Abstract
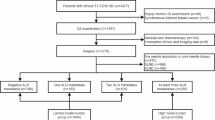
The diagnosis of axillary disease remains a challenge in the management of breast cancer and is a subject of controversy. In 1998, the Japanese Breast Cancer Society conducted a study assessing axillary lymph node involvement in breast cancer. The study included (a) clinical assessment by preoperative imaging modalities, (b) histologic assessment for peritumoral lymphatic invasion, (c) biologic assessment by gelatinolytic activity using film in situ zymography, and (d) sentinel lymph node (SLN) biopsy. Clinical assessments by CT, PET, and US as well as biologic assessment were limited in their ability to detect axillary lymph node disease, although these imaging techniques may be useful to exclude node-positive patients from the need for SLN biopsy. Histologic assessment for peritumoral lymphatic invasion was useful, particularly for detecting false-negative cases by SLN biopsy. Never-theless, the utility of SLN biopsy in assessing axillary nodal status was confirmed. Axillary lymph node dissection (ALND) can be avoided in patients with a small tumor and a negative SLN. However, further studies will be required to investigate the value of SLN biopsy for predicting regional control and survival before it can replace routine ALND as the optimal staging procedure for operable breast cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SLN:
-
Sentinel lymph node
- ALND:
-
Axillary lymph node dissection
References
Senofsky GM, Moffat Jr FL, Davis K,et al: Total axillary lymphadenectomy in the management of breast cancer.Arch Surg 126:1336–1342, 1991.
Fentiman IS, Mansel RE: The axilla; Not a no-go zone.Lancet 337:221–223, 1991.
Noguchi M, Miwa K, Michigishi T,et al: The role of axillary lymph node dissection in breast cancer management.Breast Cancer 4:143–153, 1997.
Fisher B, Redmond C, Fisher ER,et al: Ten-year results of a randomized clinical trial comparing radical mastectomy and total mastectomy with or without radiation.N Engl J Med 312:674–681, 1985.
Lythgoe JP, Palmer MK: Manchester regional breast study; 5 and 10 years results.Br J Surg 69:693–696, 1982.
Cancer Research Campaign Working Party: Cancer Research Campaign (King’s/Cambridge) trial for early breast cancer; A detailed uptake at the tenth year.Lancet 2:55–60, 1980.
Cady B: Case against axillary lymphadenectomy for most patients with infiltrating breast cancer.J Surg Oncol 66:7–10, 1997.
Veronesi U, Salvadori B, Luini A,et al: Breast conservation is a safe method in patients with small cancer of the breast; Long term results of three randomized trials on 1973 patients.Eur J Cancer 31:1574–1579, 1995.
Kissin MW, Querci della Rovere G, Easton D,et al: Risk of lymphedema following the treatment of breast cancer.Br J Surg 73:580–584, 1986.
Ivens D, Hoe L, Podd TJ,et al: Assessment of morbidity from complete axillary dissection.Br J Surg 66:136–138, 1992.
Noguchi M, Katev N, Miyazaki I: Diagnosis of axillary lymph node metastases in patients with breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res Treat 40:283–293, 1996.
March DE, Wechsler RJ, Kurtz AB,et al: CT-pathologic correlation of axillary lymph nodes in breast carcinoma.J Comput Assist Tomogr 15:440–441, 1991.
Sacre R: Modern thoughts on lymph nodes in breast cancer.Semin Surg Oncol 5:118–125, 1989.
Miyauchi M, Yamamoto N, Imanaka N,et al: Computed tomography for preoperative evaluation of axillary nodal status in breast cancer.Breast Cancer 6:243–248, 1999.
Ohta M, Tokuda Y, Saitoh Y,et al: Comparative efficacy of positron emission tomography and ultrasonography in preoperative evaluation of axillary lymph node metastases in breast cancer.Breast Cancer 7:99–103, 2000.
Yoshimura G, Sakurai T, Oura S,et al: Evaluation of axillary lymph node status in breast cancer with MRI.Breast Cancer 6:249–258, 1999.
Chadha M, Chabon AB, Friedmann P,et al: Predictors of axillary lymph node metastases in patients with Tl breast cancer.Cancer 73:350–353, 1994.
Mitsuyama S, Anan K, Toyoshima S,et al: Histopathological predictors of axillary lymph node metastases in patients with breast cancer.Breast Cancer 6:237–241, 1999.
Tsuchiya A, Kanno M, Zhang GJ,et al: Predicting axillary lymph node metastases in breast cancer patients with tumors under 2 cm in size.Breast Cancer 6:167–170, 1999.
Noguchi M, Miyazaki I: Prognostic factors in breast cancer and their controversies (Review).Oncol Rep 1:1157–1163, 1994.
Noguchi M, Ohta N, Thomas M,et al: Clinical and biological prediction of axillary and internal mammary lymph node metastases in breast cancer.Surg Oncol 2:51–58, 1993.
Davies B, Miles DW, Happerfield LC,et al: Activity of type IV collagenases in benign and malignant breast disease.Br J Cancer 67:1126–1113, 1993.
Iwata H, Kobayashi S, Iwase H,et al: Production of matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors metalloproteinases in human breast carcinomas.Jpn J Cancer Res 87:602–611, 1996.
Monteagudo C, Merino MJ, San-Juan J,et al: Immunohistochemical distribution of type IV collagenase in normal, benign, and malignant breast tissue.Am Pathol 136:585–592, 1990.
Iwata H, Yamamoto M, Nemori R,et al: The localization of gelatinolytic activity can be detected in breast cancer tissues by film in situ zymography (submitted).
Cabanas RM: An approach for the treatment of penile carcinoma.Cancer 39:456–466, 1997.
Krag DN, Weaver OJ, Alex JC,et al: Surgical resection and radiolocalization of the sentinel lymph node in breast cancer using a gamma probe.Surg Oncol 2:335–340, 1993.
Giuliano AE, Kirgan DM, Guenther JM,et al: Lymphatic mapping and sentinel lymphadenectomy for breast cancer.Ann Surg 220:391–401, 1994.
Albertini JA, Lyman GH, Cox C,et al: Lymphatic mapping and sentinel node biopsy in the patients with breast cancer.J Am Med Assoc 276:1818–1822, 1996.
Cody HS III: Sentinel lymph node mapping in breast cancer.Breast Cancer 6:13–22, 1999.
Noguchi M, Tsugawa K, Kawahara F,et al: Dye-guided sentinel lymphadenectomy in clinically nodenegative and node-positive breast cancer patients.Breast Cancer 5:381–387, 1998.
Motomura K, Inaji H, Komoike Y,et al: Sentinel node biopsy in breast cancer with clinically negative lymph-nodes.Breast Cancer 6:259–262, 1999.
Motomura K, Inaji H, Komoike Y,et al: Sentinel node biopsy guided by indocyanin green dye in breast cancer patients.Jpn J Clin Oncol 29:604–607, 1999.
Imoto S, Hasebe T: Initial experience with sentinel node biopsy in breast cancer at the National Cancer Center Hospita.East JpnJ Clin Oncol 29:11–15, 1999.
Miyauchi M: Dye-guided methods of sentinel node biopsy in breast cancer.J Clin Exp Med 192:143–146, 2000 (in Japanese).
Sato K, Uematsu M, Saito T,et al: Indications and technique of sentinel lymph node biopsy in breast cancer using 99m-technetium labeled tin colloid.Breast Cancer 7:95–98, 2000.
Tsugawa K, Noguchi M, Miwa K,et al: Dye-and gamma probe-guided sentinel lymph node biopsy in breast cancer patients: Using patent blue dye and tecnetium-99m-labeled human serum albumin.Breast Cancer 7:87–94, 2000.
Noguchi M, Motomura K, Imoto S,et al: Axillary lymph node dissection can be avoided by sentinel lymph node biopsy in patients with small breast cancer; A multicenter validation study by the Japanese Breast Cancer Society (submitted).
Noguchi M, Bando E, Tsugawa K,et al: Staging efficacy of breast cancer with sentinel lymphadenectomy.Breast Cancer Res Treat 57:221–229, 1999.
Noguchi M, Tsugawa K, Miwa K,et al: Sentinel lymph node biopsy in breast cancer using blue dye with or without isotope localization (submitted).
Imoto S,et al: Pilot study on sentinel node biopsy in breast cancer. J Surg Oncol (in press).
Motomura K, Inaji H, Komoike Y,et al: Sentinel node biopsy in breast cancer.Breast Cancer 6:289–291, 1999.
Sato K, Hiraide H, Mochizuki H: Sentinel lymph node biopsy using technetium-99m labeled tin colloids in breast cancer.J Clin Exp Med 192:147–150, 2000 (in Japanese).
Roumen RMH, Valkenburg JGM, Gueskens LM: Lymphoscintigraphy and feasibility of sentinel node biopsy in 83 patients with primary breast cancer.Eur J Surg Oncol 23:495–502, 1997.
Pijpers R, Meijer S, Hoekstra OS,et al: Impact of lymphoscintigraphy on sentinel node identification with technetium-99m-colloidal albumin in breast cancer.J Nucl Med 38:366–368, 1997.
Borgstein PJ, Pijpers R, Comans FFet al: Sentinel lymph node biopsy in breast cancer; Guidelines and pitfalls of lymphoscintigraphy and gamma probe detection.J Am Coll Surg 186:275–283, 1998.
Burak WE Jr, Walker MJ, Yee LD,et al: Routine preoperative lymphoscintigraphy is not necessary prior to sentinel node biopsy for breast cancer.Am J Surg 177:445–449, 1999.
Imoto S, Murakami K, Ikeda H,et al: Mammary lymphoscintigraphy with various radiopharmaceuticals in breast cancer. Ann Nucl Med :325–329, 1999.
Krag DN, Ashikaga T, Harlow SP, Weaver DL: Development of sentinel node targeting technique in breast cancer patients.Breast J 4:67–74, 1998.
Linehan DC, Hill ADK, Tran KN,et al: Sentinel lymph node biopsy in breast cancer; Unfiltered radioisotope is superior to filtered.J Am Coll Surg 188:377–381, 1999.
Paganelli G, De Cicco C, Cremonesi M,et al: Optimized sentinel node scintigraphy in breast cancer.QJ Nucl Med 42:49–53, 1998.
Noguchi M, Tsugawa K, Bando E,et al: Sentinel lymphadenectomy in breast cancer; Identification of sentinel lymph node and detection of metastases.Breast Cancer Res Treat 53:97–104, 1999.
Giuliano AE, Dale PS, Turner RR,et al: Improved axillary staging of breast cancer with sentinel lymphadenectomy. Ann Surg :394–401, 1995.
Giuliano AE: Sentinel lymphadenectomy in primary breast carcinoma; An alternative to routine axillary dissection.J Surg Oncol 62:75–77, 1996.
Veronesi U, Paganelli G, Galimberti V,et al: Sentinel node biopsy to avoid axillary dissection in breast cancer with clinically negative lymph node.Lancet 349:1864–1867, 1997.
Veronesi U, Paganelli G, Galimberti V,et al: Sentinel node biopsy to avoid axillary dissection in breast cancer with clinically negative lymph node.Lancet 349:1864–1867, 1997.
Viale G, Bosari S, Mazzarol G,et al: Intraoperative examination of axillary sentinel lymph nodes in breast carcinoma patients.Cancer 85:2433–2438, 1999.
Hadjiminas DJ, Burke M: Intraoperative assessment of nodal status in the selection of patients with breast cancer for axillary clearance.Br J Surg 81:1615–1616, 1994.
Fisher CJ, Boyle S, Burke M,et al: Intraoperative assessment of nodal status in the selection of patients with breast cancer for axillary clearance.Br J Surg 80:457–458, 1993.
Motomura K,et al: Intraoperative sentinel lymph node examination by imprint cytology and frozen section during breast surgery (in presss).
Rubio IT, Korourian S, Cowan C,et al: Use of touch preps for intraoperative diagnosis of sentinel lymph node metastases in breast cancer.Ann Surg Oncol 5:689–694, 1998.
Ratanawichitrasin A, Biscotti CV, Levy L,et al: Touch imprint cytological analysis of sentinel lymph nodes for detecting axillary metastases in patients with breast cancer.Br J Surg 86:1346–1348, 1999.
O’Hea BJ, Hill ADK, El-Shirbiny AM,et al: Sentinel lymph node biopsy in breast cancer; Initial experience at Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center.J Am Coll Surg 186:423–427, 1998.
Galimberti V, Zurrida S, Zucali P,et al Can sentinel node biopsy avoid axillary dissection in clinically node-negative breast cancer patients?Breast 7:8–10, 1998.
Cody HS III, Hill ADK, Tran KN,et al: Credentialing for breast lymphatic mapping; How many cases are enough.Ann Surg 229:723–728, 1999.
Chu KU, Turner RR, Hansen NM,et al: Do all patients with sentinel node metastasis from breast carcinoma need complete axillary node dissection.Ann Surg 4:536–541, 1999.
Czemiecki B, Scheff AM, Callans LS,et al Immunohistochemistry with pancytokeratins improves the sensitivity of sentinel lymph node biopsy in patients with breast carcinoma.Cancer 85:1098–1103, 1999.
Giuliano AE: Mapping a pathway for axillary staging; A personal perspective on the current status of sentinel lymph node dissection for breast cancer.Arch Surg 134:195–199, 1999.
Noguchi M, Tsugawa K, Taniya T,et al: The role of internal mammary lymph node metastases in the management of breast cancer.Breast Cancer 5:117–125, 1998.
Veronesi U, Cascinelli N, Greco M,et al: Prognosis of breast cancer patients after mastectomy and dissection of internal mammary nodes.Ann Surg 202:702–707, 1985.
Cody HS, Urban JA: Internal mammary node status; A major prognosticator in axillary node-negative breast cancer.Ann Surg Oncol 2:32–37, 1995.
Harlow S, Krag D, Weaver D,et al Extra-axillary sentinel lymph nodes in breast cancer.Breast Cancer 6:159–165, 1999.
Winchester DJ, Sener SF, Winchester DP,et al Sentinel lymphadenectomy for breast cancer; Experience with 180 consecutive patients; Efficacy of filtered technetium 99m sulfur colloid with overnight migration time.J Am Coll Surg 188:597–603, 1999.
Noguchi M, Tsugawa K, Miwa K: Internal mammary chain sentinel lymph node identification in breast cancer.J Surg Oncol 73:75–80, 2000.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Noguchi, M., Kurosumi, M., Iwata, H. et al. Clinical and pathologic factors predicting axillary lymph node involvement in breast cancer. Breast Cancer 7, 114–123 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02967442
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02967442