Abstract
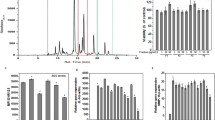
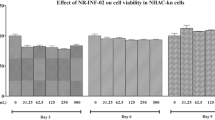
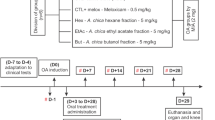
Osteoarthritis is thought to be induced by the ageing-related loss of homeostatic balance between degeneration and repair mechanism around cartilage tissue in which inflammatory mediators such as reactive oxygen species, cytokines and prostaglandins are prone to overproduction under undesirable physiological conditions. Phlorotannins are unique polyphenolic compounds bearing dibenzo-1,4-dioxin skeleton which are not found in terrestrial plants but found only in some brown algal species such asEcklonia andEisenia families. Phlorotanninrich extracts ofEcklonia cava including LAD103 showed significant antioxidant activities such as DPPH radical scavenging, ferric ion reduction, peroxynitrite scavenging, and inhibition of LDL oxidation, indicating their possible antioxidative interference both in onset and downstream consequences of osteoarthritis. LAD103 also showed significant down regulation of PGE2 generation in LPS-treated RAW 246.7 cells, and significant inhibition of human recombinant interleukin-1α-induced proteoglycan degradation, indicating its beneficial involvement in pathophysiological consequences of osteoarthritis, the mechanism of which needs further investigation. Since LAD103 showed strong therapeutic potentials in arthritic treatment through severalin vitro experiments, it is highly encouraged to perform further mechanistic and efficacy studies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed, S., Rahman, A., Hasnain, A., Lalonde, M., Goldberg, V. M., and Haqqi, T. M., Green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits the IL-1β-induced activity and expression of cyclooxygenase-2 and nitric oxide synthase-2 in human chondrocytes.Free Radical Biol. Med., 33, 1097–1105 (2002).
Benzie, I. F. F., and Strain, J. J., Ferric reducing antioxidant power assay: Direct measure of total antioxidant activity of biological fluids and modified version for simultaneous measurement of total antioxidant power and ascorbic acid concentration.Methods Enzymol., 299, 15–27 (1999).
Blois, M. S., Antioxidant determinations by the use of a stable free radical.Nature, 26, 1199–1200 (1958).
Buege, J. A., and Aust, S. D., Microsomal Lipid Peroxidation.Methods Enzymol., 52, 302–310 (1987).
Choi, J. H., Kim, D. Y., Yoon, J. H., Youn, H. Y., Yi, J. B., Rhee, H. I., Ryu, K. H., Jung, K., Han, C. K., Kwak, W. J., and Cho, Y. B., Effects of SKI 306X, a new herbal agent, on proteoglycan degradation in cartilage explant culture and collagenase-induced rabbit osteoarthritis model.Osteoarthritis and Cartilage, 10, 471–478 (2002).
Corvol, M. T., The chondrocytes: from cell aging to osteoarthritis.Joint Bone Spine, 67, 557–560 (2000).
Dalle-Donnea, I., Rossib, R., Giustarinib, D., Milzania, A., and Colombo, R., Protein carbonyl groups as biomarkers of oxidative stress.Clin. Chim. Acta 329, 23–38 (2003).
Evans, C. H., and Stefanovic-Racic, M., Nitric oxide in arthritis.METHODS: A Companion to Methods in Enzymology, 10, 38–42 (1996).
Fukuyama, Y., Kodama, M., Miura, I., Kinzyo, Z., Kido, M., Mori, H., Nakayama, Y., and Takahashi, M., Structure of an antiplasmin Inhibitor, Eckol, Isolated from the brown alga Ecklonia kurome OKAMURA and inhibitory activities of its derivatives on plasmin inhibitors.Chem. Pharm. Bull., 37, 349–353 (1989).
Fukuyama, Y., Kodama, M., Miura, I., Kinzyo, Z., Mori, H., Nakayama, Y., and Takahashi, M., Anti-plasmin Inhibitor. VI. Structure of phlorofucofuroeckol A, a novel phlorotannin with both dibenzo-1,4-dioxin and dibenzofuran elements, from Ecklonia kurome OKAMURA.Chem. Pharm. Bull., 38, 133–135 (1990).
Glombitza, K. W., and Gerstberger, G., Phlorotannins with dibenzodioxin structural elements from the brown alga Eisenia arborea.Phytochemistry, 24, 543–551 (1985).
Haenen, G. R. M. M., Paquay, J. B. G., Korthouwer, R. E. M., and Bast, A., Peroxynitrite scavenging by flavonoids.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 236, 591–593 (1997).
Henrotin, Y. E., Bruckner, P., and Pujol, J. P. L., The role of reactive oxygen species in homeostasis and degradation of cartilage.Osteoarthritis Cartilage, 11, 747–755 (2003).
Kang, K., Park, Y., Hwang, H. J., Kim, S. H., Lee, J. G., and Shin, H. C., Antioxidtive properties of brown algae polyphenolics and their perspectives as chemopreventive agents against vascular risk factors.Arch. Pharm. Res., 26, 286–293 (2003).
Kaur, H., and Halliwell, B., Evidence for nitric oxide-mediated oxidative damage in chronic inflammation-Nitrotyrosine in serum and synovial fluid from rheumatoid patients.FEBS Lett., 350, 9–12 (1994).
Kooy, N. W., Royall, J. A., Ischiropoulos, H., and Beckman, J. S., Peroxynitrite-mediated oxidation of dihydrorhodamine 123.Free Radical Biol. Med., 16, 149–156 (1994).
Li, M., Rosenfeld L., Vilar R. E., and Cowman, M. K., Degradation of hyaluronan by peroxynitrite.Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 341, 245–250 (1997).
Marinia, S., Fasciglionea, G. F., Monteleoneb, G., Maiottib, M., Tarantinob, U., and Colettaa M., A correlation between knee cartilage degradation observed by arthroscopy and synovial proteinases activities.Clin. Biochem., 36, 295–304 (2003).
Martel-Pelletier, J., Alaaeddine, N., and Pelletier, J. P., Cytokines and their role in the pathophysiology of osteoarthritis.Front. Biosci., 4, 694–703 (1999).
Mathy-Hartert, M., Deby-Dupont, G. P., Reginster, J. Y. L., Ayache, N., Pujol, J. P., and Henrotin, Y. E., Regulation by reactive oxygen species of interleukin-1, nitric oxide and prostaglandin E2 production by human chondrocytes.Osteoarthritis Cartilage, 10, 547–555 (2002).
Morisset, S., Patry, C., Lora, M., and de Brum-Fernandes, A. J., Regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 expression in bovine chondrocytes in culture by interleukin 1α, tumor necrosis factor-α, glucocorticoids, and 17β-estradiol.J. Rheumatol., 25, 1146–1153 (1998).
Nakagawa, T., Akagi, M., Hoshikawa, H., Chen, M., Yasuda, T., and Mukai, S., Lectin-like oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor 1 mediates leukocyte infiltration and articular cartilage destruction in rat zymosan induced arthritis.Arthritis Rheum., 46, 2486–2494 (2002).
Nakamura, T., Nagayama, K., Uchida, K., and Tanaka, R., Antioxidant activity of phlorotannins isolated from the brown alga Eisenia bicyclis.Fisheries Sci., 62, 923–926 (1996).
Nakayama, Y., Takahashi, M., Fukuyama, Y., and Kinzyo, Z., An antiplasmin Inhibitor, eckol, isolated from the brown alga Ecklonia kurome.Agric. Biol. Chem., 53, 3025–3030 (1989).
Sandy, J. D., Brown, H. L. G., and Lowther, D. A., Degradation of proteoglycan in articular cartilage.Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 543, 36–44 (1978).
Schuerwegh, A. J., Dombrecht, E. J., Stevens, W. J., Van Offel, J. F., Bridts, C. H., and De Clerck, L. S., Influence of proinflammatory (IL-1, Il-6, TNF-α, IFN-γ) and anti-inflammatory (IL-4) cytokines on chondrocyte function.Osteoarthritis and Cartilage, 11, 681–687 (2003).
Shibata, T., Nagayama, K., Tanaka, R., Yamaguchi, K., and Nakamura, T., Inhibitory effects of brown algal phlorotannins on secretory phospholipase A2S, lipoxygenases and cycloxygenases.J. Appl. Phycol., 15, 61–66 (2003).
Taskiran, D., Stefanovic-Racic, M., Georgescu, H., and Evans, C., Nitric oxide mediates suppression of cartilage proteoglycan synthesis by Interleukin-1.Biochem. Biophysics. Res. Commun., 200, 142–148 (2000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shin, HC., Hwang, H.J., Kang, K.J. et al. An antioxidative and antiinflammatory agent for potential treatment of osteoarthritis fromEcklonia cava . Arch Pharm Res 29, 165–171 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02974279
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02974279