Abstract
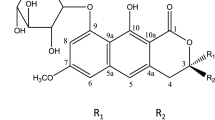
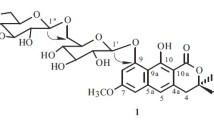
Three naphthopyrone glucosides, cassiaside (1), rubrofusarin-6-O-β-D-gentiobioside (2), and toralactone-9-O-β-D-gentiobioside (3), were isolated from the BuOH-soluble extract of the seeds ofCassia tora as active constituents, using an,in vitro bioassay based on the inhibition of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) to monitor chromatographic fractionation. The structures of1–3 were determined by spectroscopic data interpretation, particularly by extensive 1D and 2D NMR studies. All the isolates (1–3) were evaluated for the inhibitory activity on AGEs formationin vitro.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bucala, R. and Vlassara, H., Advanced glycosylation end products in diabetic renal and vascular disease.Am. J. Kidney Dis. 26, 875–888 (1995).
Choi, J. S., Lee, H. J., and Kang, S. S., Alatemin, cassiaside and rubrofusarin gentiobioside, radical scavenging principles from the seeds ofCassia tora on 1,1-diphenyl-2-prcyyl-hydrazyl (DPPH) radical,Arch. Pharm. Res., 17, 462–466 (1994).
Choi, J. S., Lee, H. J., Park, K. Y., Jung, G. O., and Kang, S. S.,In vitro antimutagenic effects of naphthopyrone glycosides fromCassia tora.Planta Med., 64, 100–104 (1998).
Choi, J. S., Lee, H. J., Park, K. Y., Jung, G. O., and Kang, S. S.,In vitro antimutagenic effects of anthraquinone aglycones and naphthopyrone glycosides fromCassia tora.Planta Med., 63, 11–14 (1997).
Forbes, J. M., Cooper, M. E., Oldfield, M. D., and Thomas, M. C., Role of advanced glycation end products in diabetic nephropathy.J. Am. Soc. Nephrol., 14, S254-S258 (2003).
Hatano, T., Uebayashi, H., Ito, H., Shiota, S., Tsuchiya, T., and Yoshida, T., Phenolic constituents of Cassia seeds and antibacterial effect of some naphthalenes and anthraquinones on methicillin-resistantStaphylococcus aureus.Chem. Pharm. Bull., 47, 1121–1127 (1999).
Kalousova, M., Zima, T., Tesar, V., Stipek, S., and Sulkova, S., Advanced glycation end products in clinical nephrology.Kidney Blood Press Res., 27, 18–28 (2004).
Kim, J. S., Kim, H., and Ko, J. H., Studies on the processing of herbal medicines (III)-HPLC analysis of magnolol and inhibitory effects on the formation of advanced glycation endproducts (AGEs)in vitro of unprocessed and processed Magnolia Bark.Kor. J. Phamacogn. 33, 308–311 (2002).
Kim, Y. M., Lee, C. H., Kim, H. G., and Lee, H. S., Anthraquinones isolated fromCassia tora (Leguminosae) seed show an antifungal property against phytopathogenic fungi.J. Agric. Food Chem., 52, 6096–6100 (2004).
Larkins, R. G. and Dunlop, M. E., The link between hyperglycaemia and diabetic nephropathy.Diabetologia, 35, 499–504 (1992).
Makita, Z., Radoff, S., Rayfield, E. J., Yang, Z. H., Skolnik, E., Delaney, V., Friedman, E. A., Cerami, A., and Vlassara, H. N., Advanced glycosylation end products in patients with diabetic nephropathy,N. Eng. J. Med., 325, 836–842 (1993).
Matsuda, H., Wang, T., Managi, H., and Yoshikawa, M., Structural requirements of flavonoids for inhibition of protein glycation and radical scavenging activities.Bioorg. Med. Chem., 11, 5317–5323 (2003).
Namba, T., Colored Illustrations of Wakan-Yaku. Hoi-kusha Publishing Co. Ltd. Vol. 1. pp. 226 (1980).
Shinohara, R., Mano, T., Nagasaka, A., Sawai, Y., Uchimura, K., Hayashi, R., Hayakawa, N., Nagata, M., Makino, M., Kakizawa, H., Itoh, Y., Nakai, A., and Itoh, M., Effects of thyroid hormone on the sorbitol pathway in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1425, 577–586 (1998).
The Diabetes Control and Complication Trial Research Group, The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus.N. Engl. J. Med., 329, 977–986 (1993).
Vinson, J. A. and Howard III, T. B., Inhibition of protein glycation and advanced glycation end products by ascorbic acid and other vitamins and nutrients.J. Nutr. Biochem., 7, 659–663 (1996).
Wong, S. M., Wong, M. M., Seligmann, O., and Wagner, H., Anthraquinone glycosides from the seeds ofCassia tora.Phytochemistry, 28, 211–214 (1989a).
Wong, S. M., Wong, M. M., Seligmann, O., and Wagner, H., New antihepatotoxic naphtho-pyrone glycosides from the seeds ofCassia tora.Planta Med. 55, 276–280 (1989b).
Zhang, Z. and Yu, B., Total synthesis of the antiallergic naphtho-α-pyrone tetraglucoside, cassiaside C2, isolated fromCassia seeds.J. Org. Chem., 68, 6309–6313 (2003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, G.Y., Jang, D.S., Lee, Y.M. et al. Naphthopyrone glucosides from the seeds ofCassia tora with inhibitory activity on advanced glycation end products (AGEs) formation. Arch Pharm Res 29, 587–590 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02969270
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02969270