Abstract
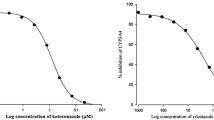
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of morin, a flavonoid, on the pharmaco-kinetics of diltiazem and one of its metabolites, desacetyldiltiazem in rats. Pharmacokinetic parameters of diltiazem and desacetyldiltiazem were determined after oral administration of diltiazem (15 mg/kg) in rats pretreated with morin (1.5, 7.5, and 15 mg/kg). Compared with the control group (given diltiazem alone), pretreatment of morin significantly increased the absorption rate constant (Ka) and peak concentration (Cmax) of diltiazem (p<0.05, p<0.01). Area under the plasma concentration-time curve (AUC) of diltiazem in rats pretreated with morin were significantly higher than that in the control group (p<0.05., p<0.01), hence the absolute bioavailability (AB%) of diltiazem was significantly higher than that of the control group (p<0.05, p<0.01). Relative bioavailability (RB%) of diltiazem in rats pretreated with morin was increased by 1.36-to 2.03-fold. The terminal half-life (t1/2) and time to reach the peak concentration (Tmax) of diltiazem were not altered significantly with morin pretreatment. AUC of desacetyldiltiazem was increased significantly (p<0.05) in rats pretreated with morin at doses of 7.5 and 15 mg/kg, but metabolite-parent ratio (MR) of desacetyldiltiazem was decreased significantly (p<0.05), implying that pretreatment of morin could be effective to inhibit the CYP 3A4-mediated metabolism of diltiazem. There were no apparent changes of Tmax and t1/2 of desacetyldiltiazem with morin pretreatment. Collectively, the pretreatment of morin significantly altered pharmacokinetics of diltiazem, which can be attributed to increased intestinal absorption as well as reduced first-pass metabolism. Based on these results, dose modification should be taken into consideration when diltiazem is used concomitantly with morin or morin-containing dietary supplements in clinical setting.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhattacharya, R. K. and Firozi, P. F., Effect of plant flavonoids on microsome catalyzed reactions of aflatoxin B1 leading to activation and DNA adduct formation.Cancer Letter, 39, 85–91 (1988).
Buckley, M. M.-T., Grant, S. M., Goa, K. L., McTabish, D., and Sorkin, E. M., Diltiazem: A reappraisal of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic use.Drugs, 39, 757–806 (1990).
Na, J. H., Choi, J. S., Effect of naringin on the pharmacokinetics of nifedifine in rabbits.J. Kor. Pharm. Sci., 35, 101–106 (2005).
Chaffman, M. and Brogden, R. N., Diltiazem: a review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic efficacy.Drugs, 29, 387–454 (1985).
Choi, J. S., Choi, B. C., and Choi, K. E., Effect of quercetin on the pharmacokinetics of oral cyclosporine.Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm., 61, 2406–2409 (2004).
Choi, J. S., Jo, B. W., and Kim, Y. C., Enhanced paclitaxel bioavailability after oral administration of paclitaxel or prodrug to rats pretreated with quercetin.Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm., 57, 313–318 (2004).
Choi, J. S. and Han, H. K., The effect of quercetin on the pharmacokinetics of verapamil and its major metabolite, norverapamil, in rabbits.J. Pharm. Pharmacol., 56, 1537–1542 (2004).
Choi, J. S. and Shin, S. C., Enhanced paclitaxel bioavailability after oral coadministration of paclitaxel prodrug with naringin to rats.Int. J. Pharm., 292, 149–156 (2005).
Dixon R. A. and Steele, C. L., Flavonoids andisoflavonoids-a gold mine for metabolic engineering.Trends Plant Sci., 4, 394–400 (1999).
Dupuy, J., Larrieu, G., Sutra, J. F., Lespine, A. and Alvinerie, M., Enhancement of moxidectin bioavailability in lamb by a natural flavonoid: quercetin.Vet. Parasitol., 112, 337–347 (2003).
Fang, S. H., Hou, Y. C., Chang, W. C., Hsiu, S. L., Chao, P. D., and Chiang, B. L., Morin sulfates/glucuronides exert anti-inflammatory activity on activated macrophages and decreased the incidence of septic shock.Life Sci., 74, 743–756 (2003).
Fraile, L. J., Aramayona, J. J., Bregante, M. A., Garcia M. A., and Aradia, A. R., Deacetylation of diltiazem by several rabbit tissues.Pharm. Res. 13, 1875–1880 (1996).
Francis, A. R., Shetty, T. K., and Bhattacharya, R. K., Modulating effect of plant flavonoids on the mutagenicity ofN-methyl-N-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine.Carcinogenesis, 10, 1953–1955 (1989).
Goebel, K. J. and Kolle, E. U., High performance liquid chromatographic dertermination of diltiazem and four of its metabolites in plasma.J. Chromatogr., 345, 355–363 (1985).
Gottesman, M. M. and Pastan, I., Biochemistry of multidrug resistance mediated by the multidrug transporter.Annu. Rev. Biochem., 62, 385–427 (1993).
Hanasaki, Y., Ogawa S., and Fukui, S., The correlation between active oxygens scavenging and antioxidative effects of flavonoids.Free Radic. Biol. Med., 16, 845–850 (1994).
Han, H. K. and Choi, J. S., Enhanced diltiazem bioavailability after oral administration of diltiazem with naringin in rats.Int. J. Pharm., Submitted for publication (2005).
Hodek, P., Trefil, P., and Stiborova, M., Flavonoids-potent and versaltile biologically active compounds interacting with cytochromes P450.Chem. Biol. interact., 139, 1–21 (2002).
Homsy, W., Caille, G., and du Souich, P., The site of absorption in the small intestine determines diltiazem bioavailability in the rabbit.Pharm. Res., 12, 1722–1726 (1995a).
Homsy, W., Lefebvre, M., Caille, G., and du Souich, P., Metabolism of diltiazem in hepatic and extrahepatic tissues of rabbits:in vitro studies.Pharm. Res., 12, 609–614 (1995b).
Kim, H. S., Cheon, B. S., Kim, Y. H., Kim, S. Y., and Kim, H. P., Effects of naturally occurring flavonoids on nitric oxide production in the macrophage cell line RAW 264.7 and their structure-activity relationships.Biochem. Pharmacol., 58, 759–765 (1999).
Kim, H. S., Choi, J. S., and Choi, I., Effect of naringin on tamoxifen pharmacokinetics in rats.Kor. J. Clin. Pharm., 15, 55–60 (2005).
Kim, H. J. and Choi, J. S., Effect of pretreatment of naringin on the bioavailability of diltiazem and deacetylditiazem in rabbits.Yakhak Hoeji, 49, 230–236 (2005).
Kok, L. D., Wong, Y. P., Wu, T. W., Chan, H. C., Kwok, T. T., and Fung, K. P., Morin hydrate: a potential antioxidant in minimizing the free-radicals-mediated damage to cardio-vascular cells by anti-tumor drugs.Life Sci., 67, 91–99 (2000).
Kolars, J. S., Schmiedlin-Ren, P., Dobbins, W. O. 3rd, Schuetz, J., Wrighton, S. A., and Watkins, P. B., Heterogeneity of cytochrome P450IIIA expression in rat gut epithelia.Gastroenterology, 102, 1186–1198 (1992).
Lefebvre, M., Homsy, W., Caille, G., and du Souich, P., First-pass metabolism of diltiazem in anesthetized rabbits: role of extrahepatic organs.Pharm. Res., 13, 124–128 (1996).
Li, X. and Choi, J. S., Erhanced diltiazem bioavailability after oral administration of diltiazem with quercetin to rabbits.Int. J. Pharm., 297, 1–8 (2005).
Molden, E., Asberg, A., and Christensen, H., CYP2D6 is involved inO-demethylation of diltiazem-anin vitro study with transfected human liver cellsEur.J. Clin. Pharmacol., 56, 575–579 (2000a).
Molden, E., Christensen, H., and Sund, R. B., Extensive metabolism of diltiazem and P-glycoprotein-mediated efflux of desacetyl-diltiazem (M1) by rat jejunumin vitro.Drug Metab. Dispos., 28, 107–109 (2000b).
Nguyen, H., Zhang, S., and Morris, M. E., Effect of flavonoids on MRP1-mediated transport in Panc-1 cells.J. Pharm. Sci., 92, 250–257 (2003).
Pichard, L. G., Gillet, G., Fabre, I., Dalet-Beluche, I., Bonfils, C., and Thenot, J. P.,et al., Identification of the rabbit and human cytochromes P-450IIIA as the major enzymes involved in theN-demethylation of diltiazem.Drug. Metab. Dispos, 18, 711–719 (1990).
Pool, P. E., Diltiazem. In: F. H. Messerli Editor, Cardiovascular Drug Therapy (2nd ed.) Saunders Philadelphia, pp. 931–971, (1996).
Ramanathan, L., Das, N. P., and Li, Q. T., Studies on lipid oxidation in fish phospholipid liposomes.Biol. Trace Elem. Res., 40, 59–70 (1994).
Raso, G.M., Meli, R., Di Carlo, G., Pacilio, M., and Di Carlo, R., Inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 expression by flavonoids in macrophage J774A. 1.Life Sci., 68, 921–931 (2001).
Rocci, M.L. and Jusko, W.J., LAGRAN program for area and moments in pharmacokinetic analysis.Computer Programs in Biomedicine, 16, 203 (1983).
Saeki, T., Ueda, K., Tanigawara, Y., Hori, R., and Komano, T., P-glycoprotein-mediated transcellular transport of MDR-reversing agents.FEBS Lett., 324, 99–102 (1993).
Vaclavikova, R., Horsky, S., Simek, P., and Gut, I., Paclitaxel metabolism in rat and human liver microsomes is inhibited by phenolic antioxidants.Nauyn. Schmiedebergs. Arch. Pharmacol., 368, 200–209 (2003).
Wacher, V. J., Salphati, L., and Benet, L. Z., Active secretion and enterocytic drug metabolism barriers to drug absorption.Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev., 46, 89–102 (2001).
Watkins, P. B., Wrighton, S. A., Schuetz, E. G., Molowa, D. T., and Guzelian, P. S., Identification of glucocorticoid-inducible cytochromes P-450 in the intestinal mucosa of rats and man.J. Clin. Invest., 80, 1029–1036 (1987).
Weir, M. R., Diltiazem: ten years of clinical experience in the treatment of hypertension.J. Clin. Pharmacol., 35, 220–232 (1995).
Yeung, P. K., Feng, J. D. Z., and Buckley, S. J., Pharmacokinetics and hypotensive effect of diltiazem in rabbits: Comparison of diltiazem with its major metabolites.J. Pharm. Pharmacol., 50, 1247–1253 (1998).
Yusa, K. and Tsuruo, T., Reversal mechanism of multidrug resistance by verapamil: direct binding of verapamil to P-glycoprotein on specific sites and transport of verapamil outward across the plasma membrane of K562/ADM cells.Cancer Res., 49, 5002–5006 (1989).
Zhang, S. and Morris, M. E., Effects of the flavonoids biochanin A, morin, phloretin, and silymarin on P-glycoprotein-mediated transport.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 304, 1258–1267 (2003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article is available at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BF02973918.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, H.J., Choi, JS. Effects of morin pretreatment on the pharmacokinetics of diltiazem and its major metabolite, desacetyldiltiazem in rats. Arch Pharm Res 28, 970–976 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02973885
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02973885