51, (2001).
Woodfork, K. A., Schuller, K. C., and Huffman, L. J., Cytokine and nitric oxide release by J774A.1 macrophages is not regulated by estradiol.Life Sci., 69,2287–2294 (2001).
Yoo, S. D., Shin, B. S., Lee, B. M., Lee, K. C., Han, S. Y., Kim, H. S., Kwack S. J., and Park, K. L., Bioavailability and mammary excretion of bisphenol A in Sprague-Dawley rats.J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A., 64,417–426 (2001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pyo, M.Y., Kim, H.J., Back, S.K. et al. Downregulation of peritoneal macrophage activity in mice exposed to bisphenol a during pregnancy and lactation. Arch Pharm Res 30, 1476–1481 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02977374
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02977374