Abstract
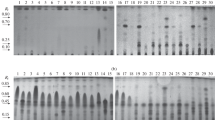
Deoxynivalenol (DON) transformation products from selected time course experiments were analyzed by thin-layer chromatography. With the strainAlternaria alternata f. sp.lycopersici AS27-3, one major metabolite of DON in ethyl acetate was observed. This unidentified metabolite was more polar than DON and has a Rf value of 0.71. Derivatization indicated that this metabolite was probably an unidentified trichothecene. Screening of 29 other microbial isolates (bacteria, yeast, filamentous fungi) for DON transformation did not result in any active organism.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sato N, Ueno Y (1977) Comparative toxicities of trichothecenes, p. 295–307.In Rodricks JV, Hesseltine CW, Mehlman MA (ed.) Mycotoxins in human and animal health. Pathotox Publishers, Inc., Park Forest South, III
Karlovsky P (1999) Biological detoxification of fungal toxins and its use in plant breeding, feed and food production. Nat. Toxins 7: 7–23
King RR, McQueen RE, Levesque D, Greenhalgh R (1984) Transformation of deoxynivalenol (vomitoxin) by rumen microorganisms. J. Agric. Food Chem. 32 (5): 1181–1183
Armstrong RN (1999) Kinetic and chemical mechanism of epoxide hydrolase. Drug Metab. Rev. 31 (1): 71–86
Völkl AE (2000) Transformation von Trichothecenen durch eine neue Bakterienart. Diss. Universität Stuttgart-Hohenheim
Rink R, Fennema M, Smids M, Dehmel U, Janssen DB (1997) Primary structure and catalytic mechanism of the epoxide hydrolase fromAgrobacterium radiobacter AD1. J. Biol. Chem. 272 (23): 14650–14657
Morisseau C, Ward BL, Gilchrist DG, Hammock BD (1999) Multiple epoxide hydrolases inAlternaria alternata f. sp.lycopersici and their relationship to medium composition and host-specific toxin production. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 65: 2388–2395
Arand M, Hemmer H, Dürk H, Baratti J, Archelas A, Furstoss R, Oesch F (1999) Cloning and molecular characterization of a soluble epoxide hydrolase fromAspergillus niger that is related to mammalian microsomal epoxide hydrolase. Biochem J. 344: 273–280
Li C, Liu Q, Song X, Di D, Ji A, Qu Y (2003) Epoxide hydrolase-catalyzed resolution of ethyl 3-phenylglycidate using whole cells ofPseudomonas sp. Biotechnol. Lett. 25 (24): 2113–2116
van der Werf MJ (1998) TheRhodococcus erythropolis DCL14 limonene-1,2-epoxide hydrolase gene encodes an enzyme belonging to a novel class of epoxide hydrolases. FEBS Lett. 438 (3): 293–296
Kroutil W, Genzel Y, Pietzsch M, Syldatk C, Faber K (1998) Purification and characterization of a highly selective epoxide hydrolase fromNocardia sp. EH1. J. Biotechnol. 61: 143–150
Visser H, Vreugdenhil S, de Bont JAM, Verdoes JC (2000) Cloning and characterization of an epoxide hydrolase-encoding gene fromRhodotorula glutinis. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 53: 415–419
Zocher F, Enzelberger MM, Bornscheuer UT, Hauer B, Wohlleben W, Schmid RD (2000) Epoxide hydrolase activity ofStreptomyces strains. J. Biotechnol. 77: 287–292
Grogan G, Roberts SM, Willets AJ (1996) Novel aliphatic epoxide hydrolase activities from dematiaceous fungi. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 141 (2–3): 239–243
Visser H, de Bont JAM, Verdoes JC (1999) Isolation and characterization of the epoxide hydrolase-encoding gene fromXanthophyllomyces dendrorhous. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 65: 5459–5463
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Theisen, S., Berger, S. Screening of epoxide hydrolase producing microorganisms for biotransformation of deoxynivalenol. Mycotox Res 21, 71–73 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02954823
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02954823