Abstract
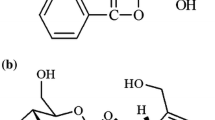
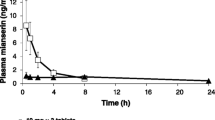
Plasma profile of niflumic acid following oral administration of talniflumate tablets (Somalgen) was compared to that of niflumic acid tablets in man. Plasma niflumic acid was assayed by HPLC method. Plasma niflumic acid profile from the talniflumate tablets was similar to that from the niflumic acid tablets resulting in no differences in AUC,C max,t max and MRT. It demonstrates that talniflumate is a prodrug of niflumic acid, and undergoes extensive first-pass biotransformation to niflumic acid. However, plasma niflumic acid concentration at 30 min after talniflumate dosing was significantly (p<0.05) higher than that of niflumic acid dosing. The more potent analgesic activity of talniflumate than niflumic acid might be related to this higher plasma drug concentration at the earlier phase. Considering that talniflumate is less irritant to gastrointestinal mucosa than niflumic acid, talniflumate seems to be advantageous over niflumic acid in therms of activity and side effects.
Similar content being viewed by others
References Cited
Avgerinos, A. and Malamataris, S., High performance liquid chromatographic determination of niflumic acid in human plasma and urine.J. Chromatogr., 533, 271–274 (1990).
Grossman, A. and Besser, G.M., Prolactinomas.Br. Med. J., 290, 182–184 (1985).
Kim, H. J., Pharmacokinetics of talniflumate, a prodrug of niflumic acid, following oral administration to human. MS theis, College of Pharmacy, Seoul National University, 1994.
Lan, S. J., Chando, T. J., Weliky, I. and Schreiber, E. C., Metabolism of niflumic acid-14C: absorption, excretion and biotransformation by human and dog.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 186, 323–330 (1973).
Lancranjan, I., The endocrine profile of bromocriptione: its application in endocrine diseases.J. Neural. Transm., 51, 61–82 (1981).
Los, M., Boned, J. E. and Piccininali, C., Nuevos esteres de acidos anilinonicotinicos Y N-fenilantranilicos sustituidos (New esters of substituted anilinonicotinic and phenylanthranilic acids).Farmaco. Ed. Sci., 36, 372–385 (1981).
Martindale,The Extra Pharmacopoeia. The Pharmaceutical Press, London, 29th ed., 1989, p. 31.
Nightingale, C. H., French, M. A. and Quintiliani, R., Cephalosporin pharmacokinetics in beta-lactam antibiotics, ed. by Muranishi, S., Japan Scientific Societies Press, (1981). pp.259–298.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, HJ., Han, YH., Chung, SJ. et al. Pharmacokinetics of talniflumate, a prodrug of niflumic acid, following oral administration to man. Arch. Pharm. Res. 19, 297–301 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02976244
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02976244